316L不锈钢渗碳强化层对抗氢性能的影响毕业论文
2020-06-21 19:50:57
摘 要
目前,能源对于一个国家来说是发展的源泉,而氢,这种清洁的能源在这几年也是受到国家和社会的关注。但是,氢能源的开发利用过程中必然接触金属,并且对其腐蚀, 那么,储运氢的容器材料就成了关注点,一般工业上会对氢容器的材料进行工艺处理来降低氢对它的影响。我们本次课题,就是研究对316L奥氏体不锈钢进行低温气体渗碳后,渗碳强化层对它的抗氢性能的影响。
整个研究包括以下几个主要实验:1.对试样进行低温气体渗碳2.采用电化学预充氢实验对试样充氢3.单轴拉伸试验,即对各个试样拉伸,用电子显微镜观察断口形貌,研究原试样,渗碳试样,充氢试样,渗碳充氢试样的氢致塑性减损行为,把这个用来表示其氢脆敏感性的高低。
结果显示,伴随大量的氢进入试样,经过渗碳处理的试样发生了明显的塑性减损,说明相比单单充氢不渗碳的试样,渗碳后试样有更好的金属机械性能和抗氢性能。
关键词: 氢脆 奥氏体不锈钢 渗碳 充氢试验 拉伸试验
Influence of 316L carburized layer on hydrogen resistance
Abstract
At present, energy is a source of development for a country, and hydrogen, this clean energy in recent years is also subject to national and social concerns. However, the development and utilization of hydrogen energy in the process of the inevitable contact with the metal, and its corrosion, then the storage and transportation of hydrogen container material has become a concern, the general industry will be the material of the hydrogen container process to reduce the impact of hydrogen on it. Our subject is to study the 316L austenitic stainless steel after low temperature gas carburization, carburized reinforced layer on its impact on the hydrogen resistance.
The whole study included the following main experiments: 1. Low temperature gas carburization of the sample 2. Hydrogenation of the sample by electrochemical pre-hydrogenation experiment 3. Uniaxial tensile test, that is, the tensile test of each sample Electron microscopy was used to observe the fracture morphology of the original specimen, the carburized specimen, the hydrogen donor specimen, the hydrocracking behavior of the carburized and hydrogenated specimen, and used to express the hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity.
The results show that with the large amount of hydrogen entering the sample, the carburized sample undergoes significant plastic damage, indicating that the carburized sample has better metal mechanical properties compared to the sample And hydrogen resistance.
Key words: Hydrogen crisp; Austenitic stainless steel; carburization; Hydrogen charge test; Stretching test
目录
摘 要 I
abstract Ⅱ
第一章 绪论 1
1.1引言 1
1.3不锈钢的发展现状 1
1.4本文主要研究的意义 2
1.5 渗碳工艺发展趋势 2
1.5.1渗碳处理的基本分类 3
1.5.2低温气体渗碳的好处 3
1.5.3低温气体渗碳对质子膜燃料电池的重要意义 3
第二章 316L不锈钢低温气体渗碳充氢及拉伸试验 5
2.1 引言 5
2.2 试验内容和方法 6
2.2.1 试验的材料和试样 6
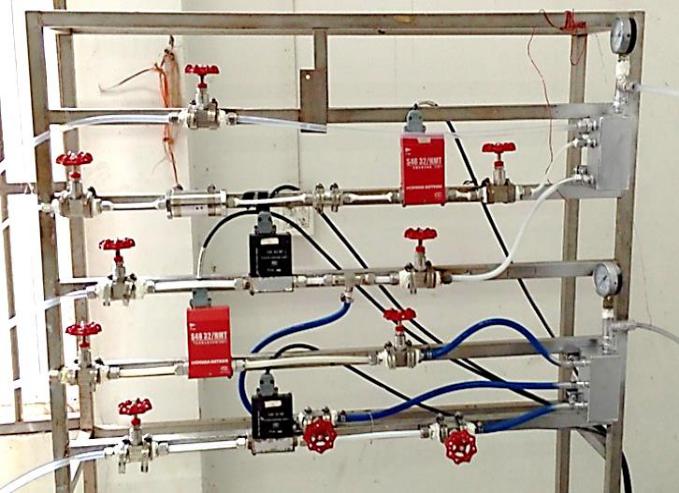
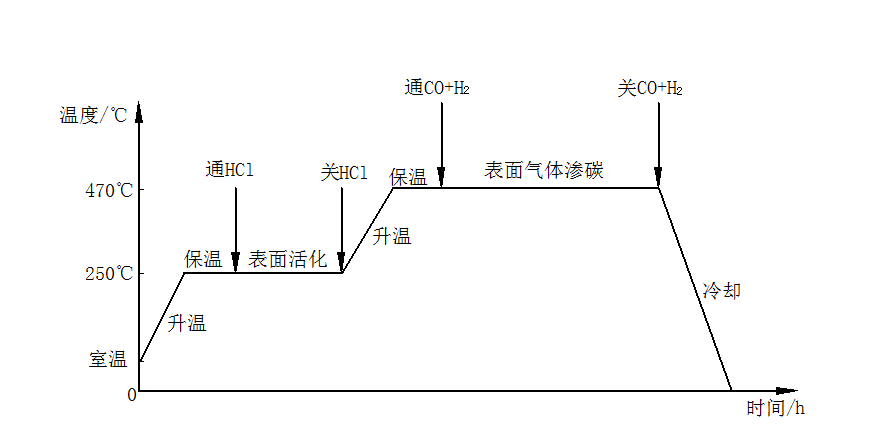
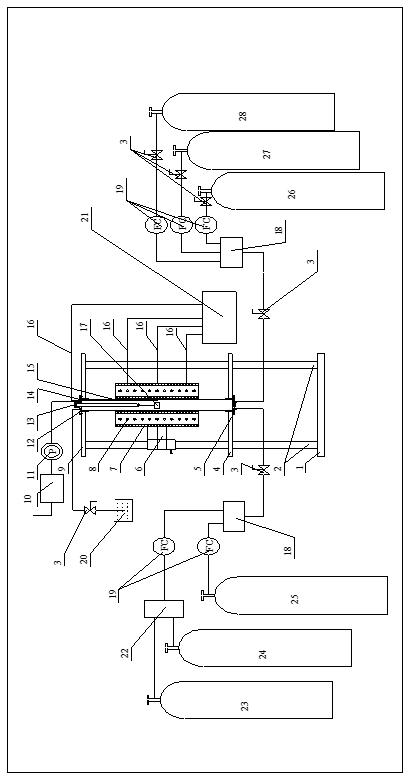
2.2.2低温气体渗碳试验 7
2.2.3 316L不锈钢充氢试验 11
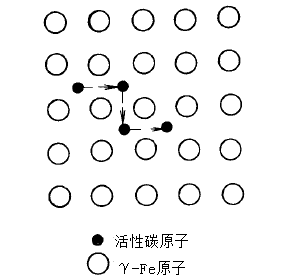
2.2.3.1 氢扩散的机理 11
2.2.3.2 材料中的缺陷对氢扩散的影响 12
2.2.3.3 寻找316L不锈钢充氢试验最优条件 13
2.2.3.4 316L不锈钢充氢试验步骤 14
2.2.4单轴拉伸试验 15
2.2.4.1岛津试验机的基本介绍 15
2.2.4.2拉伸试验步骤 15
第三章 试验结果及价值 17
3.1引言 18
3.2材料的氢脆敏感性高低的表示方法 17
3.3拉伸试验结果 18
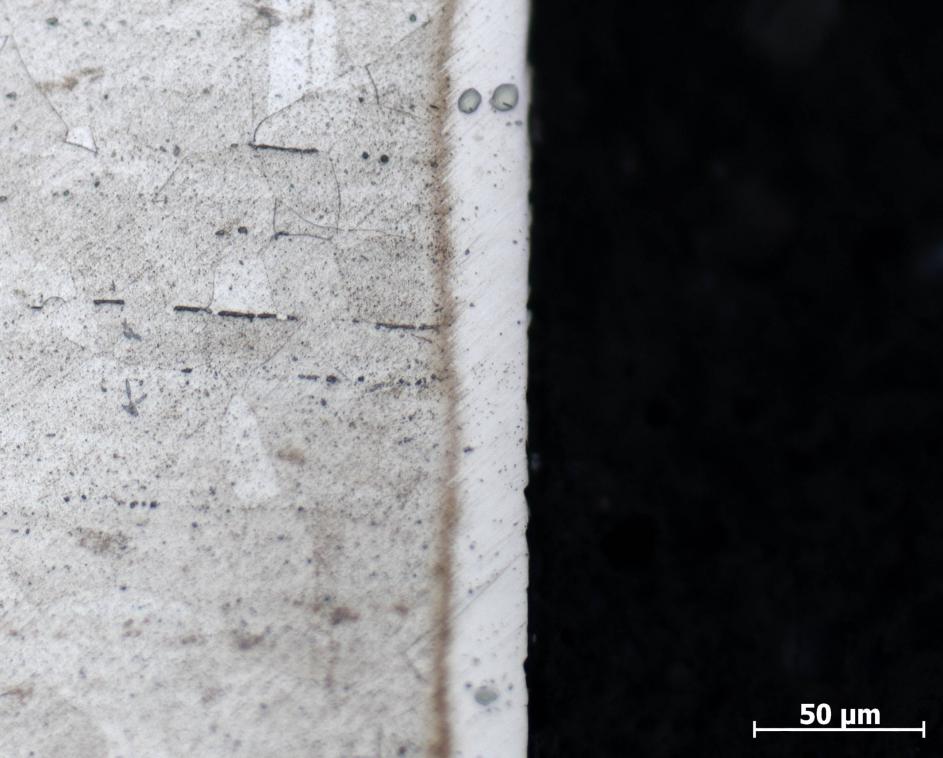
3.4断口形貌观察结果 18
第四章 总结与展望 21
4.1研究结果 21
4.2后期工作展望 22
第五章 经济性分析 22
5.1成本分析 22
5.2社会效益分析 23
参考文献 24
第一章 绪论
1.1引言
当下,迫切需要实施各种对策,寻求拓展各种方法,以解决环境污染与能源危机给我们造成的问题[[1]]。但是,今下我们现代工业中,几乎完全依靠化石燃料制取得到能源来提供使用,如果能找到一种可以大力开发使用的新型能源来代替化石燃料,这问题就迎刃而解了。近几年,氢能源被广泛关注,因为氢清洁,含量多,因此,我们如果能回收利用工程废氢和开采地球上的储量氢,每年大约可以回收到大约1亿立方米,这个数字相当可观。
氢能源作为一种潜在的可再生能源,如果能被利用为新的工业能源,那么就要解决他 的储运问题。用什么材料来做氢能源的储运设备就是一个值得研究的问题。通常,工业上会用不锈钢来作为各种储运氢的设备材料。但是,氢在储运过程中对和它直接接触的容器有的腐蚀和破坏的倾向。因此当下,储氢技术的研究和发展也是重中之重,目的就是要减少这种腐蚀,这样才能推进氢能源的发展利用。
1.2储氢技术的发展现状
储氢技术的发展是氢能走向实用化、现代工业化的重要一环[[2]]。对碳系列储材料的研究是最近的非常火热的课题。由于碳原子对气体分子的特殊吸引作用,碳对大多数的气体有吸附作用。因此,把碳作为一种储氢材料来实验讨论也就是无可厚非的事。这几年,纳米碳对于储氢技术的影响和研究可谓是十分火热,它有望作为新的清洁能源成为氢能电池的制造材料[[3]]。同时,有研究人员发现一种经处理后呈现显著储氢性能的碳纳米管,他们就是清华大学碳纳米材料队伍。他们发现,这种碳纳米管有许多优良的性能,在储氢量上,已经接近美国能源部对车用储氢技术制定的标准。
相关图片展示: