考虑运输能力的跨单元制造调度优化毕业论文
2020-04-08 13:27:43
摘 要
随着信息化的快速发展,生产制造网络化的需求日益提高,生产制造资源再分配、充分利用闲置加工资源是提高生产制造效率的关键性问题。为提高生产效率,将具有加工工艺相似性的机器放置在同一区域,形成加工能力相对独立的单元,这种模式成为单元制造系统。为适应多元化工件加工以及工件个性化需求提升,单一的加工单元无法满足加工需求,还需要其他生产单元参与,工件在不同生产单元之间的频繁运输产生了跨单元调度问题。跨单元调度问题目前普遍存在于实际的生产过程中,具有灵活可变和复杂度高的特点。本文在深入研究国内外跨单元制造调度问题研究现状的基础上,致力于提出解决跨单元调度问题的多目标优化方法,本论文的主要研究内容如下:
(1)通过提出问题假设、约束条件、符号定义、目标函数等提出了考虑运输能力限制的多目标跨单元调度模型。单元间运输采用与实际生产相似的小车运输模式,小车的运输空间有限和运输时间消耗对跨单元调度进行运输能力限制。跨单元运输调度方案包括了零件的加工方案以及小车的运输路径,优化目标为最小完工时间、最低运输成本的多目标优化。
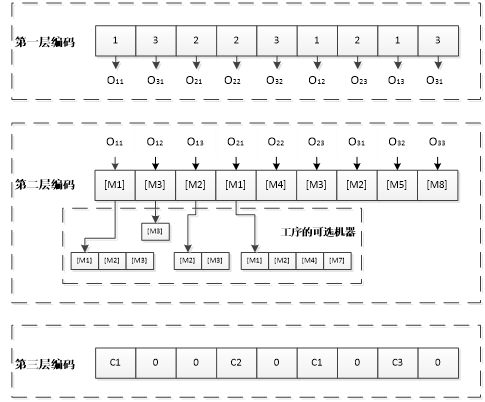
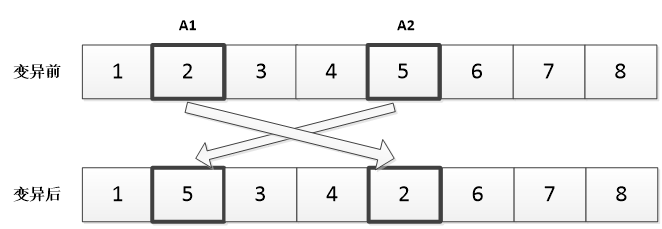
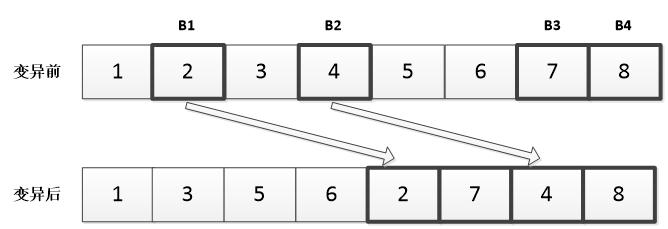
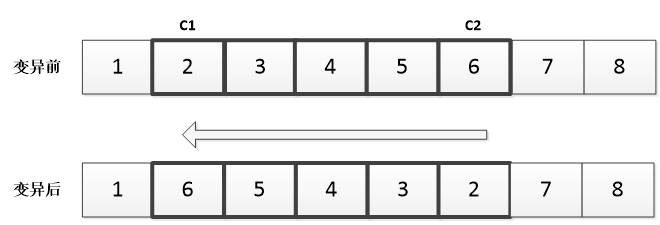
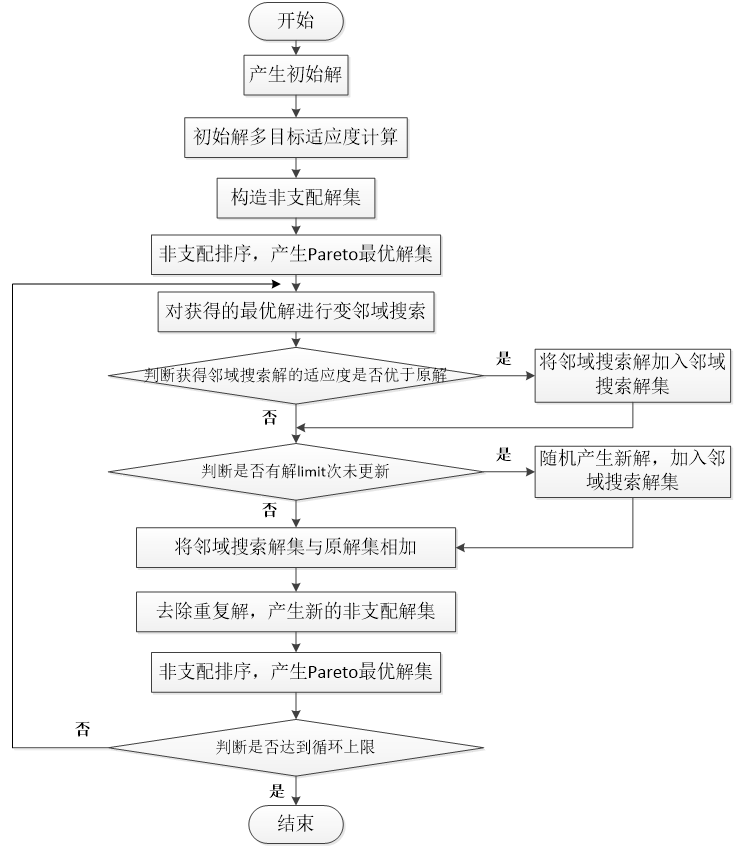
(2)为解决高复杂性的跨单元调度问题,本文在经典人工蜂群算法的基础上进行改进,提出了基于变邻域搜索的多目标人工蜂群算法。人工蜂群算法是通过引领蜂、观察蜂、侦查蜂三种蜜蜂种群相互配合来选择最优食物源。在引领蜂阶段,采用三段式编码使可行解转化为编码结构参与计算,并采用了Pareto方法来解决多目标调度问题;在观察蜂阶段,改进搜索方程,构建多元邻域,引入变邻域搜索方法,以提高全局搜索效率;在侦查蜂阶段,利用编码变异随机产生新的食物源,尽量避免陷入局部最优。
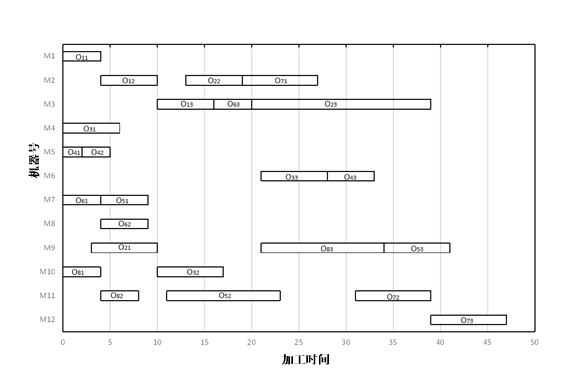
(3)针对本文提出的基于变邻域搜索的人工蜂群算法进行参数实例验证,在Python3.6平台上,编程模拟了算法解决跨单元调度问题。通过多组参数对比分析,选取了算法参数limit以及N的最优值。并展示了完工时间最优可行解,绘制了对应的甘特图。实例验证结果证明该算法对解决跨单元调度问题具有良好的收敛速度和稳定性。
总之,在解决本文提出的考虑运输能力受限的跨单元调度模型时,基于变邻域搜索的多目标人工蜂群算法具有良好的求解质量,通过变邻域搜索方法提高全局寻优能力,尽量避免陷入局部最优。
关键词:跨单元调度问题,人工蜂群算法,运输能力受限,多目标优化
Abstract
With the rapid development of informatization, the demand for manufacturing and networking is increasing day by day. The redistribution of production and manufacturing resources and the full use of idle resources are key issues in improving production efficiency. The cell manufacturing system groups the machines according to the similarity of the work process. This processing mode form a relatively independent processing cell and it has been one of the newest and most effective production line setup methods in the world. With the increasing demand for workpieces diversification and workpieces individuation. Workpieces are not only limited to one production cell but also need to be processed in other production cells. Frequent transport of workpieces between different production cells creates cross-cell scheduling problems. The cross-cell scheduling problem is very common in the actual production process at present, and it is characterized by flexibility and high complexity. Based on the deep research on the status quo of cross-cell manufacturing scheduling problems both at home and abroad, we are committed to propose a multi-objective optimization method for solving cross-cell scheduling problems in this paper. The main research contents of this paper are as follows:
(1)A multi-objective cross-cell scheduling model considering transportation capacity constraints is proposed by proposing problem assumptions, constraints Symbol definitions, objective functions, etc. The inter-cell transportation adopts a similar trolley transport mode as the actual production. The limited transportation space of the trolley and the transport time consumption limits the transportation capacity of the cross-cell scheduling. The cross-cell transportation scheduling plan includes the parts processing plan and the transportation path of the trolley. The optimization goal is multi-objective optimization with the minimum completion time and the lowest transportation cost.
(2) In order to solve the high complexity of the cross-cell scheduling problem, this paper proposes a multi-objective artificial bee colony algorithm based on variable neighborhood search on the basis of classical artificial bee colony algorithm. The artificial bee colony algorithm is divided into three stages: leading bee, observing bee and investigating bee. In the lead bee stage, three-stage coding is used to transform feasible solutions into coding structures and participate coding structures in the calculation. The Pareto method is used to solve the multi-objective scheduling problem. At the observation bee stage, the search equation was improved, multivariate neighborhoods were constructed, and a variable neighborhood search method was introduced to improve the global search efficiency. At the bee detection stage, a new food source was randomly generated using the coding mutation to avoid falling into a local optimum.
(3) Aiming at the parameter experimental verification of the improved artificial bee colony algorithm presented in this paper, the cross-unit scheduling problem is programmed and simulated on the Python 3.6 platform. The Pareto processing method of the multi-objective problem is used to obtain the corresponding Pareto solution set. The experimental results show that the algorithm has good convergence speed and stability for solving cross-cell scheduling problems, and it also fully validates the algorithm's powerful search capability.
In a word, when solving the cross-unit scheduling model considering transport capacity limitation proposed in this paper, the multi-objective artificial bee colony algorithm based on variable neighborhood search has good solution quality, and the global search ability is improved by changing the neighborhood search method. Avoid falling into a local optimum.
Keywords: Cross-cell scheduling problem, Artificial bee colony algorithm, Limited transport capacity, Multi-objective optimization
目录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第1章 引言 1
1.1 研究背景与意义 1
1.2 国内外研究现状 1
1.2.1 单元制造系统与跨单元调度问题 1
1.2.2 智能优化算法 4
1.3 本文的主要研究内容 6
第2章 跨单元调度模型 8
2.1问题描述 8
2.2 问题假设 8
2.3 符号列表 9
2.3.1索引参数 9
2.3.2变量参数 9
2.3.3决策变量 9
2.4 约束条件 10
2.5目标优化函数 11
2.6本章小结 11
第3章人工蜂群算法的原理 12
3.1蜂群智能规律 12
3.2人工蜂群算法流程 12
3.2.1初始化食物源 13
3.2.2计算食物源的收益率 13
3.2.3食物源的邻域搜索方法 13
3.2.4观察蜂选择食物源 13
3.2.5人工蜂群算法的详细流程框架 14
3.3人工蜂群算法的特点 15
3.4 本章小结 15
第4章 基于变邻域搜索的多目标人工蜂群算法 17
4.1解的表示 17
4.1初始解产生 18
4.2 构建Pareto解集 18
4.3变邻域搜索方法 18
4.3.1构建邻域 19
4.3.2变邻域搜索策略 20
4.4 基于变邻域搜索的多目标人工蜂群算法整体流程 20
4.5 本章小结 22
第5章 实例分析 23
5.1实例描述 23
5.2 算法参数设置 24
5.2结果分析 26
5.2.1收敛性分析 26
5.2.2最优解分析 28
5.3 本章小结 29
第6章 结论与展望 30
6.1总结 30
6.2展望 30
参考文献 32
致谢 34
第1章 引言
1.1 研究背景与意义
单元制造系统(cellular manufacturing systems,CMS)是将一组工艺相似的机器进行整合,整合后形成一组具有相对独立、加工效益高的生产制造单元,单元制造系统CMS是目前生产制造最新、最有效的加工方式之一。随着现代化生产中对产品加工工艺需求复杂化、多样化程度不断提高,单一的生产制造单元无法满足制造要求,工件的某些特定工序需要在其他单元的机器上;另外,生产方由于生产成本以及加工空间的约束,难以为多种复杂需求购买所有的设备。因此,一些工件需要运输至其他加工单元进行加工,加工零件在不同生产制造单元间的运输就产生了跨单元转移(inter-cell transfer)的现象。
通过实际的调研结果显示,在我国的装备制造中,零部件的生产制造过程中,一个复杂设备的生产需要数百台设备的配合,上千种零件的组装以及多达万道工序,单一的生产单元难以满足如此庞大的生产需求。以某个大型的军工装备企业为例,某综合传动装置有超过51%的零部件需要跨车间加工;而有47%以上的零件延迟交付的原因是跨单元协作效率低下。此外,我国装备制造工业快速发展的国情造成了大量传统设备与先进设备穿插存在于现代化生产线中,产品各品种混线生产的情况普遍存在,使得跨单元运输次数显著增加。[1]工件的加工路径中存在加工柔性,工件工序有多个单元可供选择,工件的加工路径跨多个生产单元,造成了跨单元写作的加工模式。
国外的制造业中跨单元调度问题也普遍存在、亟待解决。统计显示,单元制造模式的在国外企业的普及达到72%,而单元制造过程中平均有20%以上的工件需要跨单元加工,仅仅只有10%的单元无需其他单元协作。[2]
在目前的生产条件下,跨单元调度问题成为提高生产制造效率的重要障碍;研究该问题具有现实的迫切性以及长远的考虑。因此,本文解决跨单元调度问题为研究目标。
1.2 国内外研究现状
1.2.1 单元制造系统与跨单元调度问题
单元制造系统(Cellular Manufacturing Systems, CMS)是将加工工艺相似的机器整合于同一生产单元中,进行集中的零件加工,对加工零件要求有相似的加工路径,从而使单元制造有良好的规模效应。构建单元主要包括以下三个步骤:单元搭建、单元分布布局和单元内调度。单元搭建和单元分布布局属于单元的前期设计阶段,将机器和工件按照相似性分成机器组和工件族,机器空间布局是在空间允许的前提下保证工件加工流程的顺畅。单元内部调度主要解决决策工件在本单元内部以及跨单元调度问题。目前构建单元的研究现状如下:
(1)单元构建:单元构建首先需要确定工件的工艺路径,根据其工艺路径将具有相应加工能力的机器分组。单元不仅包括需要加工的零件族还包括加工零件对应的机器族。目前单元构建技术在国内外研究已取得一定成果,技术已经较为成熟。曹振新等人[3]在单元制造构建过程中,通过同步优化单元构建、设备布置与成组排产三个步骤,建立单元制造系统的非线性规划模型,并通过遗传算法求解该问题。Safaeia等人[4]在综合考虑了加工需求和设备动态变化的因素影响,引入了模糊规划的理念,实现了转运成本最低和机器加工成本最低;Iraj等人[5]使用遗传算法来构建单元制造系统,从而减少了异常零件的数目,提升了机器的使用效率;Jose[6]等人尽量减少跨单元调度次数为优化目标,应用了图论中的结点着色思想来搭建单元。
(2)单元布局:在单元布局的核心是将机器合理安排和分布以方便工件的运输和加工。成为众多学者研究的课题。Stefan等人[7]认为单元布局问题分为两个关键问题:机器分布问题以及路径规划问题,而单元布局需要将这两个问题综合考虑,提出运用互换、转移等操作,实现了转运成本和重新设置机器次数最小化。李志华等人[8]引入多个单元制造系统同时加工的问题,将各种制造系统优化重组,不仅仅局限于一个单元的布局问题,而是多个单元综合布局问题。
(3)单元调度:单元调度是在单元构建和单元布局之后的延续步骤,与实际的生产加工接轨的关键步骤。工件选择的机器和机器对加工工件的分配是两个核心子问题。由于加工工件在数量和种类上的差异,使得单元调度越发复杂。充分利用机器的性能,提高工件加工能力从而降低生产成本,就需要找到一个适应问题特性的调度方法,这也成为了目前学者的研究重点。
随着现代制造业的发展,单一制造单元的生产加工能力不足的缺点凸显,单元制造也不仅仅局限于单元内部独立加工,而是趋向于协作化、集成化、综合化发展。工件在不同单元之间的跨单元转移打破了传统单一制造单元的加工限制,这使得企业在不大幅度提升成本的前提下提高了生产的多元化能力。因此,跨单元的调度问题备受关注。依据单元的加工模式不同,跨单元调度可以分为跨流水线车间调度和跨作业车间调度两大类。这两种模式的特点如下[1]:
(1)跨流水线车间调度:流水线车间调度问题对工件和机器具有以下要求:
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: