钛合金中点缺陷与杂质元素的相互作用及电子结构的研究毕业论文
2020-07-05 17:39:05
摘 要
钛合金中含有等合金元素,主要为铁、氮、氧、碳杂质元素。控制这些元素的某些含量和组合可以导致具有良好整体性能的半成品,并最终作为性能优良的加工材料用于石油与化工、航空和航天等重要工业零件。研究这些合金元素、杂质元素及与空位间的相互作用机制对钛合金的设计和开发具有重要意义。
本文通过采用第一性原理计算方法计算了结构参数,杂质-空位相互作用能,电荷密度分布,态密度,从原子尺度的不同角度全面分析了Al,V不同位置固溶替代对间隙杂质元素与空位之间的相互作用的影响机理。结果表明固溶Al原子、V原子与间隙C原子表现为相互吸引,这种吸引作用降低了间隙C与空位的相互作用能,对C的通过空位机制的扩散与偏析有阻碍作用,且V原子对于C原子的相互作用强于Al和Ti原子。
关键词:钛合金; 合金元素; 杂质元素; 空位; 第一性原理计算
Influence of alloying elements on the interaction between impurity C and vacancy in titanium alloy
Abstract
Titanium alloys mainly contain Al, Mo, V, Zr and other alloying elements and impurity elements Fe, N, O, and C and so on. Controlling certain contents and combinations of these elements can result in a semi-finished product with good overall performance, ultimately for aviation, aerospace, and petroleum, chemicals and other important industrial parts provide high-quality processing blanks. Study of the interaction mechanism of alloying elements, impurity, and vacancy make sense for Ti alloys design and developing.
In this paper, first-principles calculations were used to study the effect of addition of different sites substitution of alloying elements Al and V on interaction between interstitial element C and vacancy defect. Relaxation optimized structural parameters, charge density distribution, and density of states were calculated, from the atomic level to give a multi-angle perspective of the interaction mechanisms. The results show that the solid-solution Al atoms and V atoms both exhibit attraction interaction with interstitial C atoms, which may inhibit the diffusion of C atom by vacancy path, and the interaction of V atoms with C atoms is stronger.
Keywords: Titanium alloys; Alloying elements; Impurity elements; Vacancy; First-principles calculations
目录
摘 要 Ⅰ
ABSTRACT Ⅱ
第一章 绪论 1
1.1引言 1
1.1.1 钛合金及其应用 1
1.1.2 钛合金的应用现状 2
1.2钛合金中的主要杂质元素及其对钛合金性能影响 2
1.3研究内容与意义 3
1.3.1研究意义 4
1.3.2研究内容 4
第二章 研究方法 5
2.1第一原理计算概述 5
2.1.1第一原理方法 6
2.1.2三大近似 7
2.2密度泛函理论 7
2.3 交换关联势 7
2.3.1结构驰豫 8
2.3.2静态自洽 8
2.3.3态密度计算 8
2.4计算软件 9
2.5计算步骤 9
第三章 实验结果与讨论 10
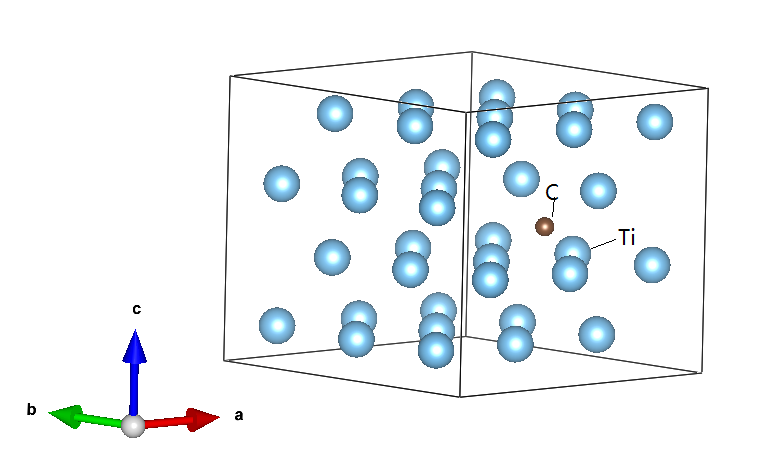
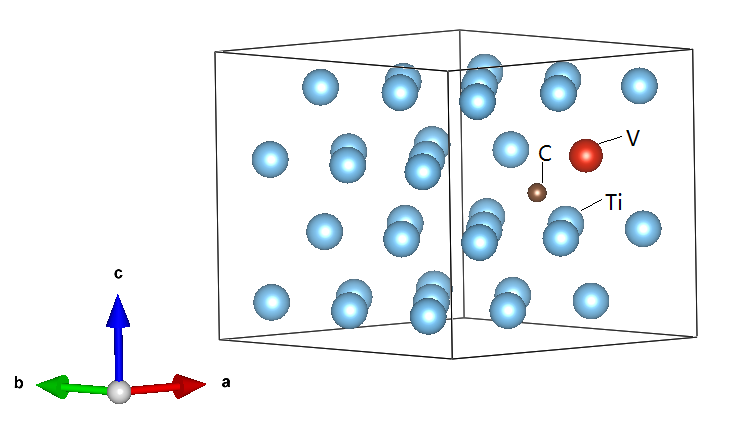
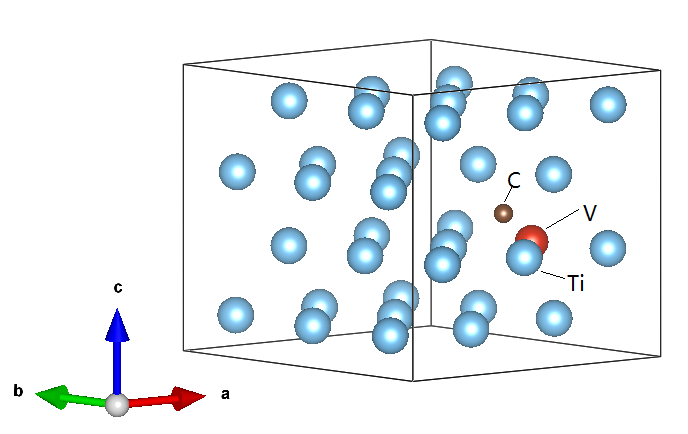
3.1建立原子模型 10
3.2结构参数表 13
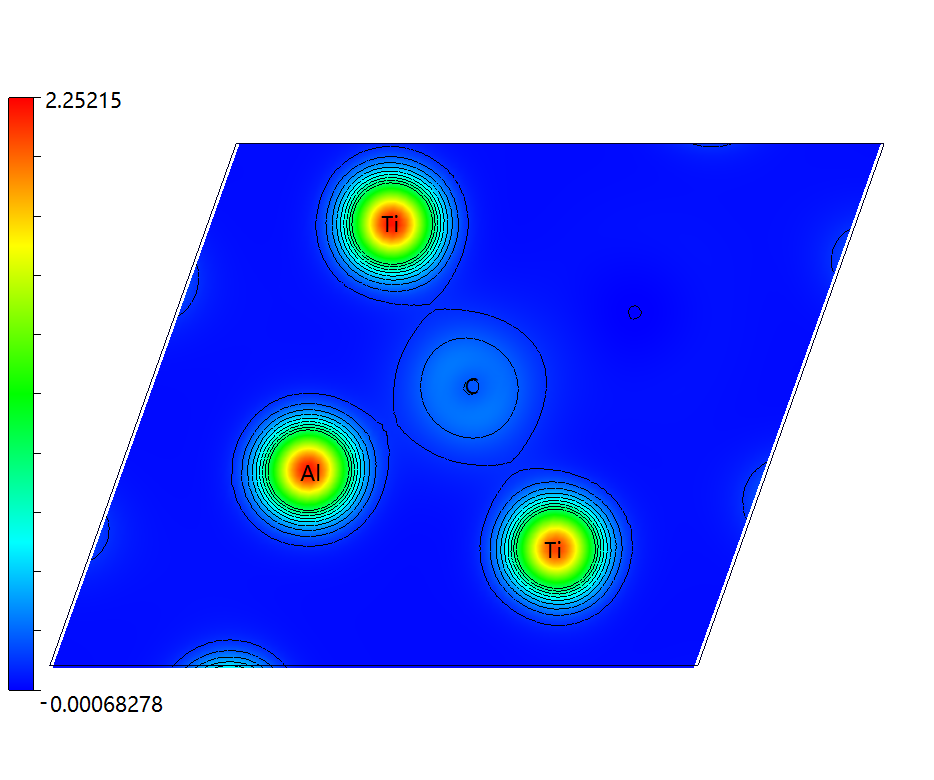
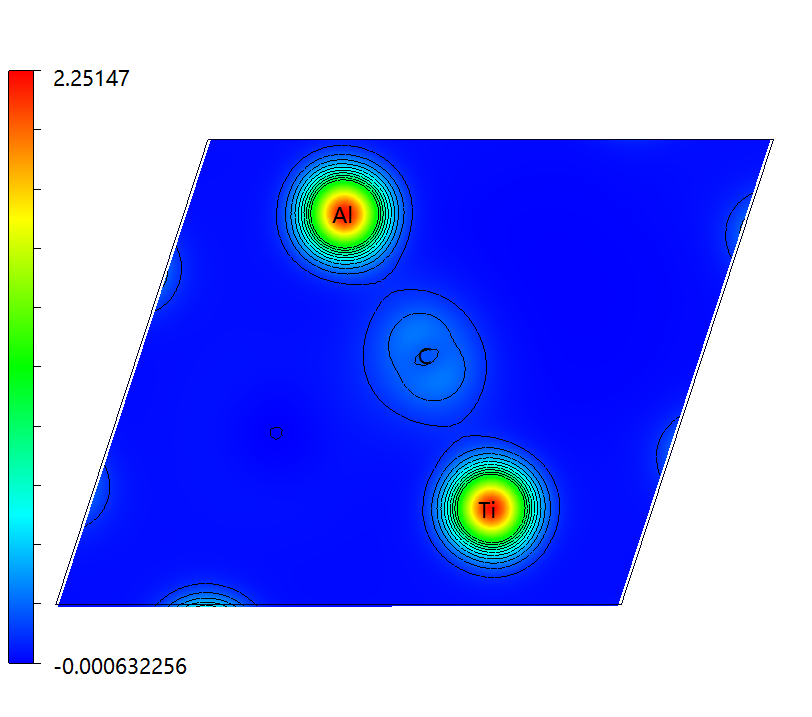
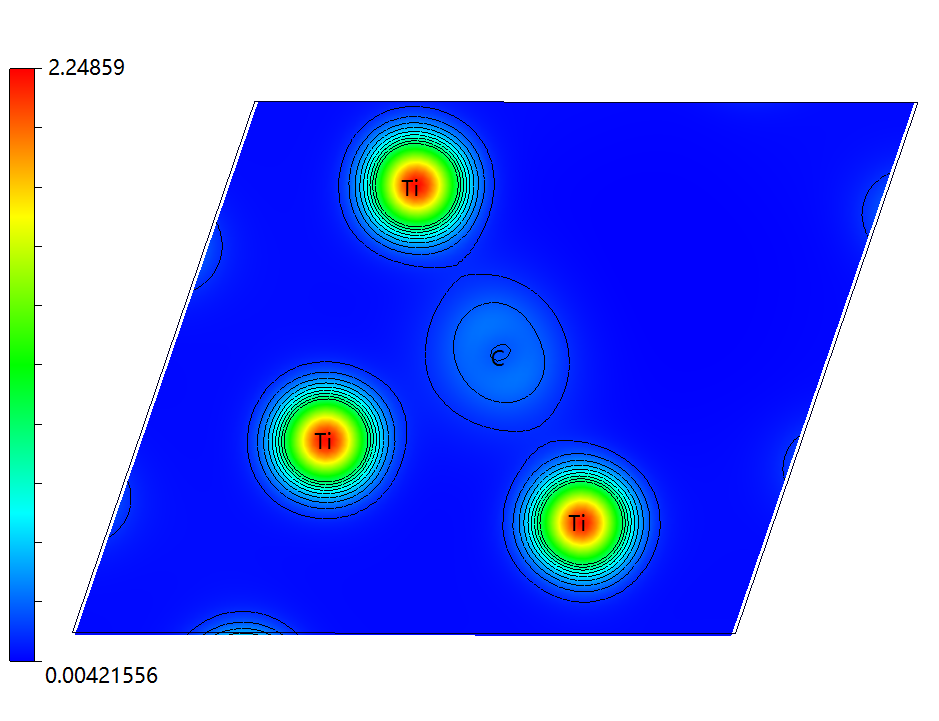
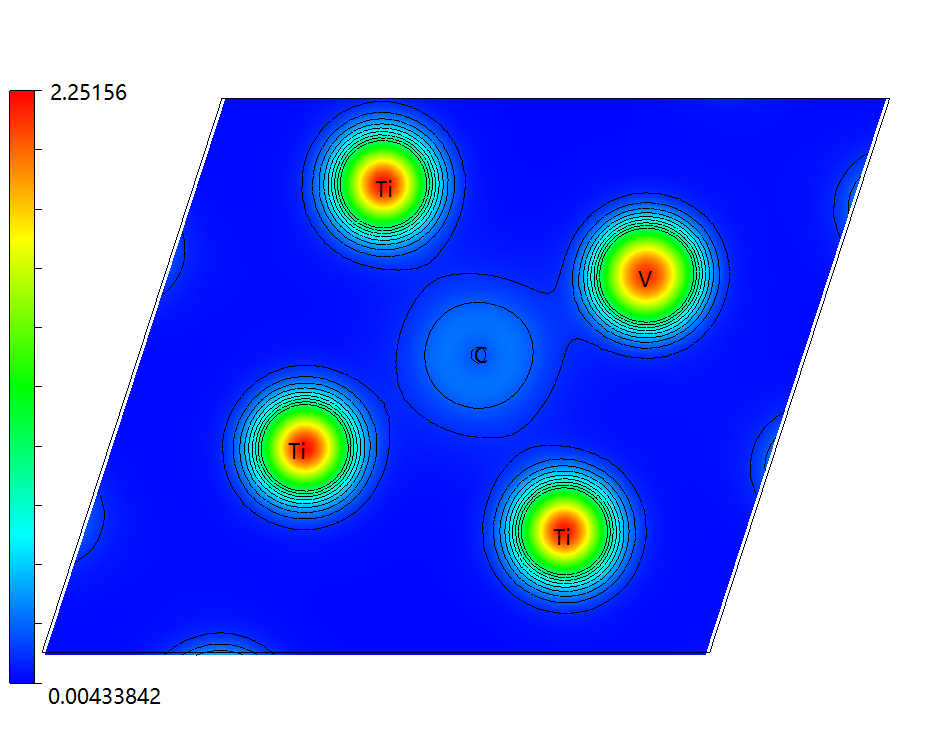
3.3 电荷密度图 14
3.4 态密度图 18
3.5 杂质空位相互作用能 22
第四章 结论 24
参考文献 25
致谢 26
绪论
引言
钛合金能成为当今世界航天领域最有发展前途的金属结构材料之一,是因为它具有高比重、低密度、耐腐蚀、耐高温、非磁性等优良的综合性能。它是一种新型金属,其所含杂质的含量决定了它的性能。
1.1.1钛合金及其应用
强度高-与其他金属相比,它的密度较小,钢的密度是它的167%,但其强度却更高,因此钛合金适用于制造那些具有更轻的质量而强度更高的部件。
热强度高-钛合金的使用温度比大部分合金高很多,可以满足在较高的的温度下长期工作的要求。钛合金的工作温度可高达五百摄氏度,而铝合金仅仅在两百摄氏度以下。
抗蚀性好-钛合金的耐腐蚀性远远优于不锈钢和其他钢材,这使得它可以在潮湿的环境和海水中工作; 它抵抗点蚀,耐酸腐蚀和抗应力腐蚀的性能优良; 对碱和氯,硝酸和硫酸具有较好的的耐蚀效果[1]。
相关图片展示: