电动汽车锂离子电池散热结构分析与优化毕业论文
2020-02-17 19:30:25
摘 要
近年来,随着传统能源的日益枯竭,电动汽车受到了越来越多的关注。动力锂电池作为最常用的电动汽车动力源,尽管有很多优点,但是仍然存在问题。在电动汽车行驶的过程中,锂电池内部反应的同时会产生大量热量。如果不进行合理的散热处理,锂电池的动力性能、使用寿命等都会大打折扣。更为危险的是,在温度达到一定程度后,锂电池可能会发生爆炸,引发安全问题。因此,研究锂电池的散热方式并优化电池组的热管理结构是非常重要的。
本文基于锂离子电池的基本热特性以及传热方式,以磷酸铁18650锂电池为研究对象,采用SolidWorks软件对磷酸铁18650电池进行三维建模,并使用SolidWorks Flow Simulation插件对锂电池的散热过程进行三维数值仿真模拟。在此基础上,以电池组最高温度和最大温差为主要监控目标,采用强制风冷的冷却方法对电池组的散热结果进行了分析和比较。本文采用建模仿真的形式,研究锂离子电池的风冷散热特性,并对其进行优化。主要工作如下:
(1)查阅大量相关文献资料,对锂离子电池有一定的了解后,分析其产热、传热特性。对SolidWorks进行练习,熟练使用建模仿真相关功能。研究锂电池散热相关理论,确定仿真时的边界条件。
(2)基于之前的练习,使用SolidWorks软件建立锂离子电池组各种排列方式下的三维模型,对电池包在不同排列方式下的温度场进行仿真研究。
(3)利用SolidWorks软件分别对电池包在不同风速、不同电池间距等条件下的温度场进行仿真。将电池包在上述不同风速、不同电池间距条件下的温度场仿真结果进行对比。
(4)通过分析仿真结果,讨论得出最佳的电池包散热模型及散热条件,并对风冷散热方式进行优化。
(5)使用冷板、热管、翅片等对散热进一步优化,了解目前尖端技术的发展。
研究结果表明:在并行交错排列基础上进行优化得到的梯形排列是一种比较理想的排布结构,这种排列方式具有良好的散热效果,并且能够满足电池包的温度均匀性。这种排列方式主要通过减少气体流动通道末端的电池数量,从而逐渐减小气流通道横截面积来提高气体流动通道末端的气流速度,进一步加强了电池包的换热效果并且保证了电池包的温度均匀性。
关键词:锂离子电池、风冷散热、仿真分析、温度场、优化
Abstract
In recent years, with the depletion of traditional energy sources, electric vehicles have received more and more attention. Power lithium batteries are the most commonly used power source for electric vehicles. Although there are many advantages, there are still problems. During the driving of an electric vehicle, the internal reaction of the lithium battery generates a large amount of heat. If the reasonable heat dissipation treatment is not carried out, the power performance and service life of the lithium battery will be greatly reduced. Even more dangerous is that after the temperature reaches a certain level, the lithium battery may explode, causing safety problems. Therefore, it is very important to study the heat dissipation method of lithium batteries and optimize the thermal management structure of the battery pack.
Based on the basic thermal characteristics and heat transfer mode of lithium-ion battery, the 18650 lithium iron phosphate battery was used as the research object. The SolidWorks software was used to model the iron phosphate 18650 battery in three dimensions, and the SolidWorks Flow Simulation plug-in was used to heat the lithium battery. 3D numerical simulation. On this basis, the maximum temperature and maximum temperature difference of the battery pack are taken as the main monitoring targets, and the cooling results of the battery pack are analyzed and compared by the forced air cooling method. In this paper, the wind-cooling heat dissipation characteristics of lithium-ion batteries are studied and optimized in the form of modeling and simulation. main tasks as follows:
(1) By consulting the relevant literature, familiar with the structural composition and working principle of lithium-ion batteries, and increase the basic understanding of lithium-ion batteries. The basic thermal characteristics, heat transfer characteristics and basic theory of computational fluid dynamics of lithium-ion batteries were studied, and theoretical preparations for the temperature field simulation of lithium-ion batteries were made.
(2) Establish a lithium-ion battery pack model and use SolidWorks software to simulate the temperature field of the battery pack in different arrangements.
(3) Using SolidWorks software to simulate the temperature field of the battery pack under different wind speeds and different battery spacing conditions. The temperature field simulation results of the battery packs under the different wind speeds and different battery spacing conditions are compared.
(4) By analyzing the simulation results, the optimal battery pack heat dissipation model and heat dissipation conditions are discussed, and the air cooling heat dissipation method is optimized.
(5) Use cold plates, heat pipes, fins, etc. to further optimize the heat dissipation and understand the current development of cutting-edge technology.
The research results show that the trapezoidal arrangement optimized on the basis of parallel staggered arrangement is an ideal arrangement structure, which has good heat dissipation effect and can meet the temperature uniformity of the battery pack. This arrangement mainly improves the airflow velocity at the end of the gas flow channel by reducing the number of cells at the end of the gas flow channel, thereby gradually reducing the cross-sectional area of the gas flow channel, further enhancing the heat exchange effect of the battery pack and ensuring the temperature of the battery pack. Uniformity.
Keywords: Lithium-ion battery, air-cooled heat dissipation, simulation analysis, temperature field, optimization
目 录
第1章 绪 论 1
1.1 课题研究背景 1
1.2 课题研究的目的及意义 1
1.3 课题研究的国内外现状 1
1.4 课题研究内容 4
1.5 课题研究的预期目标 4
1.6 本章小结 4
第2章 锂离子电池的基本结构和特性 5
2.1 锂电池的基本结构及分类 5
2.2 不同壳体外形的锂电池的比较 6
2.3 锂离子电池的制造 7
2.4 锂电池的发展前景 8
2.5 锂离子电池的产热机理 8
2.6 锂离子电池的温度特性 10
2.7 本章小结 11
第3章 锂离子电池热仿真理论 12
3.1 传热方式介绍 12
3.1.1 热传导 12
3.1.2 热对流 13
3.1.3 热辐射 14
3.2 锂离子电池的散热方式 14
3.2.1 风冷散热 14
3.2.2 液冷散热 15
3.2.3 相变材料 15
3.2.4 热管 16
3.3 仿真理论研究 16
3.4 本章小结 17
第4章 锂离子电池包的散热仿真分析 18
4.1 锂离子电池包模型建立及边界条件设定 18
4.2 通风方式及排列方式对电池包散热影响 18
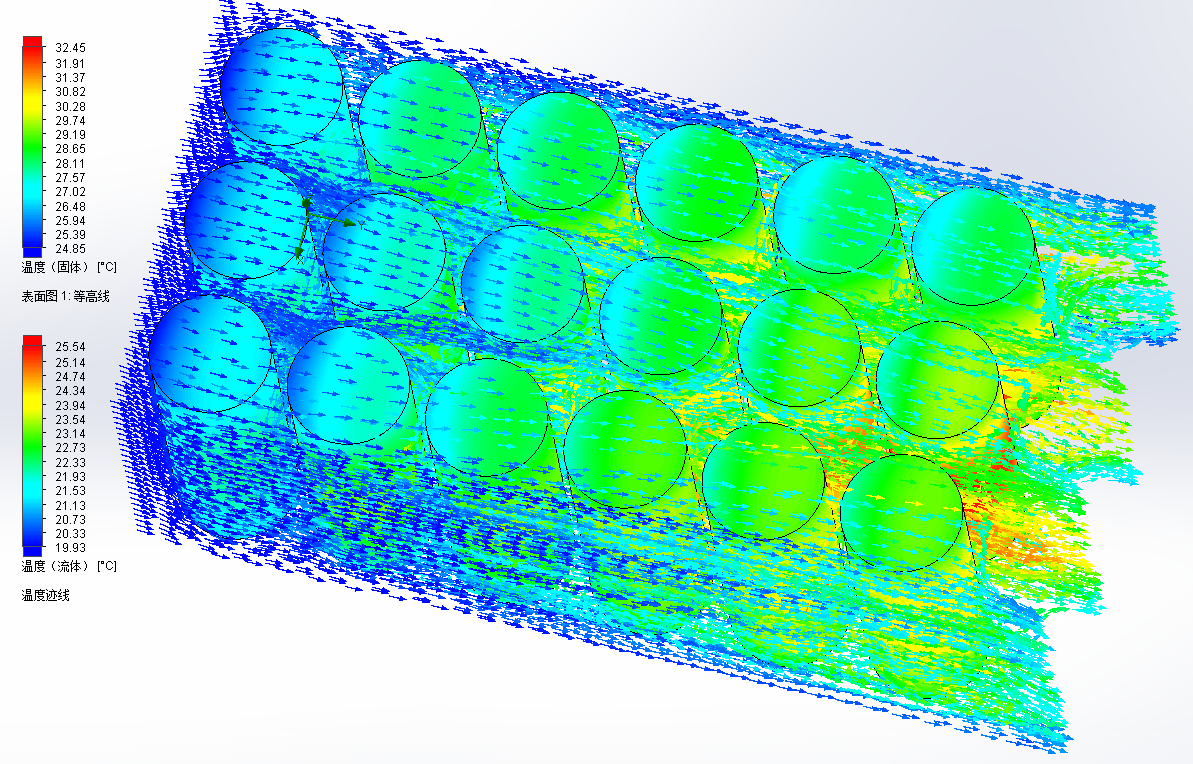
4.2.1 串行排列通风对电池包散热分析 18
4.2.2 并行排列通风对电池包散热分析 20
4.2.3 顺排排列与交错排列对电池包散热分析 22
4.2.4 本节小结 23
4.3 风速对电池包温度影响分析 23
4.3.1 风速对顺排排列电池包温度影响分析 23
4.3.2 风速对交错排列电池包温度影响分析 25
4.3.3 本节小结 26
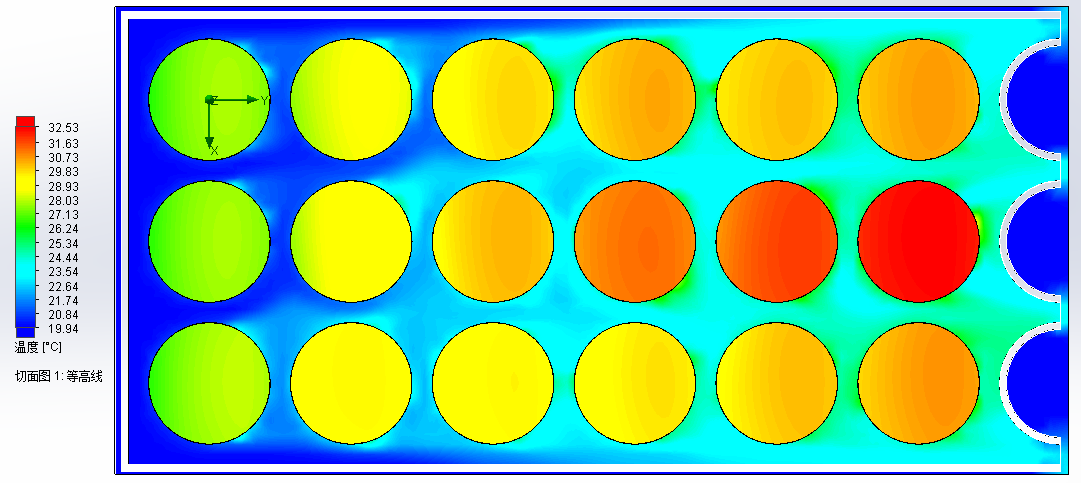
4.4 单体电池间距对电池包温度影响分析 26
4.4.1 不同间距对顺排排列电池包温度影响分析 27
4.4.2 不同间距对交错排列电池包温度影响分析 29
4.4.3 本节小结 31
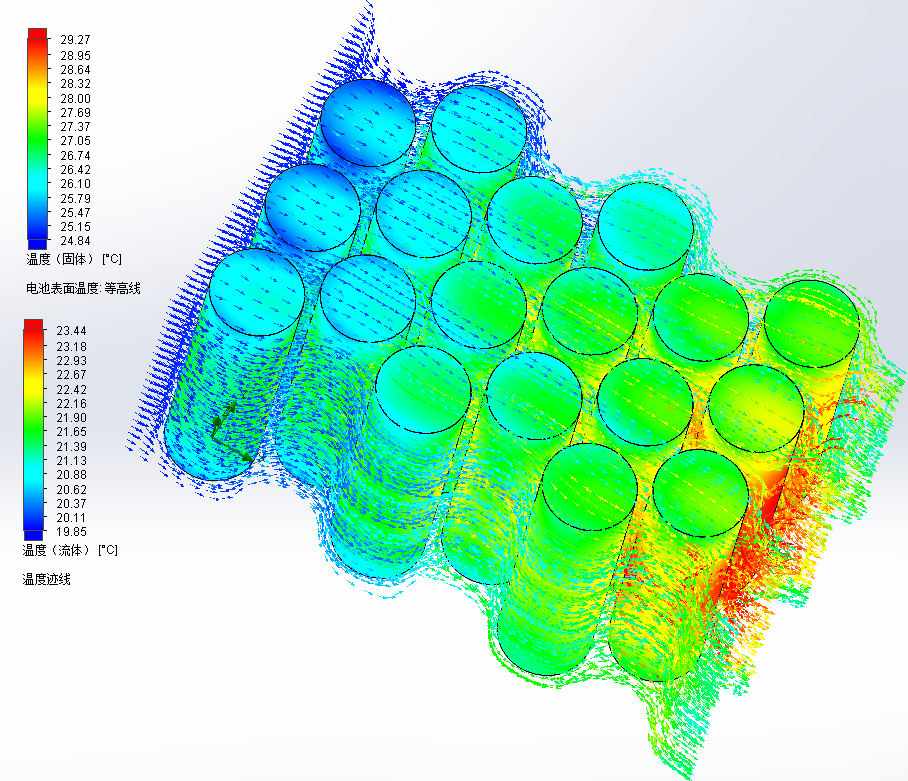
4.5 电池包风冷散热分析与优化 31
4.5.1 梯形排列的提出 31
4.5.2 梯形排列下风速对电池包温度影响分析 34
4.5.3 梯形排列下不同间距对电池包温度影响分析 35
4.5.4 本节小结 36
4.6 结论 36
4.7 本章小结 37
第5章 锂离子电池组风冷散热的发展趋势 38
5.1 风冷散热的冷却策略 38
5.2 风冷散热附加技术 38
第6章 总结与展望 39
6.1 总结 39
6.2 展望 40
参考文献 41
致 谢 43
命名法
:比热容(J··)
E:总能量(J)
E:开路电压(V)
F:法拉第常数(C·)
I:电流(A)
P:压力(Pa)
Q:发热率(W)
K:导热系数(W··)
N:电子流量(mol)
R:电阻(Ω)
:总内阻(Ω)
SOC:充电状态
:熵变(J·)
T:温度(K)或()
:温差()
:平均温度()
t:时间(s)
U:速度(m·)
V:电池电压(V)
dE/dT:熵系数(V·)
希腊语
▽梯度算子
ρ密度(kg·)
下标
dev标准差
最大值
min最小值
irr不可逆转的反应
r总反应
re可逆反应
x方向
y y方向
z z方向
缩略语
ABS丙烯腈-丁二烯-苯乙烯
BMS电池管理系统
BTMS电池热管理系统
C容量
CFD计算流体动力学
EV电动汽车
FCEV燃料电池电动汽车
HEV混合动力汽车
HPPC混合脉冲功率表征
ICEV内燃机车辆
NCM
PCM相变材料
PHEV插电式混合动力汽车
3-D三维
绪 论
课题研究背景
近几十年来,由于人类活动产生的温室气体,导致温室效应日益严重,而造成地球温室效应的一个主要原因就是二氧化碳的增多。传统汽车排放的尾气中含有大量的二氧化碳和有害气体,如今,汽车尾气排放也渐渐地成为全球性问题,传统汽车的盛行已经导致环境负担越来越重,解决汽车污染迫在眉睫。要解决汽车污染就需要从源头遏制,传统汽车的污染主要来自汽油和柴油的燃烧,而电动汽车的出现则有效地解决了这一问题。作为电动汽车的动力源——锂离子电池,具有能量密度高、使用寿命较长、绿色环保等优点广受应用,但是锂离子电池仍然存在安全性差等问题。而影响锂离子电池的主要因素就是其工作温度,所以做好锂离子电池的热管理至关重要。
课题研究的目的及意义
动力锂电池作为最常用的电动汽车动力源,尽管有很多优点,但是仍然存在问题。在电动汽车行驶的过程中,锂电池内部反应的同时会产生大量热量。如果不进行合理的散热处理,锂电池的动力性能、使用寿命等都会大打折扣。更为危险的是,在温度达到一定程度后,锂电池可能会发生爆炸,引发安全问题。并且有研究表明,锂电池在低温条件下的充放电效率和电池容量也会因极化内阻的增大而大打折扣。所以,为了解决锂电池的热管理问题,本文对锂离子电池的风冷散热方式进行分析并对电池组的散热结构进行优化。只有进行合理的热管理,保持锂电池的工作温度在一个正常范围内,锂离子电池才能进行正常的工作,电动汽车才能拥有更稳定的性能。
课题研究的国内外现状
目前,锂离子电池的散热方式主要包括风冷、液冷以及相变材料等方式。其中,虽然液冷已逐渐成为电动汽车电池的主流冷却方式,但是风冷作为最为简单、成本最低的冷却方式仍然发挥着巨大作用,特别是在一些特定位置,由于受技术限制,风冷散热仍然不可替代。因此,对锂离子电池的风冷散热进行研究仍然是有必要的。
在理论和实验分析的基础上,上海交通大学的楼英莺[1]推出了专为空间紧凑而设计的梅花形电池组和为可用空间较大的情况下设计的波浪形电池组,经过仿真及实验,结果表明,在强制风冷条件下,梅花形电池组和波浪形电池组的最高温度和温度均匀性都可以满足电池的冷却要求。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
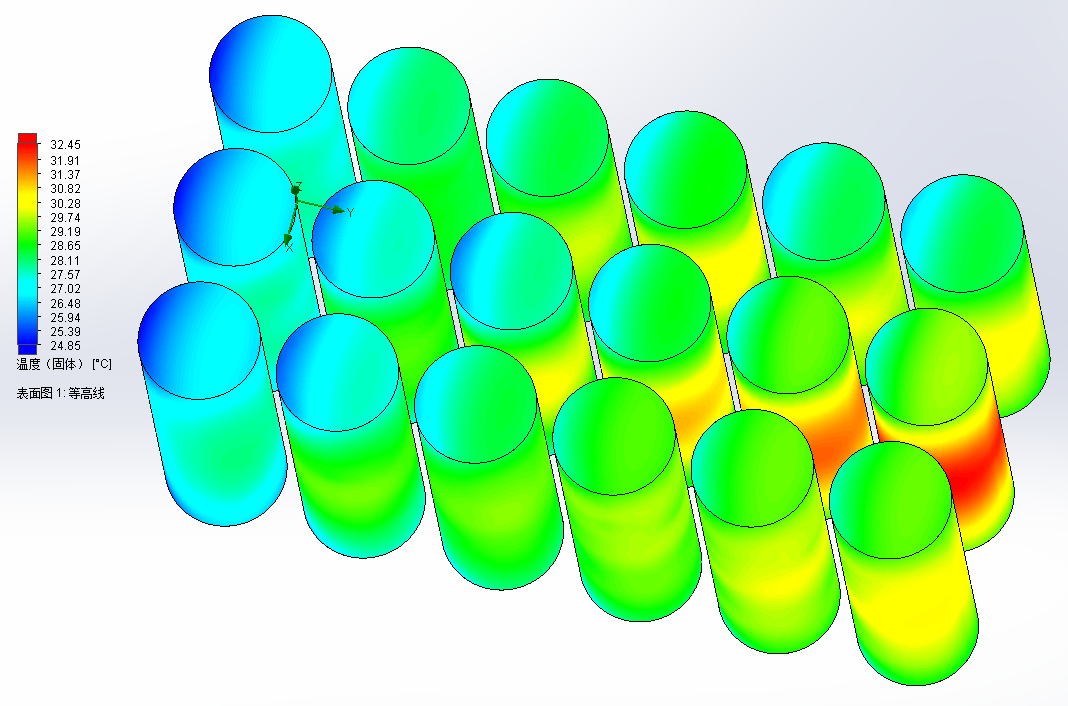
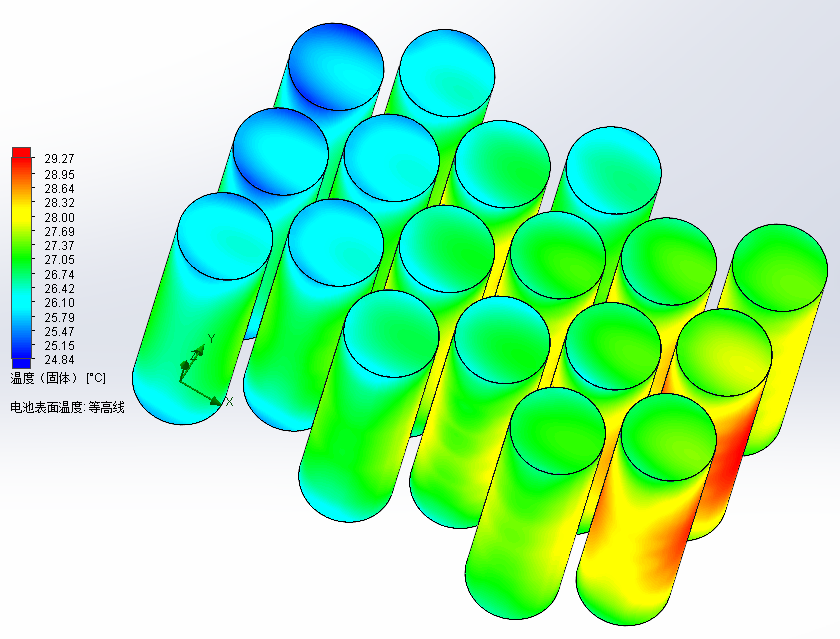
相关图片展示: