工业纯钛中低温低周疲劳行为研究毕业论文
2020-07-15 21:18:31
摘 要
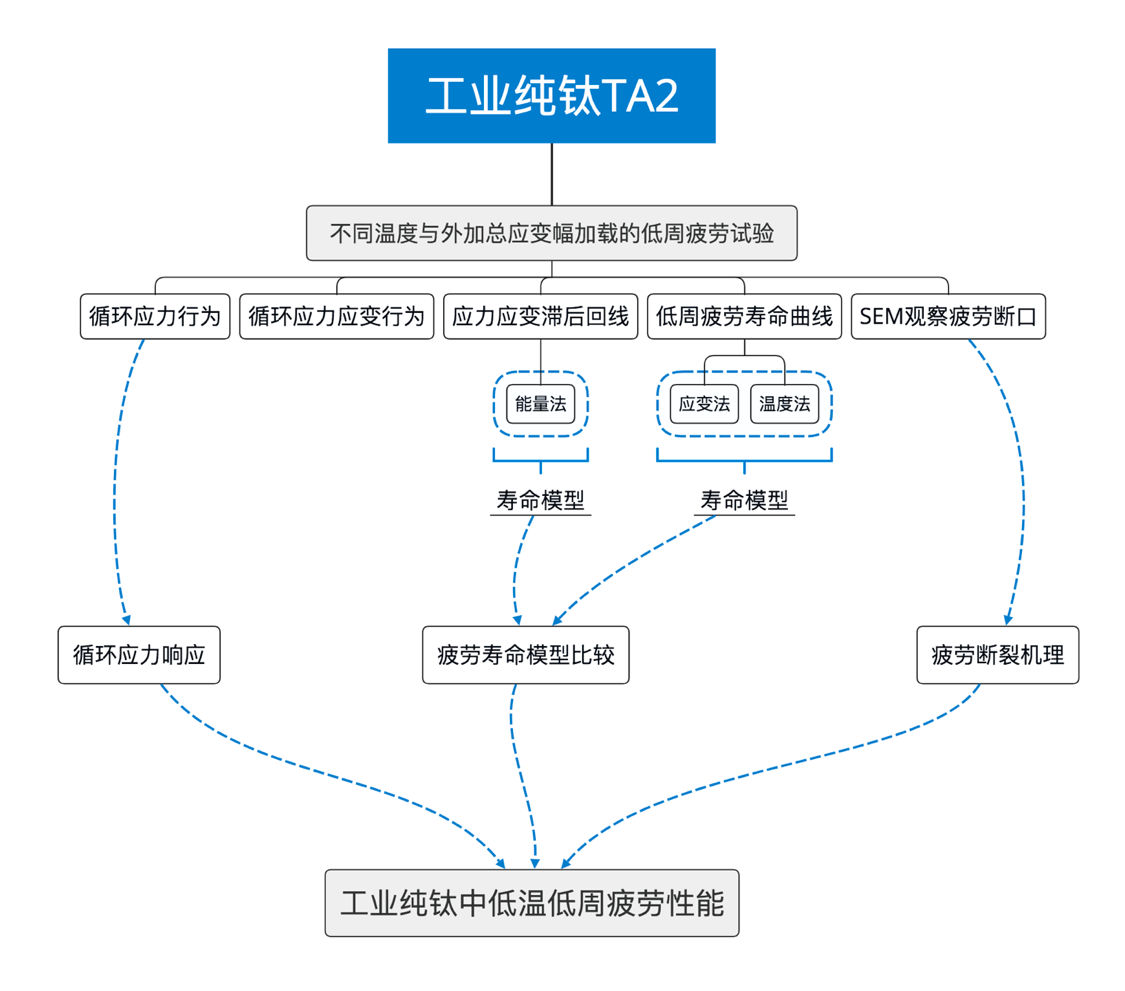
由于工业纯钛的耐腐蚀机能和可加工变形能力好,广泛应用于化工和石化行业。国内的相关研究大多集中工业纯钛的拉伸与压缩力学性能,有关低周疲劳寿命,特别是中低温环境下的低周疲劳寿命研究相对较少。本文以工业纯钛TA2为对象,开展在中低温环境下材料的低周疲劳行为研究。基于应变控制的低周疲劳试验,讨论了不同温度和不同应变幅下工业纯钛的循环应力行为、循环应力-应变行为、低周疲劳寿命行为,并通过扫描电子显微镜对断口微观结构进行观察与分析,讨论了疲劳断裂的损伤机理。
工业纯钛在室温与150℃环境下,应变控制的低周疲劳寿命初期出现了短暂的循环硬化现象,随后产生循环软化并持续至试样失效断裂。在250℃环境下,在整个寿命周期内都表现出循环硬化的特征直至试样失效断裂。
基于应变控制的低周疲劳试验得出疲劳曲线,分别采用应变法(Manson-Coffin公式)、能量法建立寿命预测模型。根据Manson-Coffin公式中四个参数随温度近似线性变化关系,进一步提出温度相关的Manson-Coffin公式。对于室温与150℃,应变法所得预测寿命误差最小;而对于250℃,能量法预测寿命最优。温度相关的Manson-Coffin低周疲劳寿命预测模型与其它两种模型相比,优点在于将不同温度下的应变疲劳参数统一为与温度相关的表达式,,但其精度有一定程度的下降。
扫描电子显微镜观察疲劳断口表明,工业纯钛在150℃和250℃下受不同外加应变作用下产生的疲劳裂纹均萌生于疲劳试样表面,并以穿晶方式扩展至瞬断区,最后产生韧性断裂。
关键词:工业纯钛;低周疲劳;循环硬化; 循环软化;寿命预测模型
Low cycle fatigue behaviors of commercial purity titanium at low and intermediate temperature
Abstract
Because of its corrosion resistance and good deformability, commercial pure titanium is wildly used in the chemical and petrochemical industry. Most of the domestic researches focus on its tensile, compression properties. There is less research on the low cycle fatigue life, especially the low cycle fatigue life in medium and low temperature environments. In this thesis, commercial pure titanium TA2 is used to study the influence of low-cycle fatigue behavior of materials under medium and low temperature conditions. The cyclic stress behavior and cyclic stress-strain of commercial pure titanium at different temperatures and different strain amplitudes were discussed. The fracture morphology of post-fatigued samples was observed by scanning electron microscopy, and the damage mechanism of fatigue fracture was discussed.
Under the low-cycle fatigue loading conditions with total strain amplitude control at room temperature and 150°C, commercial pure titanium undergoes transient cyclic hardening at the initial stage of life, followed by cyclic softening till failure. At 250 °C environment, commercial pure titanium shows cyclic hardening characteristics until the sample is failed throughout the life cycle.
Based on the fatigue curves obtained by low-cycle fatigue tests with total strain amplitude control, the fatigue life prediction models were constructed using the Manson-Coffin formula and the energy method. The four parameters in the Manson-Coffin formula were approximately linearly related to temperature. The temperature-dependent Manson-Coffin formula is further proposed. At room temperature and 150°C, the life prediction error obtained by the Manson-Coffin formula is the smallest; and at 250°C, the energy method is optimal. Compared with other two models, the temperature-dependent Manson-Coffin low-cycle fatigue life prediction model has the advantage is that the strain fatigue parameters at different temperatures are unified into a temperature-dependent expression, but its accuracy has a little drop.
Scanning electron microscopy observations of fatigue fractures show that the fatigue cracks of commercial pure titanium at 150°C and 250°C under different applied total strain amplitudes are initiated on the surface of fatigue specimens and extended to the fracture zone by the transgranular mode with massive dimples.
Key Words: Commercial purity titanium, Low cycle fatigue, Cycle hardening,
Cycle softening, Life prediction model
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract III
目 录 V
第1章 绪论 1
1.1研究背景 1
1.1.1工业纯钛的基本性质 1
1.1.2工业纯钛的应用前景 1
1.2研究现状 1
1.2.1材料的低周疲劳 1
1.2.2工业纯钛的循环硬化与循环软化 2
1.2.3循环应力-应变行为 4
1.2.4疲劳寿命预测模型 4
1.2.5低周疲劳寿命影响因素 6
1.3研究内容及研究手段 8
1.3.1研究内容 8
1.3.2研究手段 8
第2章 工业纯钛中低温低周疲劳试验方法及设备 10
2.1试验材料 10
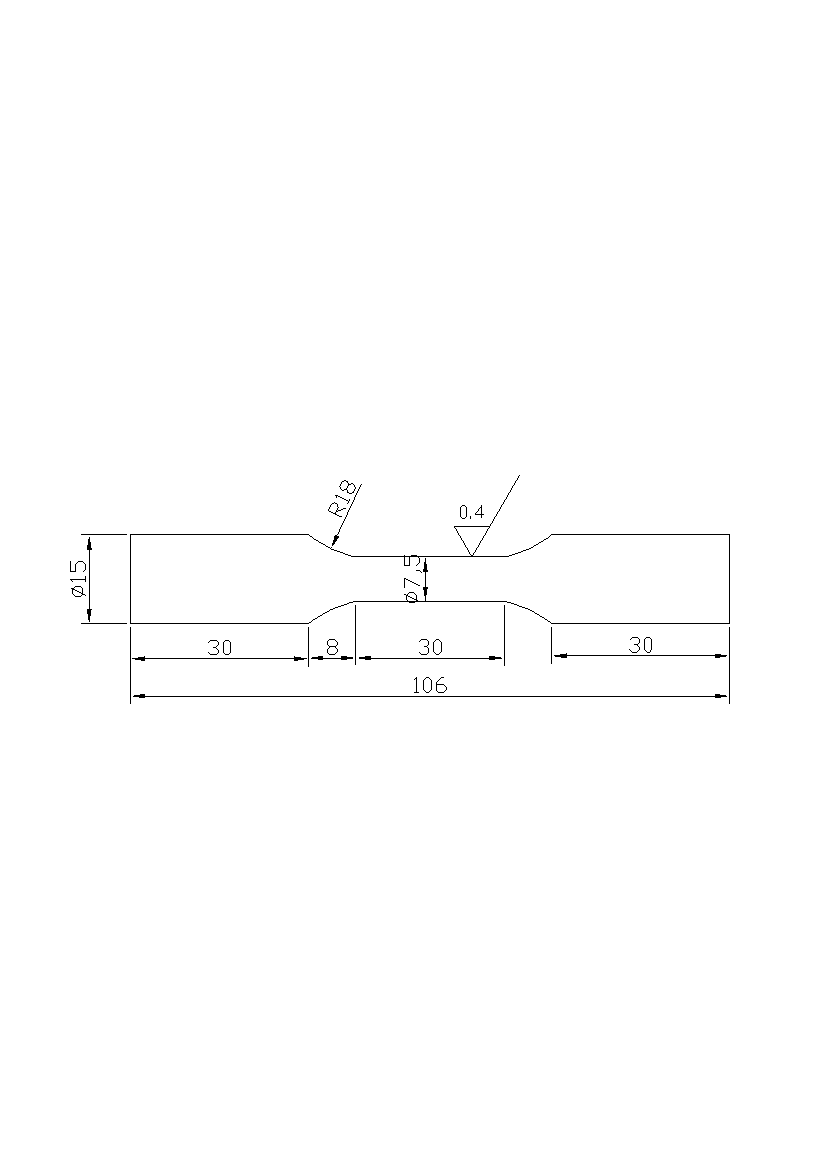
2.2试验方法 10
2.2.1低周疲劳试验 10
2.2.2扫描电子显微镜观察断口 11
2.3试验设备 11
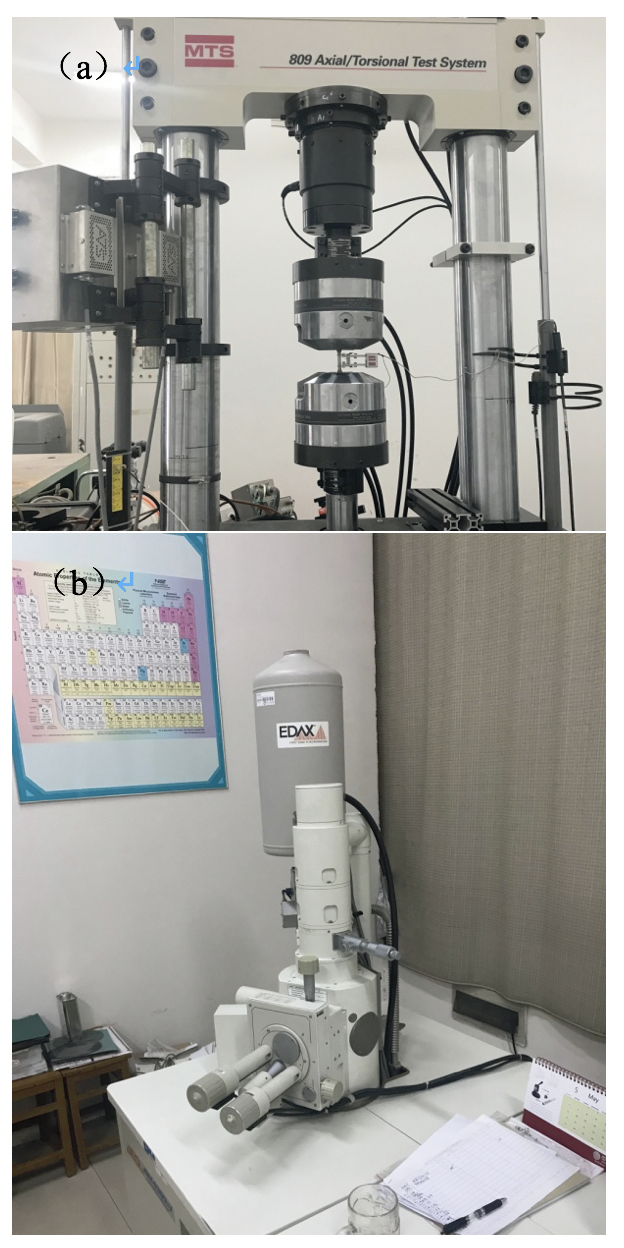
2.3.1 MTS809材料测试系统 11
2.3.2 JSM-6360LV扫描电子显微镜 12
2.4小结 13
第3章 工业纯钛中低温低周疲劳试验结果与讨论 14
3.1低周疲劳试验 14
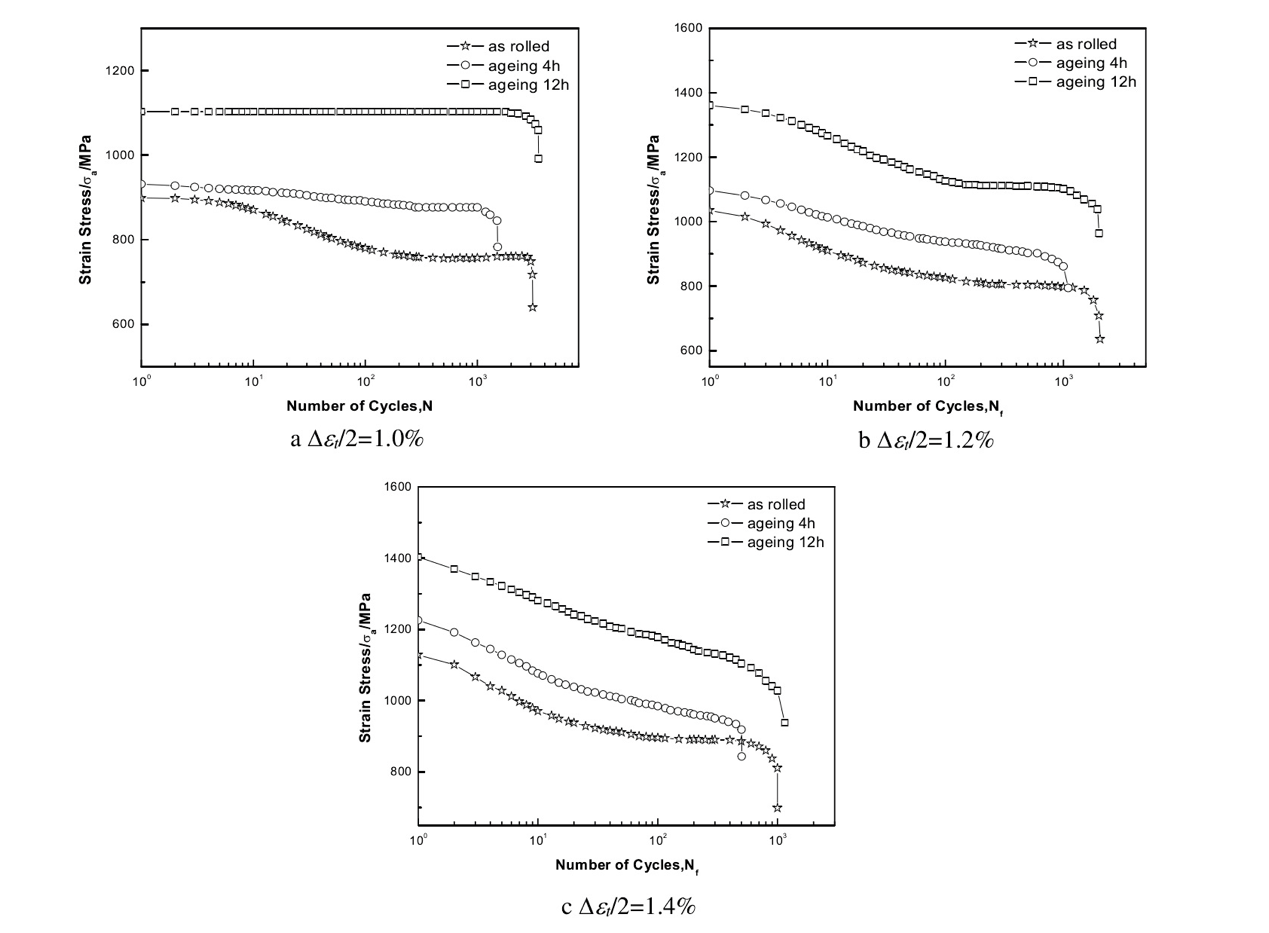
3.1.1循环应力行为 14
3.1.2循环应力-应变行为 16
3.1.3应力-应变滞后回线 17
3.1.4低周疲劳寿命曲线 20
3.1.5低周疲劳寿命预测(应变法) 22
3.1.6引入温度的低周疲劳寿命预测模型 26
3.1.7低周疲劳寿命预测(能量法) 28
3.2疲劳断口观察 31
3.2.1疲劳裂纹源区 32
3.2.2疲劳裂纹扩展区 35
3.2.3疲劳裂纹瞬断区 37
3.3分析与讨论 39
3.3.1工业纯钛的循环应力响应行为 39
3.3.2工业纯钛低周疲劳寿命预测模型比较 39
3.3.3工业纯钛的疲劳断裂机理 40
3.4小结 42
第4章 结论 44
参考文献 45
致谢 48
绪论
1.1研究背景
1.1.1工业纯钛的基本性质
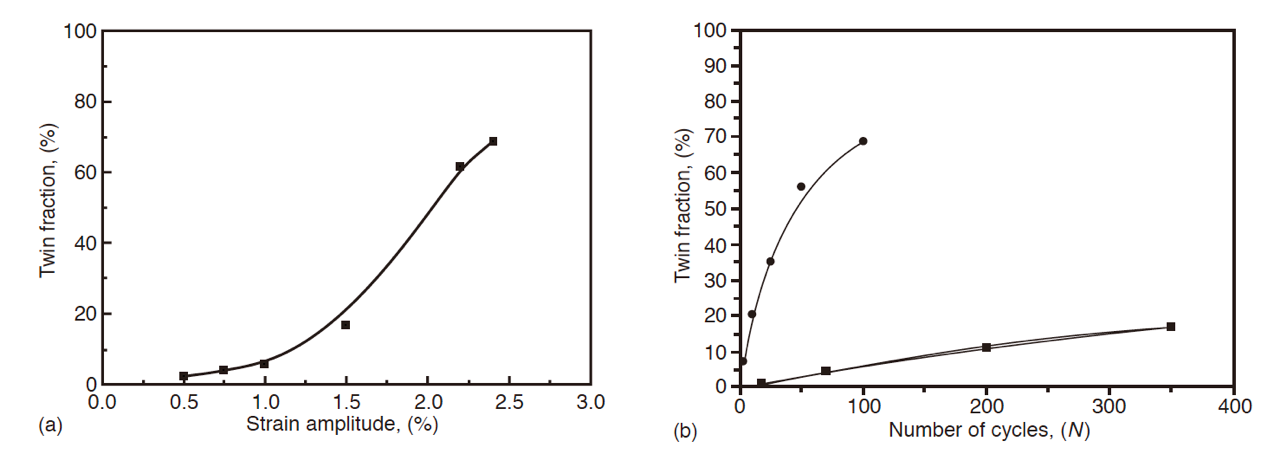
纯钛的密度为4.51g/cm3,与另一工业常用材料-钢相比仅相当于其的57%,故属于轻金属[1]。{张喜燕, 2005 #55}纯钛的晶体在室温下为密排六方结构[2]。纯钛在293 K单向拉伸下的变形主要为滑移,而在293 K时,其在循环载荷下随着应变幅的增加可产生孪晶。在77 K时,孪生成为纯钛的主要变形模式。在纯钛中有三种类型的孪晶,即{1012}型,{1011}型,{1122}型[3]。钛结合了钢(高强度)和铝(轻质感)的优点[4]。
工业纯钛具有α-退火结构,所以工业纯钛是一种α-钛合金。工业纯钛是指含有少量氧,氮,碳,铁和其他残留杂质的致密钛,根据杂质元素含量的差异,特别是对钛的性质有很大影响的氧元素,氮元素和铁元素的含量的差异工业纯钛被分为不同的牌号。
相关图片展示: