微通道内流体的混合流动可视化研究毕业论文
2020-05-28 06:57:47
摘 要
近年来,微尺度下的多相流体混合流动获得了很大的关注,为众多新兴微流体应用提供了不同与传统渠道技术创新的机遇。通道尺度的微细化,使得微通道中流体的传质、传热性能与常规通道相比有较大程度的提高。在微通道内的气液两相流混合流动通常表现出相比于宏观尺寸通道内混合流动不同的流动特性,其允许流体粒子的运动轨迹的精确控制。目前已有数据的表明,微通道内出现的流型有:Taylor流、泡状流、环状流、非稳态弹状流、搅拌流、弹状-环状流、扰动流和波状流等流型。微通道中,表面张力和惯性力是影响流型形态的主要因素,重力的影响可以忽略不计。
本文将研究重点着眼于T型微通道内气液两相混合流动的可视化研究,搭建了一套可视化T形微通道实验平台,通过实验的方法对流体在微尺度通道中的流动状态开展研究。研究气泡流动特性,有利于丰富微流体的理论基础,为新的开发应用提供指导。本文以空气为气相工作介质,以水为液相工作介质,对矩形截面为300μm×300μm的T形微通道内的气液混合流进行了可视化实验。利用可视化观察的方法,观察到了泡状流、弹状流、环状流和扰动流等流型气泡,综述了微通道内的气液两相流行为及特性。
关键词:微通道 混合流动 可视化研究
ABSTRACT
Multiphase flow in microchannels has gained much interest in recent years given the numerous emerging applications of microfluidics that promise to provide technological innovations not realizable with conventional channels. Channel scale miniaturization, making the microchannel fluid mass transfer, heat transfer performance compared to the conventional channel have a greater extent. Gas–liquid two-phase flows in microchannels often exhibit different flow behavior than macrosized conduits, which allows for the precise control of the trajectory of fluidic particles. As surface data shows, flow patterns appear within the microchannel has: Taylor flow, bubble flow, annular flow, unsteady slug flow, stirring flow, Slug - annular flow, disturbance flow, wavy flow and so on. In microchannels, surface tension and inertial forces are the main factors affect the flow’s pattern shape, and the effect of gravity is negligible.
This article will focus on research the visualization of the inner T-shaped microchannel mixed gas-liquid two-phase flow, build a visualization T-shaped microchannel experimental platform, research in micro-scale fluid flow channel state by the method of experimental. Formation mechanism and flow characteristics of bubbles or droplets, in favor of the rich microfluidic theoretical basis to provide guidance for the development of new applications. In this paper, using air as the vapor working medium , water as the liquid working medium, do visualization experiment with rectangular cross-section of the gas-liquid 300μm × 300μm T-shaped microchannel mixing flow. Using visual observation method, we observed the bubble flow, slug flow, annular flow and disturbance flow and other flow-type bubble reviewed two-phase flow behavior and summary characteristics of the micro-channel.
KEYWORDS: Microchannel;Mixed flow;Visualization Research
目 录
摘 要 I
ABSTRACT Ⅱ
第一章 绪论 1
1.1背景意义 1
1.2微通道 1
1.3微通道内气液二相流流型研究 2
1.4本文研究内容及目标 5
第二章 微通道实验系统 6
2.1引言 6
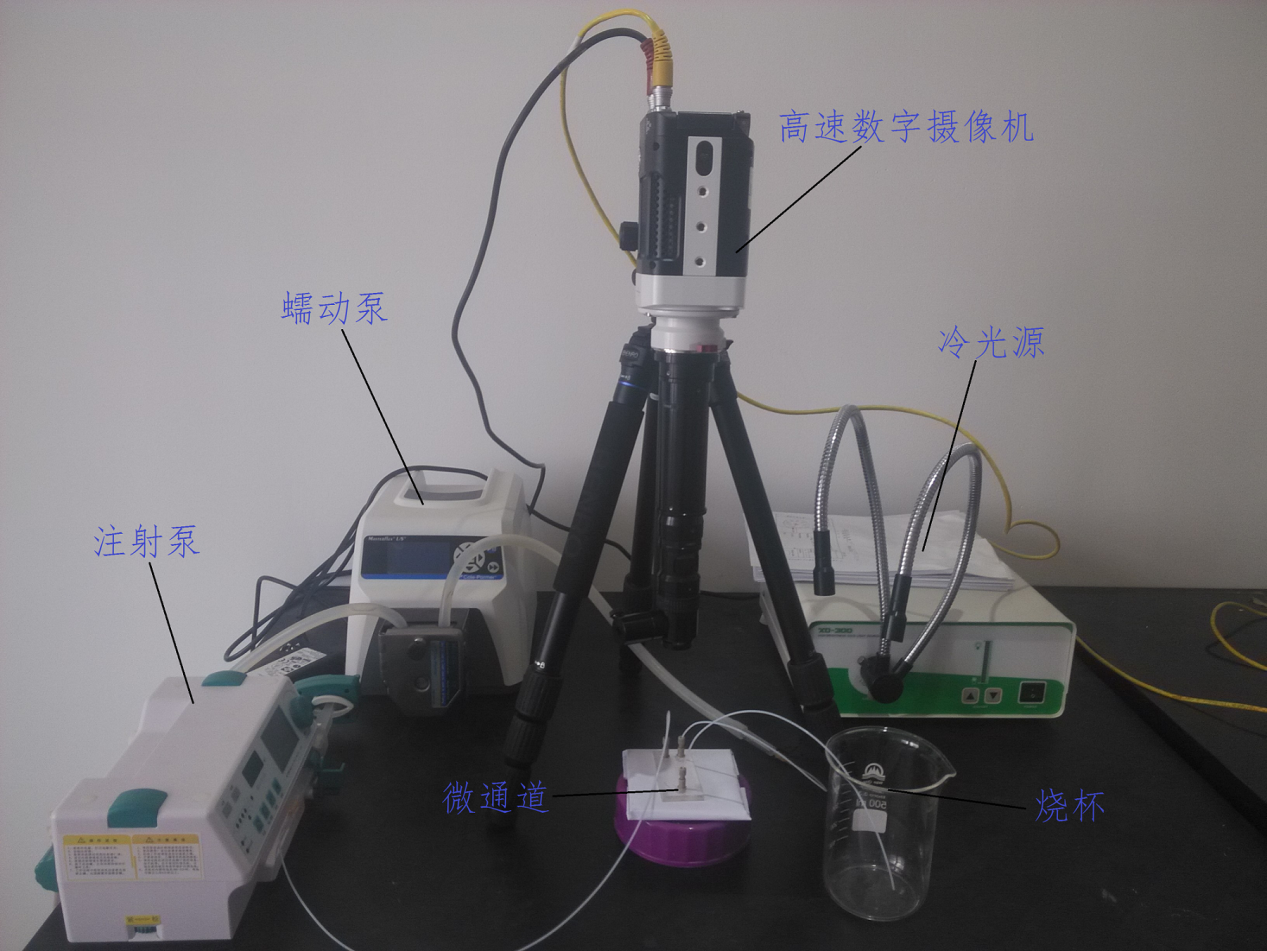
2.2实验系统 6
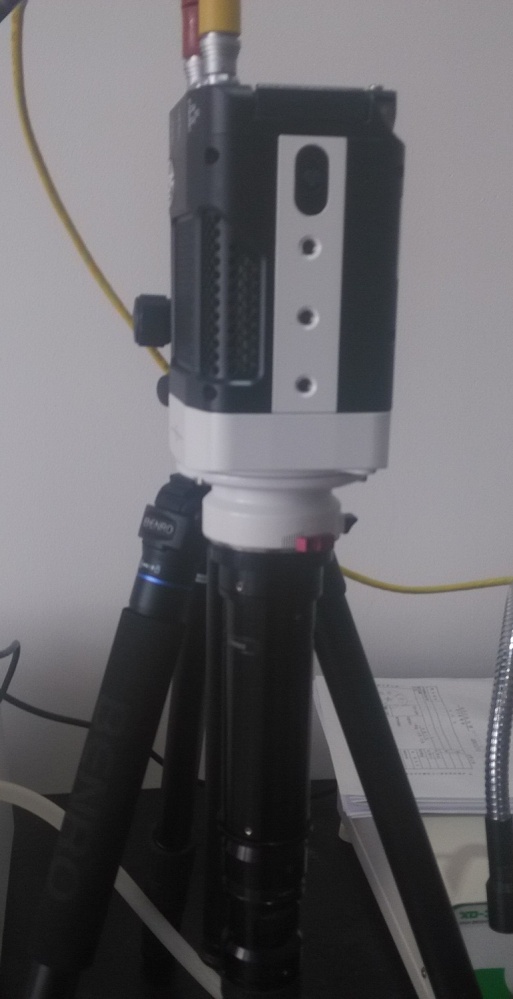
2.3实验仪器和装置 6
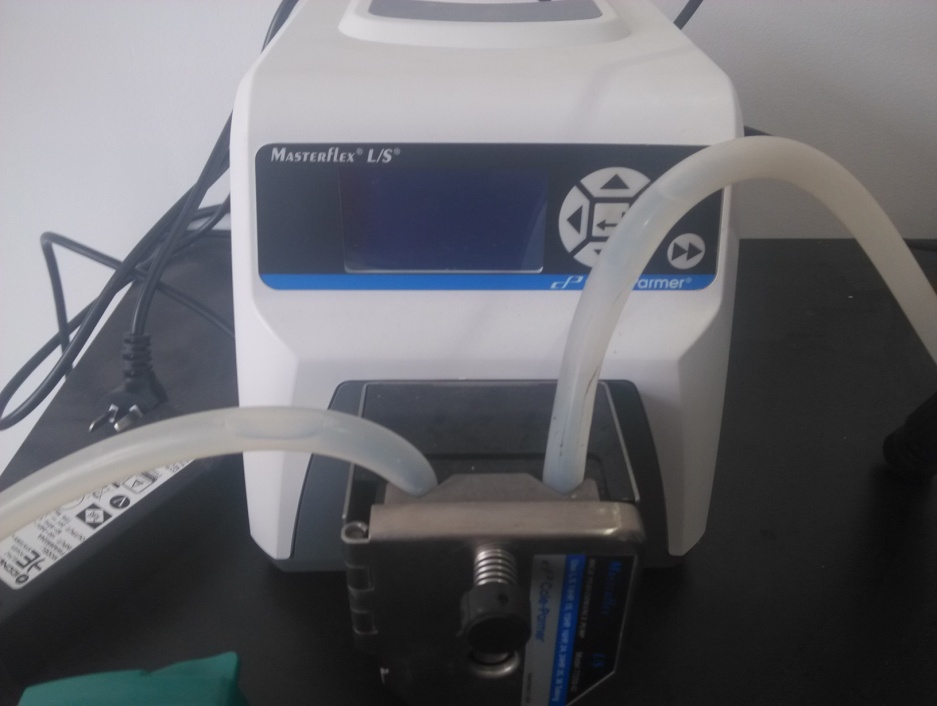
2.3.1蠕动泵 7
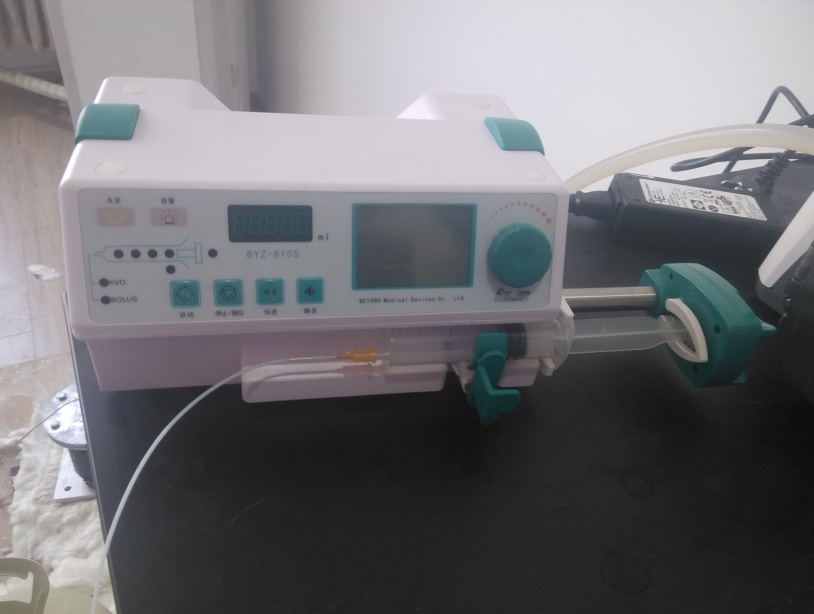
2.3.2注射泵 8
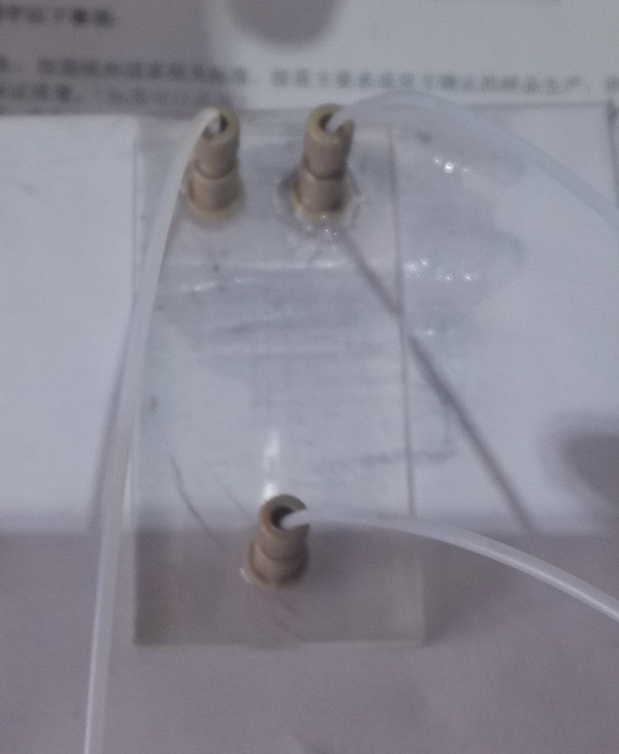
2.3.3微通道 9
2.3.4 其他装置 9
2.4误差分析 11
2.5本章小结 11
第三章 实验原理与步骤 12
3.1引言 12
3.2微通道内混合流体的主要流型 12
3.3研究方法 13
3.3.1气泡大小 13
3.3.2气泡速度 13
3.4实验原理 13
3.5实验步骤 14
3.6本章小结 15
第四章 实验结果及讨论 16
4.1引言 16
4.2实验结果及讨论 16
4.2.1气泡的形成及流动模式 16
4.2.2气泡大小 19
4.2.3气泡速度 20
4.3本章小结 22
第五章 总结与展望 23
5.1.内容总结 23
5.2前景展望 23
参考文献 25
致谢 28
第一章 绪论
1.1背景意义
微机电系统(Microelectro-mechanical systems MEMS)是结合微电了技术和精密加工技术发展起来的高科技前沿学科。随着微机电系统(MEMS)的提出和发展,微化工技术成为现代学科发展的重要方向之一[1-2],与微机电系统有关的流体在微通道中流动的研究也越来越引起人们的重视。一些研究者提出了对微化工应用前景的设想一一迷你工厂(miniplant〕:迷你工厂由英国Edinburg大学的Ponton[3]首先提出。近年来,微尺度下的多相流体混合流动获得了很大的关注,为众多新兴微流体应用提供了不同与传统渠道技术创新的机遇。通道尺度的微细化,使得微通道中流体的传质、传热性能与常规通道相比有较大程度的提高。因此,对微通道进行系统深入的研究具有重要意义。
1.2微通道
微通道,也称为微通道换热器,就是通道当量直径范围为10-1000μm的换热器。微流体器件主要通过构建各种样式复杂的微通道来实现不同的操作。微通道既是各种混合流体运动的反应场所,也将各个微流体系统中的元部件连接到一起。
自上个世纪80年代Tuckerman和Pease 首次提出“微通道散热器”的概念以来,微设备就以迅猛的态势进入到化学化工领域,微化工技术以其简单高效、易直接放大、快速灵活和可持续性等优势受到科研者和生产厂家的青睐。
相关图片展示: