P92钢热机械疲劳力学行为毕业论文
2020-06-21 19:50:42
摘 要
P92钢具有优良的高温蠕变断裂强度,还有优异的常温冲击韧性和还有抗氧化性能。因而被广泛应用于火力发电厂的超临界机组和超超临界机组之中。
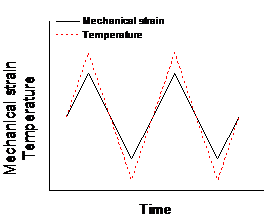
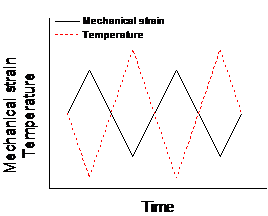
本文主要研究了P92钢在不同条件下的热机械疲劳力学行为。热机械疲劳试验是在计算机辅助控制伺服液压疲劳试验机MTS809上进行。温度的波形为三角波,应变亦然,周期120s,温度范围550-650℃,应力最大值时温度也达到最大值称为同相(IP),反之,称为反相(OP)。样品加载直至断裂,或者定义应力范围下降30%为失效。实验结果表明,机械应变幅不变时,同相位的热机械疲劳的寿命高于反相位的热机械疲劳的寿命。在不同的机械应变幅下,P92钢的寿命有着很明显的差异,在机械应变幅为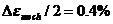 条件下无论是正相位还是反相位热机械疲劳的寿命都远远高于机械应变幅为
条件下无论是正相位还是反相位热机械疲劳的寿命都远远高于机械应变幅为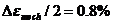 下的寿命,而且通过循环应力响应曲线可以明显看出,试验材料都有着循环软化的现象。
下的寿命,而且通过循环应力响应曲线可以明显看出,试验材料都有着循环软化的现象。
关键词:P92钢 同相 反相 循环软化
Thermomechanical fatigue behavior of P92 steel
Abstract
P92 steel has excellent high temperature creep rupture strength, excellent impact toughness and excellent oxidation resistance at room temperature. P92 steel is widely used in super-critical units of thermal power plants and ultra-supercritical units.
In this paper, the thermomechanical fatigue behavior of P92 steel under different conditions is studied. The thermomechanical fatigue test is carried out on the computer-aided servo hydraulic fatigue testing machine MTS809. The temperature and strain waveforms are triangular wave, where the period is 120s, and the temperature range is 550-650 ℃. When the maximum stress is reached, the temperature reaches the maximum value, which is called in-phase (IP). Conversely, it is called out-of-phase (OP). The sample is loaded repeatedly to fracture, or the 30% drop of stress range. Test results show that in-phase thermo mechanical fatigue life is higher than that of out-of-phase thermomechanical fatigue. The thermomechanical fatigue life of P92 steel changes a lot under different mechanical strain amplitudes. When the mechanical strain changes from 0.4% to 0.8, both in-phase and out-of-phase thermomechanical fatigue life drop a lot. It is obvious that P92 steel has a circular softening phenomenon through the cyclic stress response curve.
Key words: P92 steel, Thermomechanical fatigue, In-phase, Out-of-phase, Circular softening
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1引言 1
1.2 热机械疲劳国内外研究现状 1
1.3研究的目的及意义 5
1.4 本文主要研究内容 5
第二章 热机械疲劳试验方法 6
2.1 试验设备 6
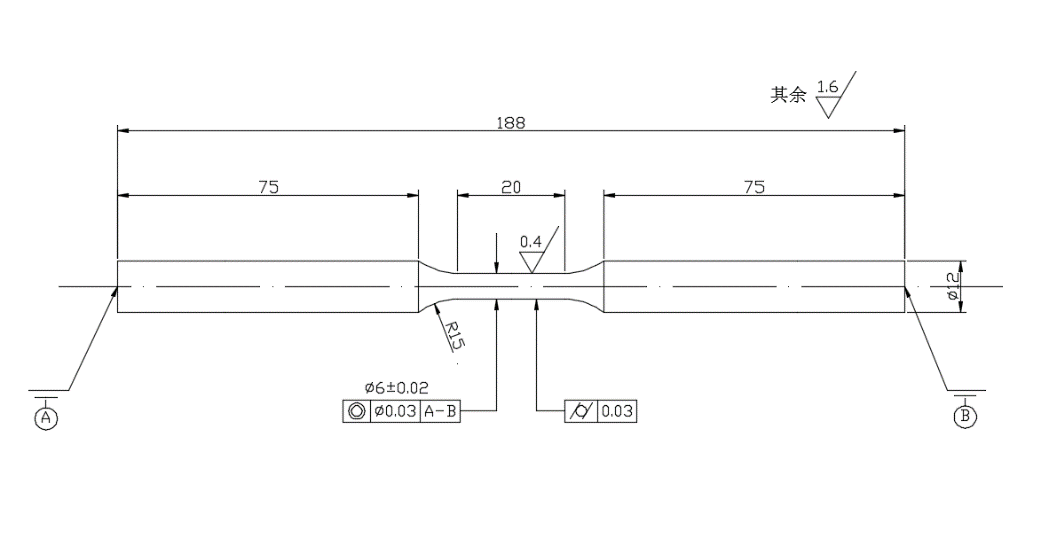
2.2 试验材料与试样尺寸 7
2.3 试验条件的确定 9
2.4 试验调试 9
2.4.1试验周期的确定 10
2.4.2温度梯度的校准 11
2.5 试验方法 12
2.6 试验注意事项 12
2.7 本章小结 13
第三章 试验结果与讨论 14
3.1 P92钢循环应力应变响应行为 14
3.2 P92钢热机械疲劳循环应力响应行为 17
3.2.1 峰值应力 17
3.2.2 应力范围 19
3.2.3 平均应力 21
3.3 P92钢热机械疲劳寿命行为 22
3.4 本章小结 23
第四章 总结与展望 24
4.1工作总结 24
4.2展望 24
参考文献 25
主要符号注释表 28
致谢 29
第一章 绪论
1.1引言
随着锅炉蒸汽压力和温度参数的提高,新型耐热钢的选择制造和安装都将成为超临界机组的关键技术,对今后监督和预防有着深远影响。我国超临界机组主蒸汽管道和耐高温管道基本为SA335 P92。在实际服役条件下,这些部件运行过程处于较恶劣工况条件,受到热交变载荷作用、机械振动等,大部分机组不但承担基本负荷,而且还承担调峰任务,启停也日趋频繁。对于这些高温构件,由于启停中内外温差而造成循环变化的热应力,将产生疲劳损伤。
火力发电中,会产生二氧化碳,随着二氧化碳排入大气,会造成温室效应,现有的火力发电都提高热效率进行节能减排。通过提高发电厂蒸汽的温度和压力可以提高机组热效率。目前,全国范围内新建大量的超(超)临界机组取代亚临界机组或更小型的机组。研究表明,将蒸汽参数从18MPa/530-540℃提高到30MPa/600℃可以减少约30%的二氧化碳排放量。当蒸汽温度与压力提高时,发电厂结构部件材料的高温强度自然成为人们最为关心的问题,据不完全统计,自1995年至今,国内发生整齐管道爆炸事故很多,2000年之后,也发生了很严重的爆炸事故。为了保证设备的安全可靠地运行,进一步研究P92钢的热机械疲劳力学行为有很深远的意义 。
。
1.2 热机械疲劳国内外研究现状
一些专家对P92钢在本构关系、材料性能、温度疲劳和热机械疲劳都有了一些研究。
陈立锋等 开展了P92钢在625℃下的高温拉伸、高温疲劳和蠕变-疲劳性能试验,详细开展了P92的影响寿命的因素。
开展了P92钢在625℃下的高温拉伸、高温疲劳和蠕变-疲劳性能试验,详细开展了P92的影响寿命的因素。
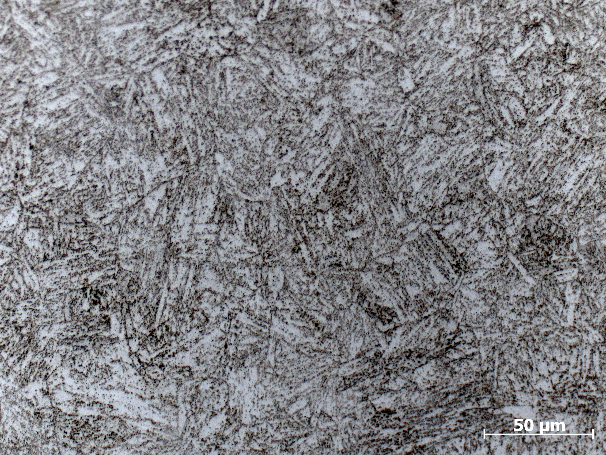
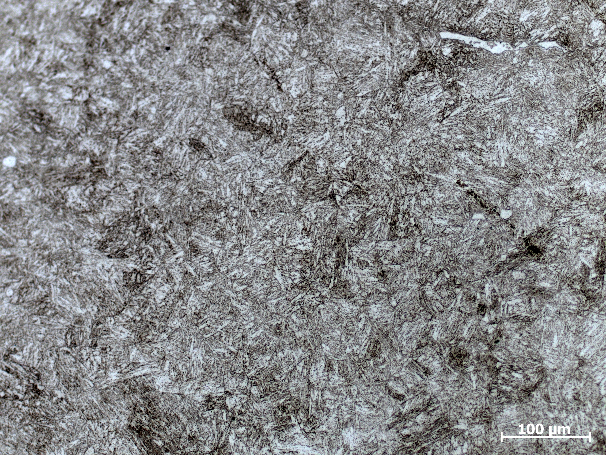
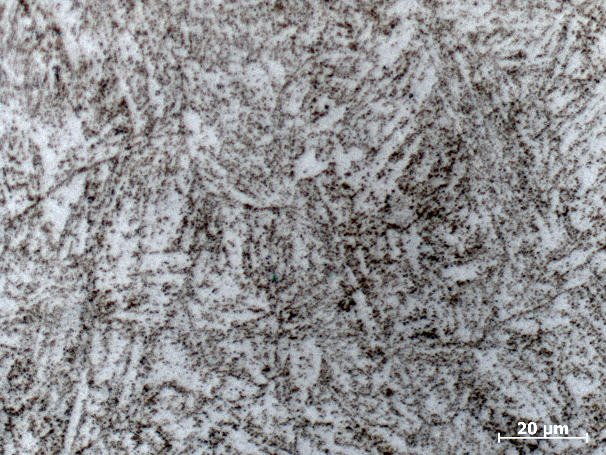
相关图片展示: