水平光管内液体的沸腾换热研究毕业论文
2020-05-28 06:57:19
摘 要
人类生活离不开能源,随着能源问题的出现和新型能源技术的发展,如何实现能源的清洁、高效利用成为当前研究的热点。由于管内沸腾换热广泛用于化工、电力以及制冷行业中,例如化工过程中的换热器、核电站二回路的蒸汽发生器、青藏铁路建设过程中所使用的热管等。并且目前空调制冷行业正在积极寻找清洁的制冷剂替代工质,在这个过程中,制冷剂的凝结蒸发特性是研究的重要内容,因此开展光管内流体的沸腾换热研究具有重要意义。
本文研究的主要内容:通过对本课题相关文献的查阅和理解,借鉴国内外关于水平光管内流体沸腾传热的实验研究和数值模拟研究方面所取得的研究成果。具体内容如下:建立管径分别为10mm、20mm、40mm的理模型,运用ICEM CFD进行六面体网格划分,边界条件为圆管壁面温度恒定,进口压力为常压,速度进口,远流出口。模拟工况分别为进口速度变化范围为01m/s ~0.2m/s、圆管壁面温度变化范围为463.15K~573.15K。运用Fluent软件,采用Mixture混合模型和标准湍流方程k-ε,自定义函数采用Fluent自带的蒸发冷凝模型对管内流体进行三维稳态数值模拟,进而得出相应工况下的温度场、速度场、压力场、气体体积分数沿管长的变化情况。通过改变进口流速、管子壁温、管径等参数,分析不同工况下换热系数和管内压降的变化情况,进一步了解沸腾换热机理。
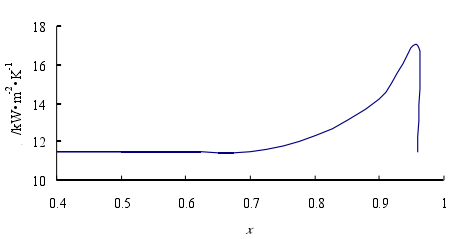
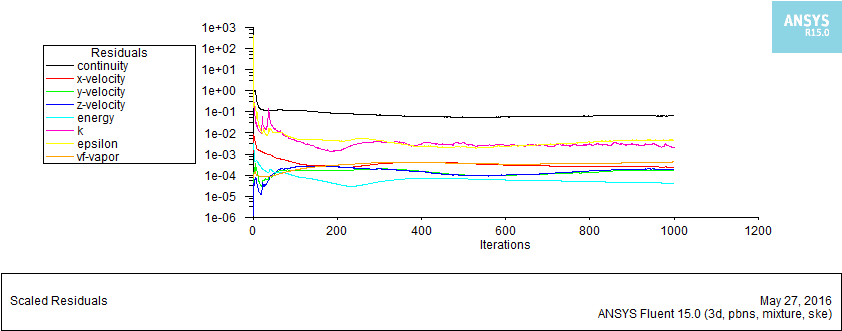
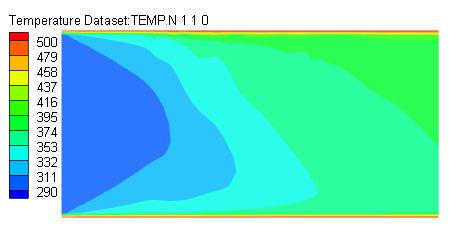
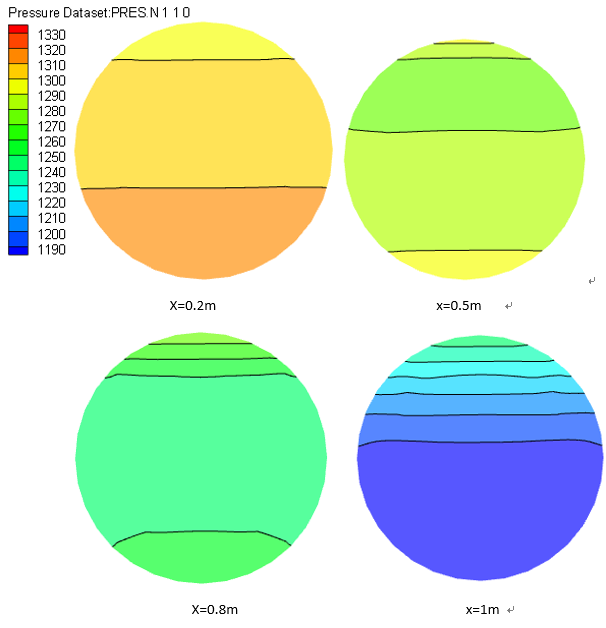
本文结论:通过对模拟数据进行统计分析,得出沿管长方向流体的温度、速度、气体体积分数增大,压力减小;液相区压力大于气相区,且压力梯度较大;速度较大区域集中在管子中心偏上部分,因为随着气体体积分数不断增大,在相同的压力梯度下,密度较小的气体获得较大流速;由于重力作用,密度较小的气体主要集中在管子上壁面附近,但随着进口流速的增大,这种气液分布不均的现象得到改善,重力作用被减弱;换热系数随截面气体体积分数的增大而出现先增大后减小的现象,随进口流速、圆管壁面温度的增大而增大,随管径的增大而减小;管内压降随进口流速、壁温增大而增大,随管径增大而减小。气体体积分数沿管长方向增大,且靠近管子上壁面附近的数值明显大于下壁面附近区域的气体体积分数。
关键词:水平光管 沸腾换热 数值模拟 两相流
Abstract
Human life is inseparable from energy, with the emergence of the problem of energy and the development of new energy technology, how to realize clean, efficient use of energy is becoming a hot spot of current research. Due to tube boiling heat transfer is widely used in chemical industry, electric power and refrigeration industries, such as chemical industry the use of heat exchanger, nuclear power plant in the process of heat exchanger steam generator of the secondary circuit, the use of heat pipe in the process of the Qinghai-Tibet railway construction, etc. And air conditioning refrigeration industry is currently actively looking for clean alternative refrigerants working medium, in this process, the refrigerant evaporation condensation characteristics is an important content of study, so research on the boiling heat transfer in a light tube fluid is of great significance.
The main contents of this paper: Through this project literature review and understand, learn from the research and numerical simulation studies made with regard to research on a horizontal light tube boiling heat transfer fluid. Details are as follows: Establish diameter respectively 10mm, 20mm, 40mm mathematical model, using ICEM CFD carried hexahedral meshing, boundary conditions for the pipe wall temperature constant inlet pressure to atmospheric pressure, velocity inlet, outlet away. Simulation conditions were inlet velocity varied from 0.1m / s ~ 0.2m / s, the tube wall temperature varied from 463.15K ~ 573.15K. Using Fluent software, using Mixture hybrid model and the standard turbulence equations k-ε, custom functions using Fluent evaporation condensation model comes with a three-dimensional steady-state simulation of fluid within the tube, and then draw the appropriate conditions of temperature, velocity field , pressure, gas volume fraction changes along the tube length. By changing the inlet velocity, the tube wall temperature, diameter and other parameters, analyze the changes in different conditions of heat transfer coefficient and pressure drop, to learn more about the boiling heat transfer mechanism.
This article conclusion: Through the simulation data for statistical analysis, the temperature of the fluid along the tube length direction, speed, vapor volume fraction increases, the pressure decreases; liquid region greater than the vapor pressure area, and the pressure gradient greater; greater speed concentrated in the central region of the tube section on the side, because with increasing volume fraction of the gas at the same pressure gradient, low density gas for a larger flow rate; due to gravity, the less dense gas is mainly concentrated on the tube near the wall, but with an increase in the flow rate of imports, this uneven distribution of gas and liquid is improved, gravity is weakened; heat transfer coefficient with the sectional gas volume fraction increases and then decreases after the phenomenon , with the inlet velocity, increasing the tube wall temperature increases, decreases with increasing diameter; the inner tube with inlet velocity drop, the wall temperature increases, with the diameter increases. Gas volume fraction increases in a direction along the length of the tube, and close to the wall of the tube near the gas volume fraction was significantly greater than the value at the area near the wall.
Key words :Horizontal light tube; Boiling heat transfer; Numerical simulation ; Two-phase flow
目录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第一章绪论 1
1.1研究目的及意义 1
1.2管内沸腾换热的研究现状及发展 1
1.3本文研究的主要内容与方法 4
第二章沸腾换热的气液两相流理论 5
2.1管内单组份气液两相流的基本参数 5
2.2 流体流动的力学性质及守恒原理 6
2.3水平管内沸腾换热的基本流型及换热类型 7
2.3.1管内流型分类 7
2.3.2管内换热类型 9
2.4管内压降计算 10
2.4.1 摩擦阻力压力降计算: 10
2.4.2 加速压力降的计算 12
2.4.3局部阻力压力降的计算 12
2.5水平光管内液体沸腾换热的影响参数 13
2.5.1 进口流速对沸腾换热的影响 13
2.5.2 热流密度的影响 13
2.5.3 含气量的影响 13
2.6本章小结 14
第三章水平光管内液体沸腾换热的三维模拟 15
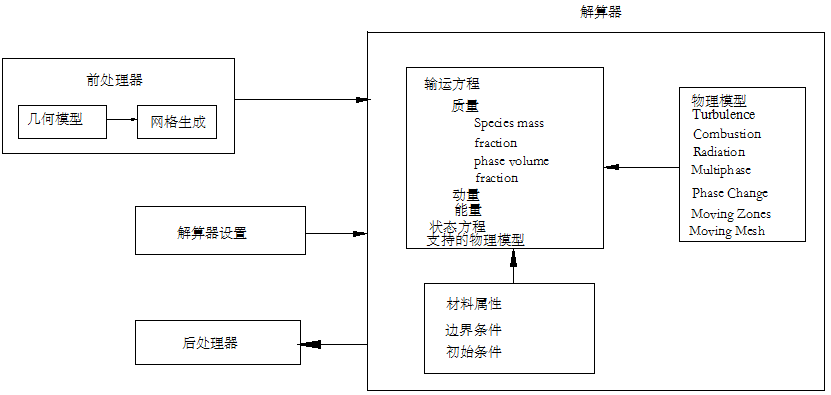
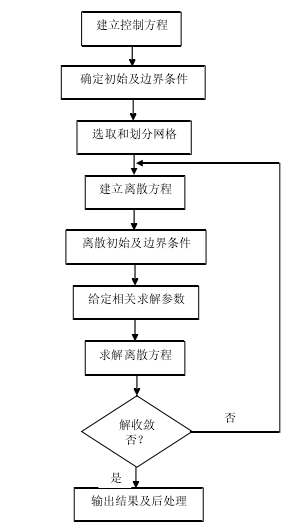
3.1数值模拟基础 15
3.2物理模型 17
3.3数学模型 18
3.3.1 Mixture多相流模型 18
3.3.2 湍流模型 19
3.3.3 相变模型 19
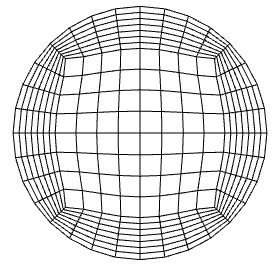
3.4网格划分 20
3.5边界条件设置 21
3.6本章小结 23
4.1数据处理 24
4.2模拟结果及分析 25
4.2.1 管内流动温度场分布 25
4.2.2 管内流动压降分布 26
4.2.3 管内流动速度分布 28
4.2.4 管内流动气相体积分数分布 29
4.3质量流速G对换热性能及压降的影响 30
4.4恒定壁温TW对换热性能及压降的影响 33
4.5管径对换热性能及压降的影响 36
4.6 本章小结 37
第五章 总结与展望 39
5.1总结 39
5.1.1本文进行的工作内容 39
5.1.2本文研究结论 39
5.2后续工作展望 40
参考文献 41
致谢 45
第一章绪论
1.1研究目的及意义
人类生活离不开能源,随着能源紧缺问题的出现和新型能源技术的发展,如何实现能源的清洁、高效利用成为当前研究的热点。空调制冷行业正在加紧了对新型清洁替代工质的研究分析,在这个过程中,水平光管内流体沸腾换热特性的研究是重要方面。此外管内沸腾换热特性普遍用于化工、电力以及空调制冷行业中,例如核电站二回路的蒸汽发生器、青藏铁路建设过程中所使用的热管、空调等都利用了沸腾换热原理。为了有效地节约能源、保护环境,提高管内流体沸腾换热设备的换热效率具有重要意义。水平管内受迫对流沸腾换热,是一个复杂的相变换热过程,对此进行深入的实验研究具有重要的学术意义[1-4]。
1.2管内沸腾换热的研究现状及发展
1756年Leidenfrost[5]观察、测量了液滴的蒸发速度,1924年Kenrick[6]等人对水在细管中的沸腾换热过程进行了研究分析,1935年Nakiyama采用金属丝为热源,将其浸没在大空间液体中进行沸腾换热实验研究,得到了沿用至今的沸腾换热曲线。1935年Becker等人得出了纯工质中气泡核化产生的的原理[7-8]。
Dand[9]等人对制冷剂HFO-1234yf在小直径水平光滑管内的沸腾换热过程进行了实验研究,得出的结论是热流密度对换热系数的影响在小干度范围内更加显著,质量流量对换热系数的影响在大干度范围内影响较大,并且比较得出Saitoh[10]关联式对实验换热系数的预测较好。Greco和Vanoli[11]对制冷剂R22、R507、R134a、R404A、R410A的沸腾换热系数进行了实验研究,实验装置:内径为6mm的光滑管。得出换热系数随饱和压力、热流密度的增大而增大。Lee[12]等人对R22与R-290、R-600a、R-1270在套管换热器内的换热系数与管内压降进行了比较。R22的换热系数和管内压降均低于上述三种制冷剂。Boissieux[13]等人对Iscen59、R407C、R404A在水平光滑管内的沸腾换热特性进行了实验研究,拟合出了混合制冷剂的沸腾换热关联式,并验证了其准确性。
相关图片展示: