多塔悬索桥施工监控毕业论文
2020-04-10 16:45:03
摘 要
三塔悬索桥与通常情况下的悬索桥主要差异在于,三塔悬索桥多了一个中主塔,桥体结构受力特性也因为这一差异而出现了不同特点。简单阐述用于悬索桥计算分析的基本理论的发展进程,从最开始的弹性理论,到后来的挠度理论,再随后到计算机电算的快速发展,有限位移理论成为在悬索桥分析计算中得到广泛应用。毕业论文是以正在建设的襄阳市庞公大桥为工程背景,对三塔两跨悬索桥施工过程中施工监控开展的相关研究。
运用MIDAS/Civil中的建模助手初步建立基本桥型,再修改成为庞公大桥的模拟成桥状态。按照加劲梁吊装形式的不同,定义了两种不同的施工阶段划分。包括襄阳庞公大桥的施工方案——从跨中开始架设加劲梁,以及从桥塔附近架设加劲梁。
选定主缆线型、主缆内力、主塔索鞍预偏量以及主梁线型作为倒拆分析中的施工监控指标。并指出选定这4个参数作为施工监控指标的来由。
采取倒拆分析法模拟已定义好的两种施工阶段,对悬索桥的整个施工过程进行非线性分析。通过单个划分方案的数据分析以及两个划分方案之间的数据对比。得到上述施工监控指标在所定义的施工阶段划分中的变化情况,以及在两个施工阶段划分方案中,施工监控指标变化情况的异同。
在主缆内力的数据分析,提出当采取从跨中附近架设加劲梁时,主缆内力在施工过程中的转变情况是先慢后快。另一种加劲梁架设方式的主缆内力转变则为先快后慢。
在主塔索鞍预偏量的数据分析中,得出当采用从桥塔附近开始架设加劲梁时,主塔索鞍偏移量在整个施工过程中分布比另一种施工方案均匀。也提出主塔索鞍的顶推次数以及顶推量,可以根据施工阶段分析数据中的主塔索鞍偏移量在施工过程中的分布情况进行索鞍顶推方案拟定。
在主梁线型分析中,获得主梁在施工过程中的转变趋势。前种架设方法的主缆线型为从开口向上的弧过渡为开口向下的弧,也即为成桥状态线型。后种架设方式,主梁的线型变化是主梁的外伸端经过下降、抬高、再下降的过程最终向成桥状态设计线型过渡。
关键词:悬索桥;多塔悬索桥;施工监控;非线性分析;有限元;倒拆分析;
Abstract
The three-tower suspension bridge is different from the usual suspension bridge. The three-tower suspension bridge has one more main tower. The characteristics of the force distribution of the bridge structure also reflect the different characteristics of this difference. The development of the basic theory for the calculation and analysis of suspension bridges is briefly explained. From the initial elasticity theory to the later deflection theory, and then to the rapid development of computer computing, the finite displacement theory has become widely used in the analysis of suspension bridges. The dissertation is based on the construction of the Panggong Bridge in Xiangyang City as the engineering background, and carries out relevant research on the construction monitoring during construction of the three-tower and two-span suspension bridge.
Using the modelling assistant in MIDAS/Civil to initially establish the basic bridge type, and then modify it to become the simulated bridge state of the Panggong Bridge. According to the different types of stiffening beams, two different stages of construction are defined. Including the construction plan for the Panggong Bridge in Xiangyang - the erection of stiffening beams from the middle of the bridge and the erection of stiffening beams near the bridge tower.
The selected main cable type, main cable internal force, main tower saddle pre-biased amount, and main beam line type were used as construction monitoring indexes in the down analysis. And pointed out that the selection of these four parameters as the cause of construction monitoring indicators.
Takedown analysis method is used to simulate the two defined stages of construction, and nonlinear analysis is performed on the entire construction process of the suspension bridge. Data analysis through a single partitioning scheme and data comparison between the two partitioning schemes. Obtain the changes of the above-mentioned construction monitoring indicators in the defined construction phase division, and the similarities and differences between the construction monitoring indicators in the two construction phase division schemes.
In the data analysis of the main cable internal force, it is proposed that when the stiffening girder is erected near the middle of the span, the internal force of the main cable during the construction process is changed slowly and quickly. Another type of stiffening beam erection method changes the internal force of the main cable to fast and slow.
In the data analysis of the saddle pre-alignment of the main tower saddle, it is concluded that when the stiffening beam is erected near the tower, the offset of the main tower saddle is distributed evenly over the entire construction process during the entire construction process. The number of pushovers and the pushing amount of the main tower saddle are also proposed. The saddle pushing scheme can be determined based on the distribution of the main tower saddle offset in the construction process during the construction process.
In the analysis of the main beam type, the transition trend of the main beam during the construction process is obtained. The main cable type of the former erection method is an arc that transitions from an opening upwards to an opening downwards, that is, it is a bridge state line type. In the latter mode of erection, the linear change of the main girder is a process in which the overhanging end of the girder descends, raises, and then descends, and finally transitions to the state of completion of the bridge design.
Key words: suspension bridge; multi-tower suspension bridge; construction monitoring; nonlinear analysis; finite element; inversion analysis;
目 录
第 1 章 绪论 1
1.1 概述 1
1.1.1 悬索桥发展 1
1.1.2 多塔悬索桥 1
1.2 研究目的与意义 3
1.3 国内外研究现状 3
1.4 本文主要研究内容 4
第 2 章 悬索桥计算分析基本理论 6
2.1 弹性理论 6
2.2 挠度理论 7
2.3 有限位移理论 9
2.4 本章小结 10
第 3 章 结构有限元模型 11
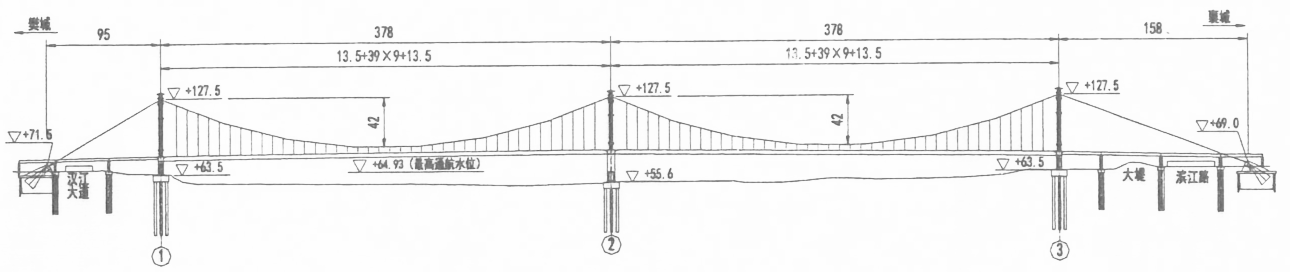
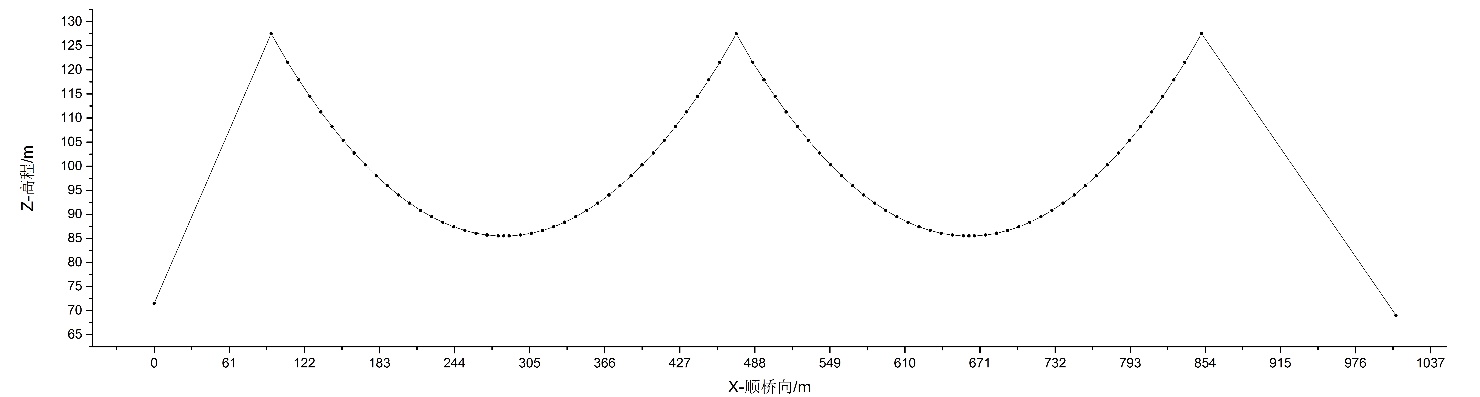
3.1 桥梁概况 11
3.2 模型建立 12
3.2.1 初始平衡状态建立 13
3.2.2 精准平衡状态分析 14
3.2.3 倒拆法空缆线形分析 18
3.3模型验证 20
3.3.1 成桥状态节点竖向位移 20
3.3.2 空缆状态主塔索鞍预偏量 20
3.3.3 主缆无应力索长 21
3.4 施工阶段划分 21
3.4.1 施工简介 21
3.4.2 施工阶段划分方案一 22
3.4.3 施工阶段划分方案二 22
3.5 本章小结 23
第 4 章 施工监控分析 24
4. 1 施工监控指标 24
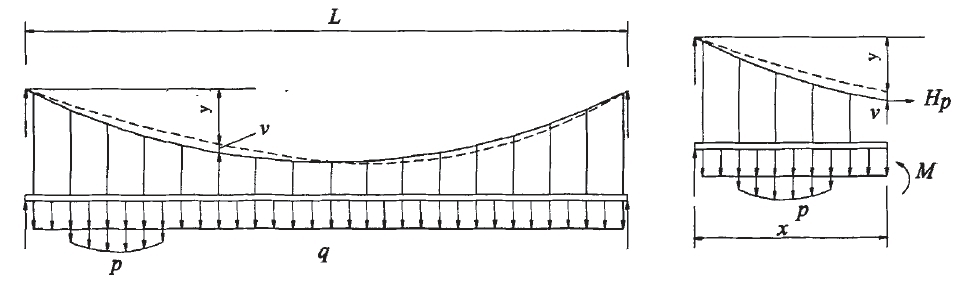
4.1.1 主缆线型 24
4.1.2 主缆内力 24
4.1.3 主塔索鞍预偏量 24
4.1.4 主梁线型 25
4.2 施工方案一数据分析 25
4.2.1 主缆线型 25
4.2.2 主缆内力 27
4.2.3 主塔索鞍预偏量 29
4.2.4 主梁线型 31
4.3 施工方案二数据分析 32
4.3.1 主缆线型 32
4.3.2 主缆内力 34
4.3.3 主塔索鞍预偏量 36
4.3.4 主梁线型 38
4.4 本章小结 38
第 5 章 结论 39
参考文献 40
附录A 42
致谢 44
第 1 章 绪论
1.1 概述
1.1.1 悬索桥发展
悬索桥也叫吊桥,是一种主梁支承在悬索(通常称主缆)上的桥梁,主要由主缆、桥塔、锚碇、主梁或者加劲梁和吊索构成[1]。主塔通常会在塔顶安装鞍形支座,该鞍形支座将在悬索桥结构体系中作为主要承重构件,然后作为桥承载承载部件的主梁通过固定在主缆上的吊杆悬吊与悬索桥的主缆上。悬索桥也以其受力性能好,跨越能力强,轻型雅观、抗震能力好,而成为逾越海峡港湾、大江大河等交通障碍的首选桥型[2]。
中国在悬索桥领域的发展以及取得成就相对较晚。新中国成立后,悬索桥的发展加速,但1980年以前,中国悬索桥的主跨不超过200米[3]。在1980年以后,中国开始加大大跨径悬索桥的开发力度,经过许多学者和工程人员的不懈努力,我国已建成许多大跨径悬索桥。如西堠门大桥、南溪长江大桥以及矮寨大桥等。
近年来,随着轻型高强材料在悬索桥领域的应用,悬索桥的跨越能力也因此得益,不断增长。丹麦的大贝尔特桥,在结构上采用了透风桥面板,其主跨达到了1624m,日本明石海峡桥的主跨达到了1991m[4]。这不仅为海上以及河道运输提供了良好的通航条件,而且通过修建浅水基础以达到增大悬索桥主跨的目的,与具有深水基础的小跨度桥梁相比,可以降低船舶与桥墩之间的撞击风险[5]。
1.1.2 多塔悬索桥
近些年来,多塔悬索桥的桥型布置形式,在一些特别情况下会被用来作为比选方案来选择。多塔悬索桥,即在桥型布置的桥塔数量多于两个,并且在中间主塔处不设置公用锚碇的悬索桥。在多塔悬索桥的各种方案中,又以三塔两跨的桥型布置方案更为瞩目。多塔悬索桥具有减少主跨跨度,大幅度降低主缆张力和锚固尺寸,降低施工成本,降低桥梁施工难度等一系列优点,使多塔悬索桥的桥型在大跨径悬索桥桥型方案选择以及施工中脱颖而出并具有一定的竞争力[6, 7]。
国内学者和桥梁工程师们也在多塔悬索桥的静力特性以及动力特性进行了深入的探索与研究。在琼州海峡跨海大桥,武汉阳逻长江大桥,马鞍山长江大桥,江苏泰州长江大桥和南京长江四桥的初步设计过程中,提出了三塔悬索桥桥梁布置方案作为方案比选。该桥型布置方案最终在泰州长江大桥工程建设中实施。泰州大桥建成后,该桥成为世界上第一座跨径超过1000米的三塔双跨悬索桥[7]。这些桥梁的建成将为众多学者在多塔悬索桥研究以及工程实践的发展做出重要贡献。
2007年12月26日。全球第一座公里级三塔连跨悬索桥—泰州大桥正式投入开工建设中。2010年3月31日,完成泰州大桥中间塔吊装。在施工数据采集中,钢塔在纵桥向的垂直度为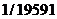 ,横桥向垂直度为
,横桥向垂直度为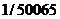 ,优于设计规定l/4000的精度要求[8]。
,优于设计规定l/4000的精度要求[8]。
作为世界上第一座1000米三塔悬索桥,泰州大桥具有开创性的历史意义。在泰州大桥设计之初,组织了一系列的研究工作,包括系统地研究多塔连跨悬索桥结构体系、中间塔刚度及鞍座抗滑安全的关键技术以及钢中塔的疲劳荷载模型等[9]。这一系列研究在桥梁结构体系中取得了创新。阐明了用梁端垂直角替换纵跨比的争论,表明中塔鞍座的纵跨比和抗滑系数是两种控制设计的主要技术指标。并统一它们计算工况,这为研究多塔悬索桥中塔刚度的适用性奠定一定基础[10]。
在国外大跨度桥梁的初步设计中,多塔悬索桥的桥型布置方案也被多次提出。早在20世纪30年代,在进行建造美国的旧金山—奥克兰海湾大桥时,就曾提出过一种五跨悬索桥桥型布置方案,如图1.1所示。从那时候起,来自不同国家的学者、桥梁工程人员提出许多的多塔悬索桥桥型布置方案。1969年,墨西拿跨海大桥举行的设计竞赛为墨西拿桥梁小组所设计的三塔两跨悬索桥布置方案颁发了一等奖,桥型布置方案如图1.2所示。
在1999年至2001年间,丹麦COWI--ICUATRO联合公司设计出三塔两跨悬索桥桥型布置方案,如图1.3所示。该方案为智利Santiago南部1000 km外的Chacao海峡大桥提供方案比选。这种桥型布置方案的两个主要跨度分别为1055米和1100米,采用了A形中间塔[11]。
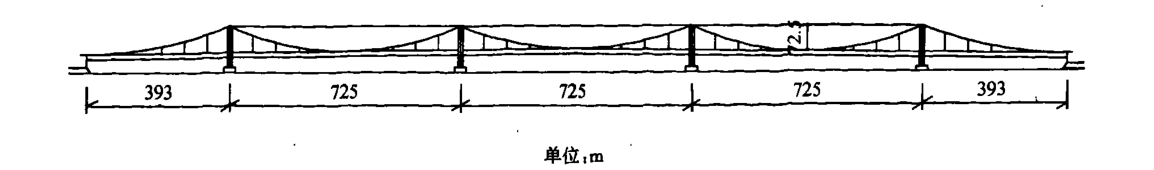
图 1.1 旧 金 山 — 奥 克 兰 海 湾 大 桥 5 跨 悬 索 桥 方 案 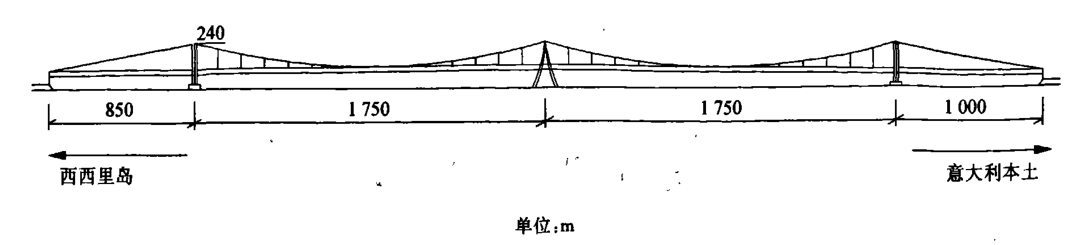
图 1 . 2 大 利 墨 西 拿 海 峡 桥 三 塔 两 跨 悬 索 桥 方 案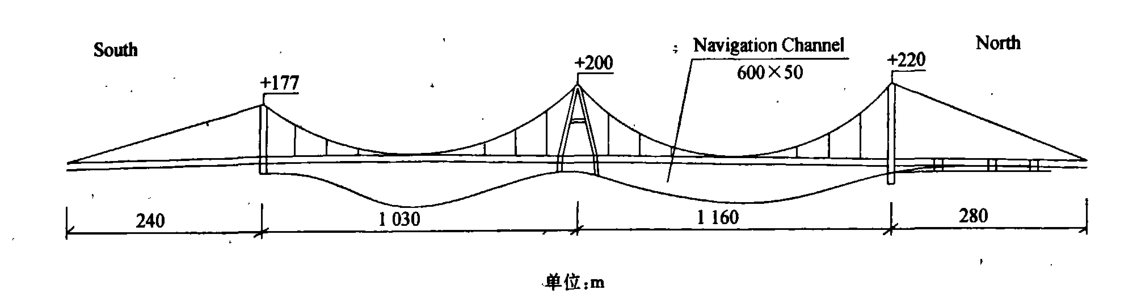
图 1 . 3 C h a c a o 海 峡 大 桥 的 三 塔 两 跨 悬 索 桥 方 案
1.2 研究目的与意义
三塔悬索桥与传统的双塔悬索桥相比,由于其在桥型布置上多了中间主塔,三塔悬索桥在荷载作用下,他结构受力特性会与传统的双塔悬索桥有所不同,不管是在桥梁设计参数的选择还是施工监控过程更加复杂。又由于三塔悬索桥的这种桥梁布置形式在现在大跨径悬索桥的建设中有新的竞争力,三塔悬索桥的桥型布置方案会得到更多被利用的机会[12]。所以对三塔悬索桥施工监控的研究,分析三塔悬索桥在施工过程中各项施工监控指标的数据变化情况,是很有必要的。这对于更加深入地了解这种桥型布置方案中的力学特点也具有积极意义。
在施工过程中的加劲梁吊装方式选择上。了解在两种不同加劲梁吊装方式下,桥梁各项施工监控指标的变化规律。对桥梁在施工前进行施工方案的拟定具有一定指导意义。
1.3 国内外研究现状
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
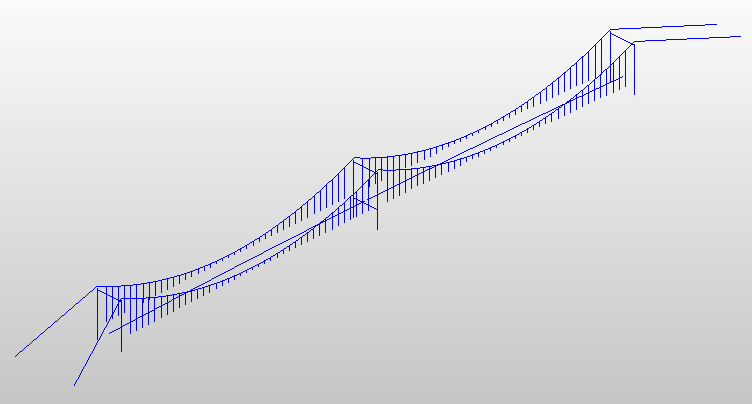
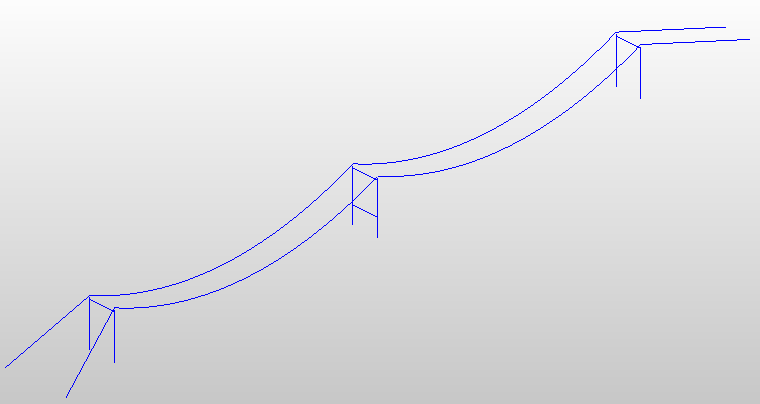
相关图片展示: