Ti73.3Fe26.7合金的悬浮熔炼及其组织特征毕业论文
2020-07-09 20:23:22
摘 要
从20世纪50年代,钛合金开始被应用于航天航空事业,β钛合金因时效处理后有其他钛合金无法比拟的高强度和塑性,从而广泛应用于机翼及机身的制造中。Fe作为β相稳定元素,可以显著降低马氏体转变温度,同时抑制ω相的生成,并且Fe在Ti中偏析形成的“TiFe相”,可降低材料疲劳特性。本次研究探讨在纯钛中加入26.7%含量的Fe元素,通过悬浮熔炼得到铁钛铸锭,利用XRD和金相分析其成分和组织,通过开路电位、极化曲线等电化学测试,揭示Ti73.3Fe26.7合金的电化学行为。实验结果表明加入23.7%的Fe元素,合金组织与铸造形貌一致,但是晶粒较为粗大,极化曲线中外部抗腐蚀性最好,开路电位显示内部性能最稳定,合金的硬度最高达到543 Mpa。
关键字:Ti73.3Fe26.7合金 熔炼 组织 性能
Levitation melting of Ti73.3Fe26.7 alloy and its microstructure characteristics
Abstract
Since 1950s, titanium alloys began to be applied to the aerospace industry. The titanium alloy has been widely used in the manufacture of wings and fuselage because of its incomparable high strength and plasticity that other titanium alloys are unparalleled after aging treatment. As a stable element of beta phase, Fe can significantly reduce the martensitic transition temperature and inhibit the formation of Omega phase, and the "beta spot" and "TiFe phase" formed by the segregation of Fe in Ti can reduce the fatigue properties of materials. In this study, the Fe element with 26.7% content was added to the pure titanium. The iron titanium ingot was obtained by suspension melting. The composition and microstructure of the Ti73.3Fe26.7 were analyzed by XRD and metallography. The electrochemical behavior of the Ti73.3Fe26.7 alloy was revealed by the open potential and polarization curves. The experimental results show that the alloy structure is the same as the casting morphology with the addition of 23.7% Fe element, but the grain is larger, the polarization curve is the best corrosion resistance at home and abroad. The open circuit potential shows the most stable internal performance and the hardness of the alloy reaches to 543 Mpa.
Keywords: Ti73.3Fe26.7 alloy; melting; organization; propert
目录
摘 要I
ABSTRACT II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 钛及钛合金的简介 1
1.1.1 钛及钛合金的概述 1
1.1.2 钛及钛合金的分类 1
1.1.3 钛及钛合金的性能 2
1.2 钛及钛合金的熔炼方式 3
1.3 铁元素对钛及钛合金的性能影响 4
1.4 铁钛合金的应用近况 5
1.5 课题研究内容和方法 6
(1) 开路电位(OCP)测试; 6
(2) 极化曲线测试。 6
第二章 实验部分 7
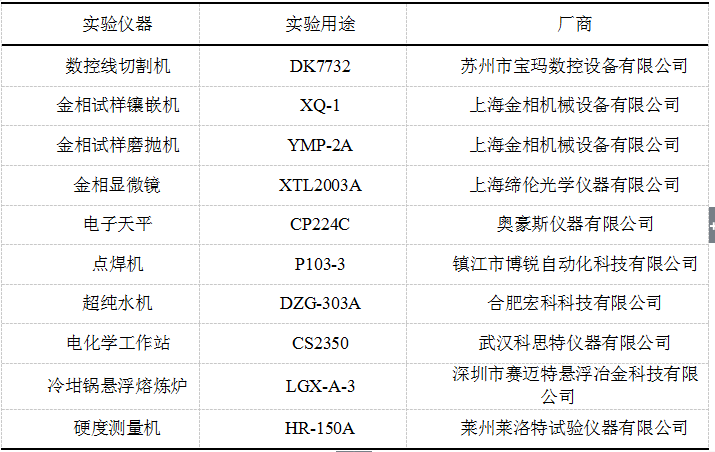
2.1 实验仪器和设备 7
2.2 实验材料 7
2.3 实验药品 7
. 8
2.4 实验内容 8
2.4.1 钛锭制备 8
2.4.2 组织成分观察 8
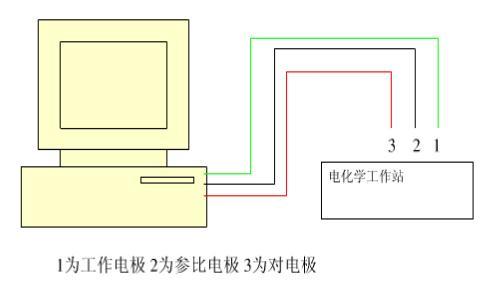
2.4.3 电化学实验 9
2.4.4 硬度实验 10
第三章 实验结果与讨论 11
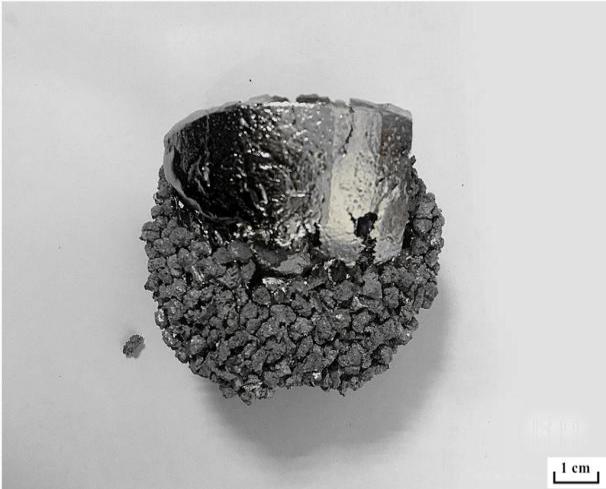
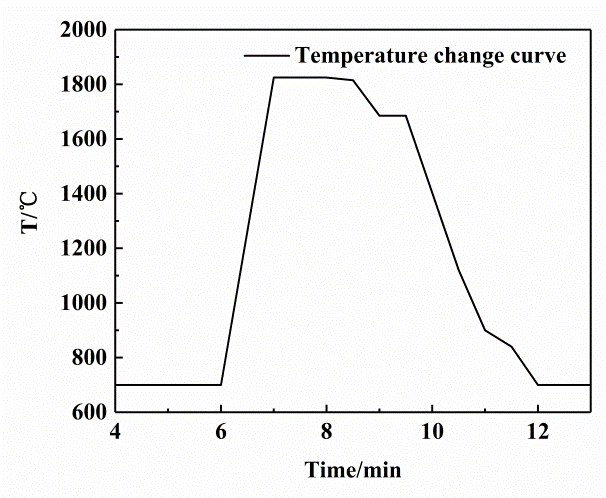
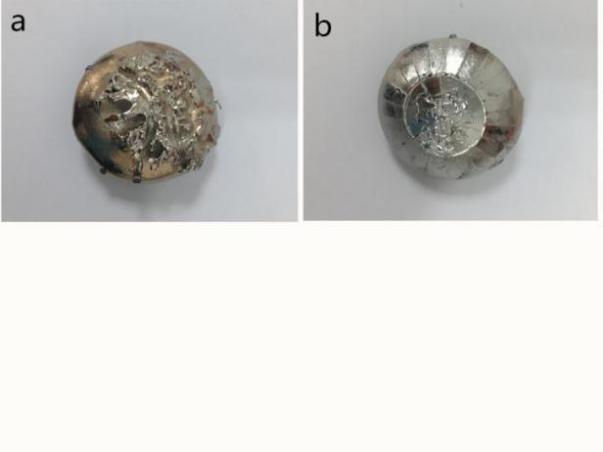
3.1 熔铸过程及结果分析 11
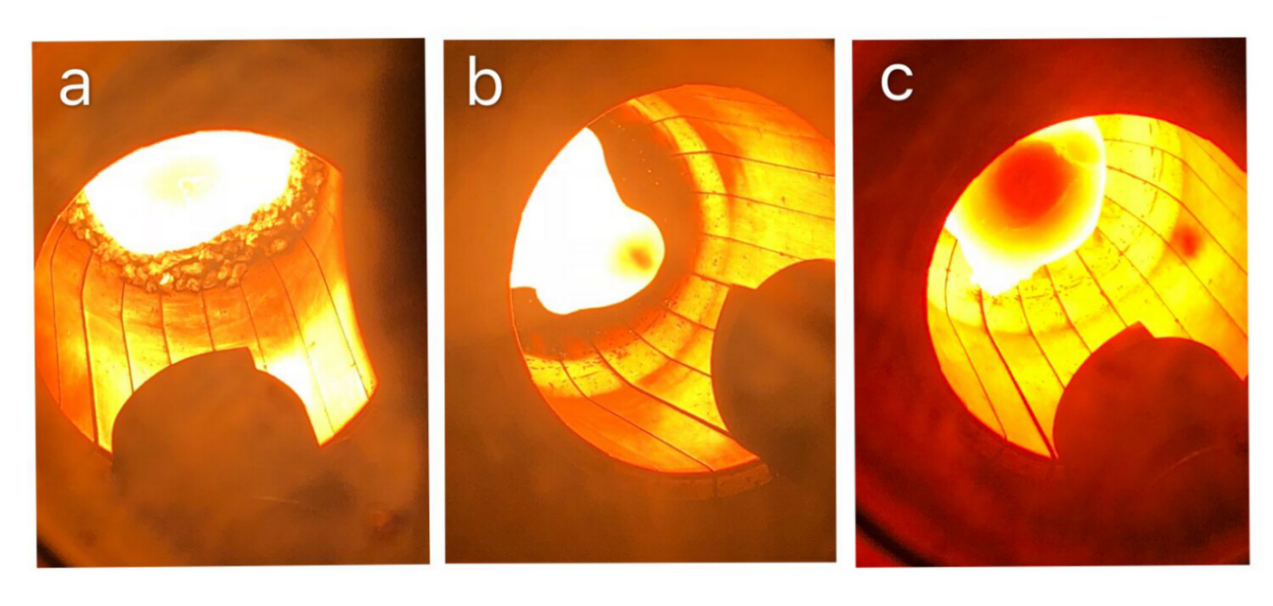
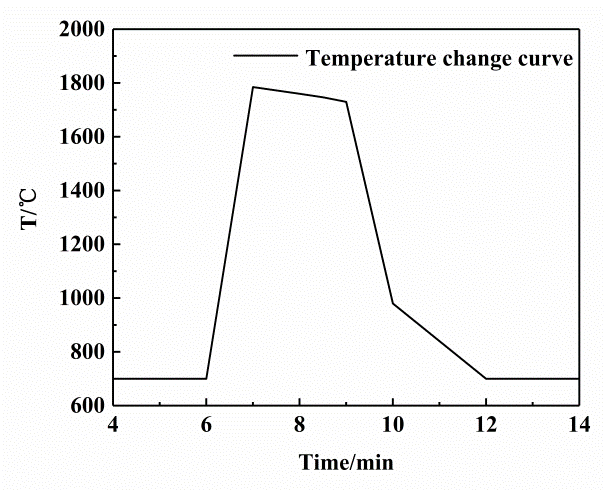
3.1.1 熔铸过程 11
3.1.2 熔铸的结果分析 11
3.2 组织成分分析 14
3.2.1 XRD分析 14
3.2.2 金相观察 15
3.3 电化学实验结果 18
3.3.1 开路电位 18
3.3.2 极化曲线 19
3.4 硬度值 20
第四章 结论及展望 21
参考文献 23
致 谢 26
第一章 绪论
1.1 钛及钛合金的简介
1.1.1 钛及钛合金的概述
随钛合金在海洋、太空、地下勘测等领域的广泛应用,新型钛合金的加工技术及多元素钛合金发展方向受到人们的广泛关注[1]。中国的钛合金蕴藏量较为丰富,是铜含量的十倍,但是在20世纪前,钛合金来没有被全球广泛使用,直到1953年,美国才将钛合金用于制造飞机发动机的防火壁,但其应用潜力,特别是在航天方面上的应用十分巨大[2]。而我国在航天航空方面使用的钛合金主要发展方向为设计制造高性能化、高加工率、低成本化的钛合金。而作为飞机使用的材料,需要承受高温、高压的环境,因此钛合金的研究又趋向于发展高强度钛合金、高温钛合金、阻燃钛合金等。但是随着钛合金在航空方面的广泛应用,一些存在的问题也逐渐暴露出来,主要表现在使用量、性能、成本方面。总的来说,航空用钛合金进一步发展仍存在着巨大的挑战[3]。
1.1.2 钛及钛合金的分类
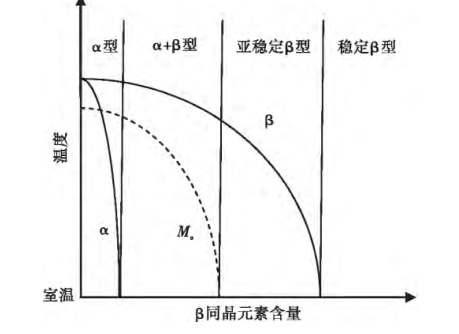
图1-1 钛合金分类示意图
相关图片展示: