Al不锈钢异种金属激光搭接接头组织与性能研究毕业论文
2020-07-15 21:20:18
摘 要
激光焊接技术目前已经在现代工业制造领域被广泛采用,尤其是其能量密度高、焊接速度快、焊接变形小等特点,对于异种材料的连接有着较大的优势和应用前景。然而铝和钢的性能差异很大,在焊接时铝和钢发生搅拌混合会产生有害的脆性金属化合物,并且引发残余应力从而导致焊接裂纹的发生。所以异种金属焊接仍有一些难点问题值得深入研究。本文通过对比研究未添加中间层和添加Ni中间层的两种铝/不锈钢搭接接头,获得了以下几方面的研究结论:
(1)激光搭接接头成形的研究。激光功率为2.5kW时,未添加中间层的试样焊道狭窄;随着热输入增加,焊道宽度增加;激光功率不变的情况下随着焊接速度增加,焊道宽度变化不明显。继续增大热输入焊接质量开始变差,出现飞溅。未添加中间层时激光功率为4kW,焊接速度为3m/min时焊缝表面成形最好;添加Ni中间层后激光功率为4.5kW,焊接速度为3m/min时焊接表面成形效果最好。添加Ni中间层的钢/铝激光叠焊接头面成形质量略优于不加中间层焊接接头。
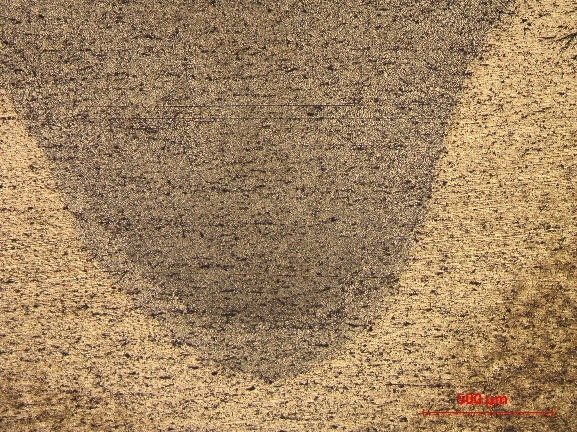
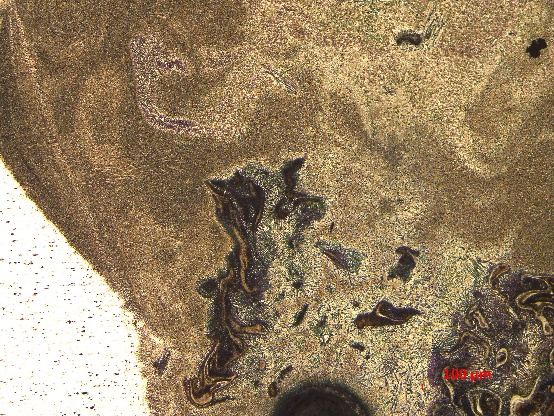
(2)焊缝内部的主要组织形态为柱状晶;界面处存在由金属化合物、金属氧化物、母材等构成的机械混合物;熔合区较窄,靠近熔合区的热影响区可观测到粗大晶粒。Ni中间层在一定程度上减少了表面裂纹的产生。不添加中间层和添加了Ni中间层的试样都有可能出现结晶裂纹。
(3)硬度测试表明,焊缝的硬度高于铝合金母材和热影响区,靠近界面的部分存在脆硬的金属化合物,硬度比两侧母材高;铝合金侧焊缝距界面越远硬度越低。
关键词:激光焊接;铝/不锈钢;Ni中间层
ABSTRACT
Laser welding technology has been widely used in modern industrial manufacturing, especially with its high energy density, fast welding speed, and small welding distortion. It has great advantages and application prospects for the connection of dissimilar materials. However, the properties of aluminum and steel are quite different. During the welding, stirring and mixing of aluminum and steel will produce harmful brittle metal compounds, and cause residual stress and lead to weld cracking. Therefore, there are still some difficult problems worthy of in-depth study of dissimilar metal welding. In this paper, through the comparative study of two aluminum/stainless steel lap joints without addition of an intermediate layer and Ni interlayer, the following conclusions are obtained:
(1) Laser lap joint forming research. When the laser power is 2.5kW, the specimen with no middle layer is narrow. With the increase of heat input, the width of the weld increases. With the increase of the laser power, the change of the width of the weld is not obvious. Continue to increase heat input welding quality began to become worse, spatter occurred. When the middle layer is not added, the laser power is 4kW and the welding speed is 3m/min. The weld surface is best formed when the welding speed is 3m/min; when the Ni middle layer is added to 4.5kW and the welding speed is 3m/min, the welding surface is the best. The forming quality of steel / aluminum laser lap welding with Ni interlayer is slightly better than that without intermediate layer welded joints.
(2) The main internal microstructure of the weld is columnar grain; there is a mechanical mixture composed of metal compounds, metal oxides, and base metal at the interface; Narrow, coarse grains are observed near the heat affected zone in the fusion zone. The Ni interlayer reduces the generation of surface cracks to some extent. There is a possibility that crystal cracks may occur in the sample without adding the intermediate layer and the Ni intermediate layer.
(3) Hardness test shows that the hardness of the weld is higher than that of the aluminum alloy base metal and heat-affected zone, and there are brittle-hard metal compounds near the interface, and the hardness is higher than the base metal on both sides; the farther the aluminum alloy side weld is from the interface The lower the hardness.
Key words: Fe/Al; laser welding; intermetallic compounds; interlayer
目录
摘要 I
ABSTRACT II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 课题研究的意义及背景 1
1.2 激光焊接的特点 1
1.3 铝/钢异种材料焊接的问题 2
1.4 铝/钢异种金属焊接的现状及进展 3
1.5 合金元素对铝/钢焊接接头的影响 4
1.6 本课题的研究内容 5
第二章 实验材料、设备和方法 6
2.1 实验材料 6
2.2 实验设备 7
2.3 实验方法 7
2.3.1 激光焊接实验 7
2.3.2金相组织分析实验 8
2.4 硬度测试 9
第三章 铝/不锈钢搭接接头焊缝成形 10
3.1 未添加中间层焊缝的表面成形 10
3.2 加Ni中间层焊缝的表面成形 12
3.3 本章小结 13
第四章 铝/不锈钢激光搭接接头微观组织与缺陷分析 14
4.1 未添加中间层铝/不锈钢搭接接头微观组织 14
4.2 添加中间层的微观组织 16
4.3 接头相组成分析 17
4.4 铝/钢焊接裂纹分析 19
4.5 接头显微硬度分析 20
4.6 本章小结 21
第五章 经济性分析 23
第六章 结论 24
参考文献 25
致谢 27
第一章 绪论
课题研究的意义及背景
铝是最常见的有色金属,铝合金的比强度较高,但是重量比较轻,所以,当需要减小构件的重量时,常常采用铝合金;钢是最常见的黑色金属,在我国工业体系中,钢材是被使用最多的金属。而就目前的形势而言,在航空航天、汽车、轮船等领域,铝/钢复合结构获得了越来越多的青睐,这种复合结构通过降低结构重量从而提高燃油效率、增续航程、节能减排[1-2]。激光焊接与其他常见的焊接方式相比,有很多的长处与优点,例如:激光焊接具有高热输入、高速度、焊道窄小、热量对焊接区域的影响范围小、焊接的材料不容易变形,并且激光焊接可以应用到多种材料,并且还能够与其它的焊接工艺相搭配。由于激光焊接具有如上的各种优点,所以利用激光焊接时,还可以避免生成各种金属化合物[3]。可是,铝/不锈钢搭接接头的激光焊接工艺不是一个简单的过程,激光焊接工艺过程也是一个复杂的物理过程,其中,我们必须考虑的问题如下:1、需要考虑金属构件对激光吸收的问题;2、需要考虑动量和能量之间的变换问题;3、需要考虑由于光致等离子体的作用而造成的激光发生散射和吸收的问题;4、需要考虑形成熔池和熔池凝固的影响因素;5、需要考虑匙孔效应问题等等。这些影响因素直接会影响到焊接搭头的性能[4]。根据目前汽车工业的工艺流程,铝/不锈钢搭接接头的激光焊接工艺已经被广泛使用,但是,上述问题依然影响着该工艺的进程,所以,本文所研究的铝/不锈钢搭接接头激光焊接具有理论和实际意义。
本文的研究内容包括研究采用添加Ni中间层下Al/不锈钢激光焊接工艺,焊接参数的选择以及焊缝成形;分析Al/不锈钢异质接头激光焊接冶金问题及其力学性能,重点研究添加Ni中间层下Al/不锈钢异质接头界面微观组织及其对硬度的影响。
激光焊接的特点
激光焊接接头可以有较大的深宽比。这是因为激光能向工件传输的能量密度很高。众所周知,激光焊接技术的应用存在两个主要问题,第一个是需要比较高的前期投入,第二个是针对于能量转换效率这个问题而言,它是不高的。事物都是有两面性的,有缺点必然也会有优点,激光焊接的主要优点有:激光焊接的热源是高能激光束,操作者可以通过调整激光发生器的各项参数来获得所需热输入;激光焊接具有高焊接速度、焊缝窄小等特点[7],并且激光焊接可以应用到多种材料,并且还能够与其它的焊接工艺相搭配。由于激光焊接具有如上的各种优点,所以利用激光焊接时,还可以避免生成各种金属化合物。因此,激光焊接工艺被广泛应用在各种工业领域[5]。与传统的焊接工艺相比较,激光焊接在各种领域的广泛应用和其无法比拟的有点,远远胜过传统焊接工艺。由于激光焊接的热源是以光路的形势来存在,并且激光焊接具有高能量、高速度、搭接处的焊缝窄小、热量对焊接区域的影响范围小的特点,激光焊接还可以被用来对微小的局部区域加热。所以,在激光焊接另一个广泛应用的领域实在电路板印刷方面,还有对微小的电子器件的焊接。根据文献资料可知,激光焊接在工作工程中,针对于非常微小的电子元器件,其能够在微小的电子元器件表面瞬间生成特别高的温度,可是,除了焊接部分以外,其他部分基本不会有影响[6-8]。
铝/钢异种材料焊接的问题
(1)铝/钢熔点相差大:由于钢的熔点比铝高很多,由于钢的熔点比铝高很多,所以,铝/钢搭接接头焊接时,在接头位置,当温度达到铝或者铝合金材料的熔点时,钢材还不会融化,钢材依然处于固态,此外,即使铝或者铝合金发生了融化,处于液态的铝对处于固态的钢的润湿性是非常差的[9]。
相关图片展示: