菠萝秸秆厌氧发酵产沼气潜力的研究毕业论文
2020-04-15 21:04:03
摘 要
厌氧发酵产甲烷是秸秆资源化利用的重要方式,我国针对不同秸秆产甲烷潜力的研究较为全面,但关于菠萝秸秆产沼气能力的研究较少,因此,本实验选取了海南菠萝秸秆作为厌氧发酵产沼气的对象,同时选取发酵产沼气中应用较普遍的玉米秸秆作为参比对象,分别研究在中温(38℃)和高温(50℃)条件下,这两种秸秆在单独发酵和添加牛粪混合发酵时的产沼气效果。本文的主要研究结果如下:
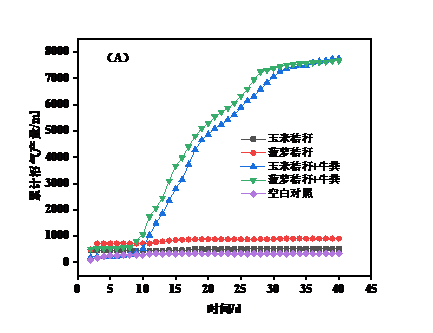
两种发酵温度下,高温体系产甲烷效率更高。高温体系中,玉米秸秆的总沼气产气量为3547 ml,总甲烷产量为519 ml,菠萝秸秆的总沼气产气量为3036 ml,总甲烷产量为177 ml,玉米秸秆 牛粪组的总沼气产气量为14045 ml,总甲烷产量为5837 ml,菠萝秸秆 牛粪组的总沼气产气量为12312 ml,总甲烷产量为5124 ml。总体来说,玉米秸秆和菠萝秸秆两者产甲烷水平相差不大,高温体系中,菠萝秸秆沼气产量为玉米秸秆的86%,甲烷产量为玉米秸秆的34%;高温添加牛粪实验组中,菠萝秸秆沼气产量为玉米秸秆的88%,甲烷产量为玉米秸秆的88%,可以看出两者产气潜力大致相当,并且添加畜禽粪便原料进行混合发酵更利于体系的高效稳定运行。
关键词:菠萝秸秆;厌氧发酵;沼气;甲烷产量
Study on Biogas Potential of Anaerobic Fermentation of Pineapple Straw
Abstract
Anaerobic fermentation of methane is an important way to utilize straw resources. China's research on the potential of different straw methane production is more comprehensive, but there are few studies on the biogas production capacity of pineapple straw. Therefore, this experiment selected Hainan pineapple straw as anaerobic. Fermenting biogas production objects, and selecting corn stalks which are more commonly used in fermentation biogas production as reference objects, respectively, under the conditions of medium temperature (38 ° C) and high temperature (50 ° C), the two straws are fermented separately and added with cattle. The biogas production effect when the manure is mixed and fermented. The main findings of this paper are as follows:
At both fermentation temperatures, the high temperature system produces higher methane efficiency. In the high temperature system,the total biogas production of corn stover is 3547 ml, the total gas production of methane is 519 ml, the total biogas production of pineapple straw is 3036 ml, the total gas production of methane is 177 ml, and the total amount of corn stalk cow dung group The gas production of biogas is 14045 ml, the total gas production of methane is 5837 ml, the total biogas production of pineapple straw cow manure is 12312 ml, and the total gas production of methane is 5124 ml. In general, the methane production levels of corn stalks and pineapple stalks are not much different. In the high temperature system,,the biogas production of pineapple stalks is 86% of corn stalks, and the methane gas production is 34% of corn stalks. Among them, the biogas production of pineapple straw is 88% of corn stalk, and the gas production of methane is 88% of corn stalk. Therefore,the gas production potential of the two is roughly the same, and the mixed fermentation of livestock and poultry raw materials is more suitable for the efficient and stable operation of the system.
Keywords: pineapple straw;anaerobic fermentation;biogas;methane production
目 录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第一章文献综述 1
1.1.能源发展与环境问题 1
1.2.我国秸秆利用现状及发展前景 2
1.2.1.我国秸秆利用现状 2
1.2.2.沼气发展前景 3
1.3.秸秆厌氧发酵技术 4
1.3.1.厌氧发酵原理 4
1.3.2.厌氧发酵影响因素 5
1.4研究目的和意义 6
第二章实验材料与方法 7
2.1实验材料 7
2.1.1试验材料 7
2.1.2仪器 7
2.1.3实验装置 8
2.2实验方法 8
2.2.1原料的预处理 8
2.2.2测定指标及方法 9
2.2.3实验内容 13
第三章结果与讨论 14
3.1.原料性质分析 15
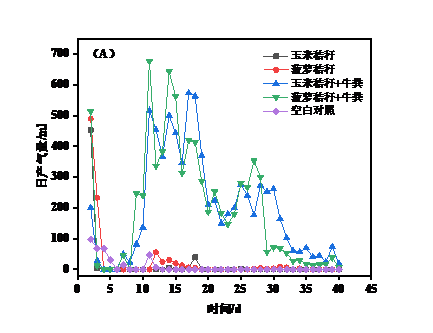
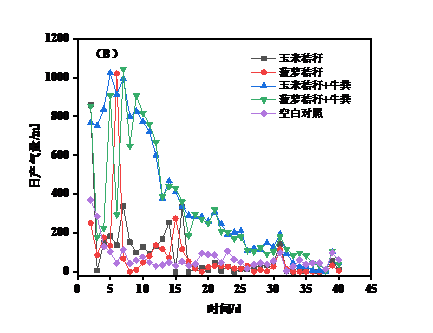
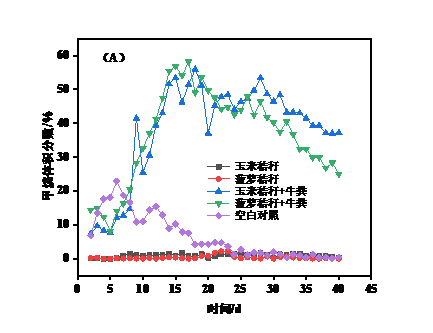
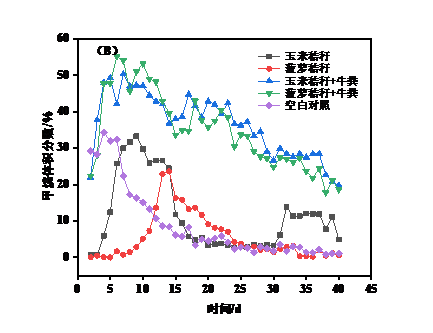
3.2沼气日产气量及甲烷含量分析 15
3.3沼气及甲烷总产气量分析 19
第四章结论与展望 22
4.1结论 22
4.2展望 23
参考文献 24
致谢 26
第一章 文献综述
1.1.能源现状与环境问题
所谓的能源,就是能够向社会,自然界提供能量转换,从而达到人类活动要求的物质,如矿物质能源、核物理能源、地理性能源等等。能源在一个国家的发展中扮演着不可或缺的角色[1]。随着中国在20世纪70年代后期实施改革开放政策,其经济经历了持续快速增长阶段,因此中国自2010年以来已成为第二大经济体。然而高消耗,高投入和高排放,使得虽然在经济方面取得了显着进步,但是伴随着的是巨大的能源消耗和严重的环境退化。近年来,由于人为活动造成了中国频繁的雾霾,气候事件,温室气体排放等严重的环境问题。根据世界环境绩效指数,2014年中国在178个国家中排名第118位。最近几年,中国政府实施了许多旨在控制固体,水和空气工业污染物等环境污染的环境法规和低点,同时根据中国工业和信息化部的数据,每单位钢材的能耗为6-7%,建筑材料为10%,石油化工为10-20%,这表明中国每单位产品的能耗高于国际惯例。因此,减轻环境污染的重要渠道引起了广大公众和学者们越来越多的关注。经济增长是社会发展的重要前提,而环境污染是经济增长的不利后果。因此,提高能源环境效率可能是实现能源可持续性,经济增长和环境保护之间平衡的关键点。因此能源问题必须得到高度重视。
中国虽然地大物博,能源资源比较丰富,煤炭储量10019亿吨,居世界第三位;石油储藏量是16000万吨,有待探明84.9亿吨。淡水总量、石油可采资源总量分别位于第6和第11位,并且全国水力资源和天然气的蕴藏量和储量也很丰富。但是中国人均占有资源量明显低于世界平均水平,与此同时,作为主要的发展中国家和最大的二氧化碳排放国之一,中国现在面临着减少能源消耗和二氧化碳排放的巨大压力。中国国务院宣布降低其目标,与2005年相比,到2020年,国内生产总值的二氧化碳排放量将减少40-45%。在即将到来的“十二五”规划中,中国政府可能会制定明确的目标,将单位GDP能耗和单位GDP二氧化碳排放量减少。由于中国的人均收入仍然很低,中国政府必将在很长一段时间内把发展经济作为我们的发展的第一任务,经济发展是解决一切问题的基础。为了在保证经济发展的同时实现能源对话与减排目标,中国政府需要寻求低碳发展等新的发展道路。另一方面,在制定区域节能减排目标或促进区域和国家低碳发展时,还必须考虑不同地区在经济发展和能源消费方面的差异。因此国家十三五规划中提出,要改变能源结构,提倡使用新型清洁能源,建设资源节约型国家,从而增加我国能源后备储量并降低传统能源的污染性,减轻环境压力[2]。
1.2.我国秸秆利用现状及发展前景
1.2.1.我国秸秆利用现状
秸秆是含有纤维素(Cellulose)、半纤维素(Hemicellulose)、木质素(Lignin)等有机组分植物生物质的统称[3]。根据国家农业技术推广服务中心(MOA) 2000年收集的土壤和肥料专业统计数据,对我国农作物秸秆的数量、利用率和养分状况进行了研究。我国以水稻、小麦和玉米秸秆为主,占总秸秆的76.1%。秸秆养分利用的等级为有机肥gt;燃料gt;饲料gt;等。秸秆还田率为47.3%。作为中国最大的农业大国,中国拥有丰富的秸秆能源资源。典型中国秸秆的特点是水分含量高,挥发分含量高,灰分含量高,堆积密度低。在我国农村,随着农村地区生活条件的改善,农民往往更多地依赖商业燃料,这导致秸秆更加开放的田间燃烧,并带来空气污染和潜在的能源浪费[4]。根据农业部《农业生物质能发展规划》调查显示,目前我国农作物秸秆综合利用现状为畜牧饲料、秸秆还田、秸秆基料、生活能源等,但是,鉴于我国秸秆综合利用产业化程度低、经济效益差等因素,造成目前我国秸秆绝大多数直接燃烧或焚烧废弃,污染大气,并造成不可预估的威胁,这引起了社会各界的广泛关注[5]。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: