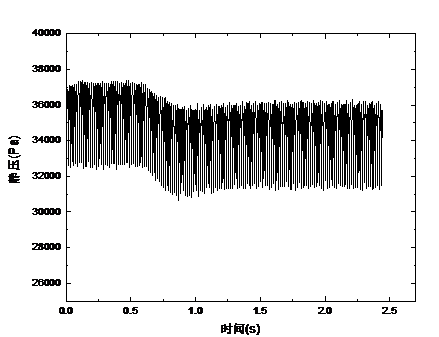气液两相流泵输气过渡过程外特性及内部流动研究毕业论文
2020-04-15 17:31:58
摘 要
离心泵广泛应用于化工、石油、冶金,制药等领域,当输送气液两相流介质时,常常会产生强烈的振动、噪音甚至发生事故。因此需要对离心泵的输气过渡过程进行研究,以提高离心泵的安全性、稳定性和使用寿命,使其功能在输送气液两相流的过程中得到更充分的发挥。本文采用RNG  湍流模型和欧拉模型,对输气过渡过程中,离心泵内部流动变化情况进行了数值研究。本文研究的主要内容和结论如下:
湍流模型和欧拉模型,对输气过渡过程中,离心泵内部流动变化情况进行了数值研究。本文研究的主要内容和结论如下:
1)研究了离心泵出口处的压力和气相体积分数随时间变化的情况,发现出口处压力与气相体积分数变化存在紧密联系,随着气相体积分数增大,压力减小。并通过对比分析得出结论:同位置上压力的变化早于气相体积分数的变化,因此通过出口处气相体积分数趋于稳定值作为输气过渡过程结束的依据,要比通过出口压力呈周期性波动作为输气过渡过程结束的依据更为准确。
2)研究了吸水室、蜗壳内气相体积分数随时间变化情况和叶轮内气体分布云图,得到了吸水室和蜗壳各监测点上气相体积分数变化曲线。发现气体从进气管进入吸水室后主要集中于吸水室上半部分,并从上部流道进入叶轮,在叶轮中也处于不均匀分布的状态,气泡团之间有较大空隙。分析了蜗壳上气相体积分数随时间变化情况,结果表明:蜗壳上各监测点气相体积分数随时间变化规律基本相似,而监测点距离叶轮越远,气相体积分数越大,波动幅度越小。
3)分析了蜗壳内各监测点上压力和气液两相速度随时间变化情况,并将各点变化曲线进行了对比分析,结果表明:各监测点上压力随时间变化规律基本相似,都是先降低到最低点后缓慢上升,最后达到稳定的周期性波动;监测点距离叶轮越远,其压力就越大;监测点距离叶轮越远,其气液两相速度就越小,速度变化曲线的波动幅度也越小;蜗壳内同一监测点上,气液两相速度基本相同。
关键词:CFD 气液两相流 离心泵 输气过渡过程 数值模拟
Study on external characteristics and internal flow of gas-liquid
two-phase flow pump during gas transfer process
Abstract
Centrifugal pumps are widely used in chemical, petroleum, metallurgy, pharmaceuticals and other fields. When transporting gas-liquid two-phase media, they often appear strong vibration, noise and even accidents. Therefore, it is necessary to study the gas transfer process of centrifugal pumps in order to improve the safety, stability and working life of centrifugal pumps, so that their functions can be fully played. In this dissertation, RNG k-ε turbulence model and Euler model were used to numerically study the flow changes in the centrifugal pump during the gas transfer process. The main contents and conclusions of this dissertation are as follows:
1) The pressure and gas volume fraction at the outlet of centrifugal pump were studied. It is found that the pressure at the outlet is closely related to the change of gas volume fraction. With the increase of gas volume fraction, the pressure decreases. Through comparative analysis, it can be seen that the change of pressure at the same position is earlier than that of the gas volume fraction. Therefore, it is more accurate to use the stable value of gas volume fraction at the outlet as the end of gas transfer process than periodic fluctuation of outlet pressure.
2) The variation of gas volume fraction with time in the suction chamber and volute and the contour of gas distribution in the impeller were studied. The variation curves of gas volume fraction at each monitoring point in the suction chamber and volute were obtained. It is found that the gas mainly concentrates in the upper part of the suction chamber after entering the suction chamber from the intake pipe, and enters the impeller from the upper runner. The gas is also in a state of uneven distribution in the impeller, and there is a large gap between the bubbles. The variation of gas phase volume fraction with time was analyzed. The results show that the variation of gas phase volume fraction with time is basically similar at each monitoring point on the volute. The farther the monitoring point is from the impeller, the bigger the gas phase volume fraction is, and the smaller the fluctuation range is.
3) The pressure and gas-liquid two-phase velocity changing with time at each monitoring point in the volute were analyzed, and the curves of pressure change at each monitoring point were compared and analyzed. The results show that the law of pressure change with time at each monitoring point is basically similar, which first reduces to the lowest point, then slowly rises, and finally reaches a stable periodic fluctuation. The farther the monitoring point is from the impeller, the greater the pressure will be monitored. The farther the point is from the impeller, the smaller the gas-liquid two-phase velocity and the smaller the fluctuation amplitude of the velocity curve. At the same monitoring point in the volute, the gas-liquid two-phase velocity is basically the same.
Key words: CFD; gas-liquid two-phase flow; centrifugal pump; transition process; numerical simulation
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 研究的背景与意义 1
1.1.1 研究背景 1
1.1.2 研究意义 2
1.2 研究现状及发展趋势 2
1.2.1 国内外研究现状 2
1.2.2 发展趋势 6
第2章 数值模拟方法 7
2.1 几何模型 7
2.1.1 三维建模软件介绍 7
2.1.2 离心泵模型建立 7
2.2 网格划分 8
2.2.1 网格生成方法 8
2.2.2 离心泵模型网格划分 9
2.2.3 网格质量检查 10
2.3 数学模型 10
2.3.1 控制方程 10
2.3.2 湍流模型 10
2.3.3 多相流模型 11
2.4 边界条件 12
2.5 收敛判据 12
2.6 本章小结 13
第3章 泵出口压力及泵内气相体积分数变化规律 14
3.1 监测点设置及过渡过程判定依据 14
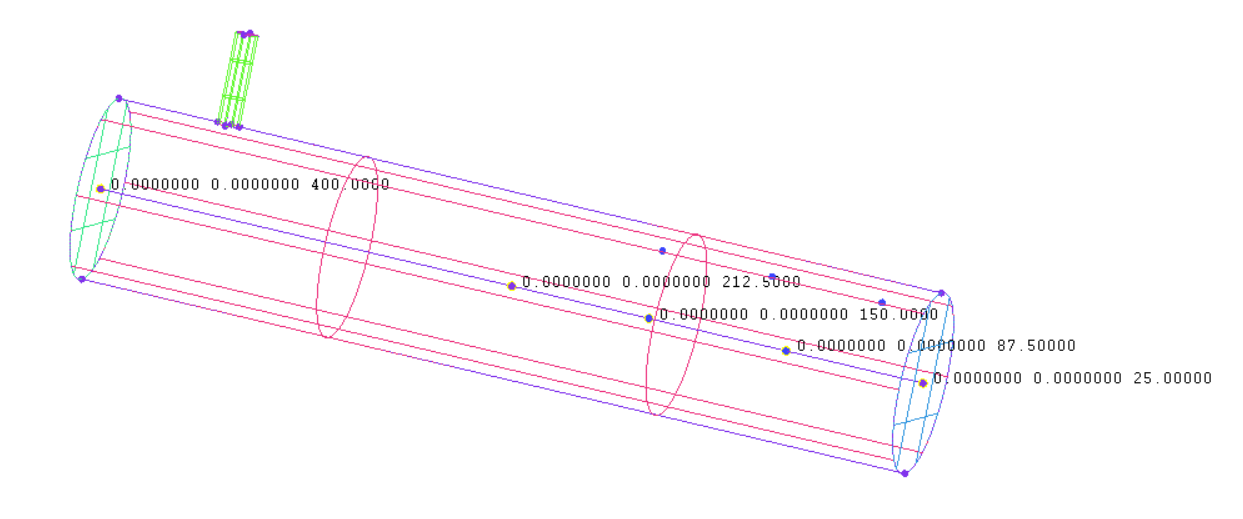
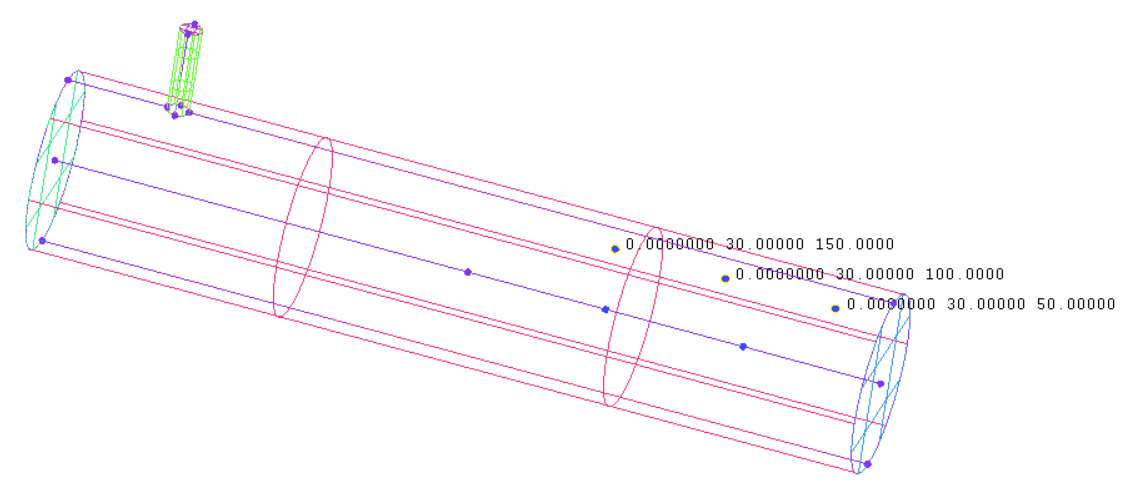
3.1.1 初始条件及监测点设置 14
3.1.2 离心泵出口处压力随时间变化规律 17
3.1.3 离心泵出口气相体积分数随时间变化规律 18
3.2 离心泵内部气相体积分数变化规律 19
3.2.1 离心泵吸水室气相体积分数随时间变化规律 19
3.2.2 叶轮内气相体积分布 22
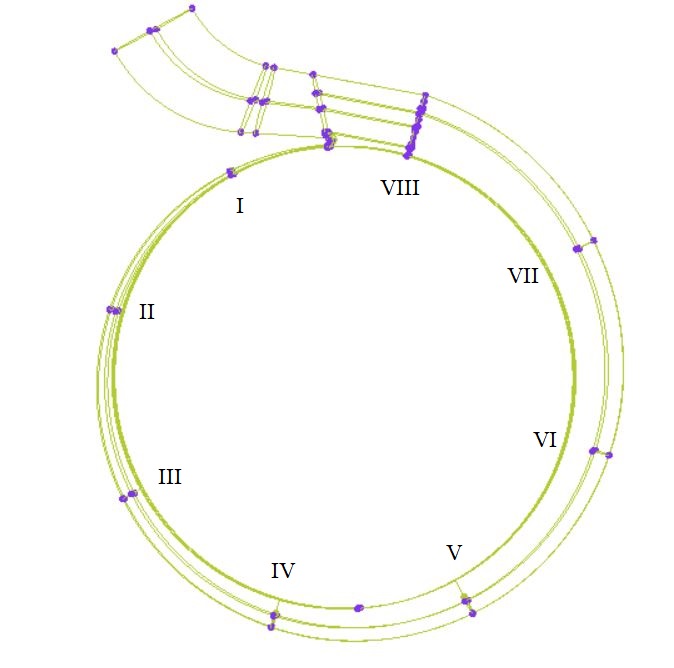
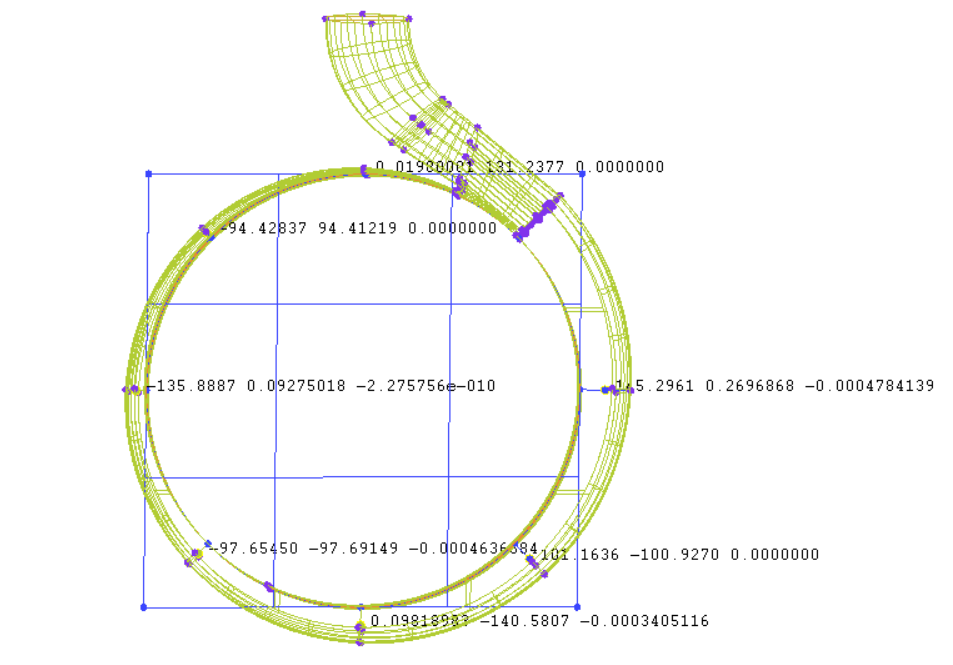
3.2.3 蜗壳I~VII截面气相体积分数随时间变化规律 24
3.2.4 蜗壳VIII截面气相体积分数随时间变化规律 28
3.3 本章小结 32
第4章 泵内压力变化及气液两相速度变化规律 33
4.1 压力变化情况 33
4.1.1 蜗壳内I~VII截面压力随时间变化规律 33
4.1.2 VIII截面上代表性监测点压力变化规律 36
4.2 气液两相速度变化及分布情况 37
4.2.1 蜗壳内各代表性监测点气液两相速度变化情况 37
4.2.2 VIII截面上气液两相速度分布情况 38
4.3 泵扬程随时间变化规律 39
4.4 本章小结 40
第5章 结论与展望 41
5.1 结论 41
5.2 展望 42
参考文献 43
致谢 47
第1章 绪论
1.1 研究的背景与意义
1.1.1 研究背景
离心泵是非常普遍使用的设备,具有结构简单、操作方便、使用周期较长等特性,并广泛应用于农田排灌、城市给排水、石油化工、采矿、食品轻工等国民经济的各行各业。泵的主要性能参数有流量Q、扬程H、转速n、气蚀余量NPSH、轴功率N和输出功率Ne等,且这些参数之间存在着一定的联系,我们将能够表现这种关系的曲线称为泵的特性曲线[1]。泵的特性曲线能够全方位地表示泵的工作性能,但由于泵内流动的复杂性,因此早期研究泵的特性曲线通常只能通过试验得到,在得到特性曲线后,用户可以此为依据充分了解泵的性能,并对泵进行选型和工况安排。
气液两相流是指气、液两相共存并相互作用的流体,气液两相流可以分为气相、气液交界面和液相三部分[2]。其中最容易变形的气液交界面可以组成不同的流型,根据两相的相对形态以及层流和湍流的概念,研究人员对不同情况的流型都做了较为深入的研究。流型根据特性参数而定,一般情况下,特征参数会随着流型的改变而改变。在水平管道条件下,典型的流型有:细泡状流、柱塞状流、环状流、弹状流、分层流等[3]。在垂直管道的条件下,典型的流型有:弹状流、细泡状流、块状流、环状流等。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: