Ti-3.5Al-3.5Fe-0.1B合金悬浮熔炼和热处理工艺对组织和性能影响毕业论文
2020-07-05 17:38:07
摘 要
本论文对使用悬浮熔炼制备的新型的Ti-3.5Al-3.5Fe-0.1B钛合金进行了研究,通过普通退火、双重退火和β退火热处理,研究了其热处理对合金显微组织和力学性能的影响。
研究结果表明:不同的退火制度,可以控制合金的α相和β相的相对含量。原样中含有许多片层状的α相,还有一些破碎的α相和少量的β相。普通退火试样中有片层状的α相和少量的β相,但出现了一些短棒状的α相。双重退火试样中,片层状的α相很少,大多为短棒状或者颗粒状的α相,而β相的含量增多,在β相基体上析出了一些细小的次生α相。β退火试样中,初生α相基本消失,组织为大的β晶粒,其内部则是许多针状的次生α相。
拉伸试验表明:双重退火制度的试样的屈服强度、抗拉强度以及伸长率都最高,分别828 MPa、963 MPa和11.22%。而硬度测试表明,β退火试样的硬度最高,为323.61HV,而双重退火的硬度最低,为302.45HV。由此可见,β退火对合金的性能的改善效果最好。
关键词:钛合金 热处理 显微组织 力学性能
Levitation Melting and Effect of Heat Treatment on
Microstructure and Properties of Ti-3.5Al-3.5Fe-0.1B Alloy
Abstract
This paper on the use of levitation melting preparation new Ti-3.5Al-3.5Fe-0.1B titanium alloy was studied, through the general annealing, double annealing and β annealing heat treatment, study the influence of heat treatment on the alloy microstructure and mechanical properties.
The results show that different annealing systems can control the relative content of α and β phases of the alloy.The original sample contains many lamellar α phases, and some broken α phases and a small number of β phases. There are lamellar α phases and a small number of β phases in the ordinary annealed samples, but there are some short rod like α phases. In the double annealing sample, the lamellar α phase is very few, most of which are short rod or granular α phase, while the content of the β phase increases, and some minor secondary α phases are precipitated on the matrix of the β phase. In the β annealed sample, the primary α phase basically disappears, the microstructure is a large β grain, and there are many needle like secondary α phases inside the β annealed sample.
The tensile test shows that the yield strength, tensile strength and elongation of the double annealing system are the highest, 828 MPa, 963 MPa and 11.22% respectively. Hardness tests showed that the hardness of beta annealed specimens was the highest, 323.61 HV, while the hardness of double annealed specimens was the lowest, 302.45 HV. It can be seen that β annealing has the best effect on improving the properties of the alloy.
Key words: titanium alloy; heat treatment; microstructure; mechanical properties
目录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1课题背景 1
1.2钛合金的概述 1
1.3合金元素对钛合金的作用 1
1.3.1铝元素的作用 1
1.3.2铁元素的作用 2
1.3.3硼元素的作用 2
1.3.4其他元素作用 2
1.4钛合金熔炼工艺 3
1.5钛合金的热处理工艺 4
1.6论文研究的目的和研究内容 4
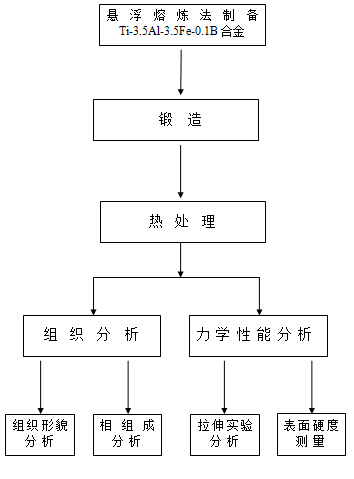
第二章 实验材料和方法 6
2.1实验材料 6
2.2实验方案 6
2.3实验方法 6
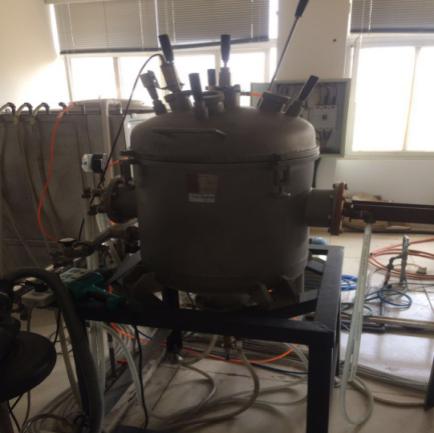
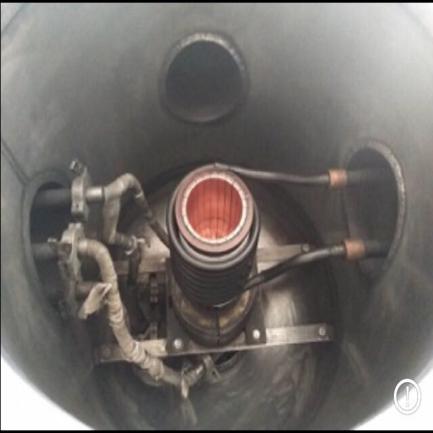
2.3.1熔炼过程 6
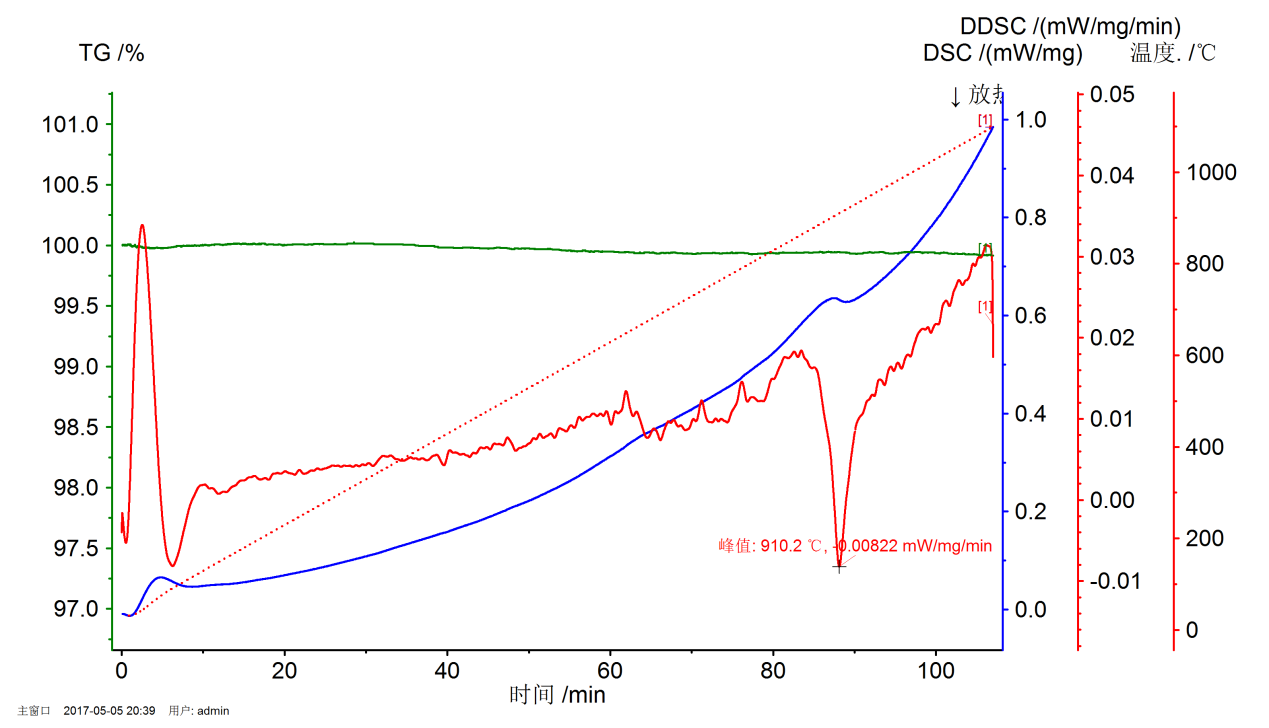
2.3.2 DSC分析 7
2.3.3锻造 8
2.3.4热处理方式 9
2.3.5金相 9
2.3.6 XRD物相分析 10
2.3.7拉伸试验 11
2.3.8硬度测试 13
第三章 热处理工艺对Ti-Al-Fe-B合金组织和 14
力学性能的影响 14
3.1 Ti-Al-Fe-B合金热处理前后XRD物相分析 14
3.2 Ti-Al-Fe-B合金热处理前后微观组织形貌 15
3.3 不同热处理工艺对Ti-Al-Fe-B合金组织的影响 18
3.4 力学性能测试 19
3.4.1拉伸实验 19
3.4.2硬度测试 22
3.5本章小结 23
第四章 结论和展望 25
4.1实验结论 25
参考文献 26
致谢 27
第一章 绪论
1.1课题背景
钛元素,于1791年被英国一个化学家发现。在20世纪初,纽约一个化学家发明了“Kroll工艺”,此工艺一直沿用至今。在1950年,钛合金首次被应用于制作飞机上的零部件,后来,随着时间的推移,钛合金逐步发展成为了航天工业中重要的金属材料。钢和铝的金属材料早已被广泛应用于各领域,但是,随着人们的需求的日益提高,我们需要性能更加优越的材料,正是在这种情况下,钛合金出现并迅速引起了人们的关注。钛合金拥有很多的优点,如:
(1)力学性能优秀,耐蚀性能好;
相关图片展示: