5CrNiMo基材预热温度对激光熔覆层组织性能影响毕业论文
2020-04-23 20:16:00
摘 要
激光熔覆技术在材料表面改性、零件修复及制造方面有重要的意义。本文用控制变量法将5CrNiMo基材预热到不同的温度后,采用相同激光加工参数利用激光熔覆技术在其表面度制备单道熔覆层,通过体式显微镜、金相显微镜、维氏显微硬度计等研究分析熔覆层组织的宏观形貌几何特征、显微组织、显微硬度及晶粒大小变化,总结其变化规律。通过实验研究发现,虽然基板预热温度不同但整体显微组织呈现出相似的变化特征,涂层由底至顶组织明显变的致密细小,晶粒的生长方向朝向中心熔化中心区域。随着预热温度的升高,熔覆层的熔高、熔宽和熔深逐渐增大;熔覆层的润湿角和热影响区逐渐增大。熔覆组织从底部到顶部的显微组织变化为底部形成大量的柱状晶和枝晶,中部长的枝晶变短,到熔覆层顶部,逐渐转变为大量的等轴晶和共晶组织。
关键词:激光熔覆 5CrNiMo钢 几何特征 显微组织 显微硬度
Effect of Preheating Temperature of 5CrNiMo Substrate on Microstructure and Properties of Laser Cladding Layer
Abstract
Laser cladding technology has important significance in surface modification, parts repair and manufacturing. In this paper, after the 5CrNiMo substrate is preheated to different temperatures by the control variable method, a single pass cladding layer is prepared on the surface by laser cladding technique using the same laser processing parameters, by stereomicroscope, metallographic microscope, Vickers microscopy. Hardness tester and other researches analyze the macroscopic physical characteristics, microstructure, microhardness and grain size of the cladding layer, and summarize the changes. Through experimental research, it is found that the preheating temperature of the substrate is different, but the overall microstructure exhibits similar variation characteristics. The coating is densely and finely changed from bottom to top, and the growth direction of the crystal grains is toward the central melting center region. As the preheating temperature increases, the melting height of the cladding layer gradually increases, and the melting width of the cladding layer gradually increases; the melting depth of the cladding layer gradually increases; the wetting angle of the cladding layer gradually becomes larger; The heat affected zone of the coating gradually increases. The microstructure of the cladding structure changes from bottom to top to form a large number of columnar crystals and dendrites at the bottom, and the dendrites of the middle minister become shorter, and to the top of the cladding layer, gradually transform into a large number of equiaxed crystals and eutectic
structures.
Key words: Laser cladding; 5CrNiMo; Geometric characteristic; Microstructure; Microhardness
目 录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 研究背景及意义 1
1.2 激光技术及其应用 1
1.2.1 激光熔覆的简介 1
1.2.2 激光熔覆的基本特点 1
1.3 激光熔覆技术的研究分析 2
1.3.1 激光熔覆的发展前景 2
1.3.2 激光熔覆的工艺领域 2
1.3.3 激光熔覆的工艺加工方式 2
1.3.4 激光熔覆技术在国内的发展状况 3
1.3.5 激光熔覆技术在国外的发展状况 3
1.4 本课题的研究目的及研究内容 4
1.4.1 研究目的 4
1.4.2 研究内容 4
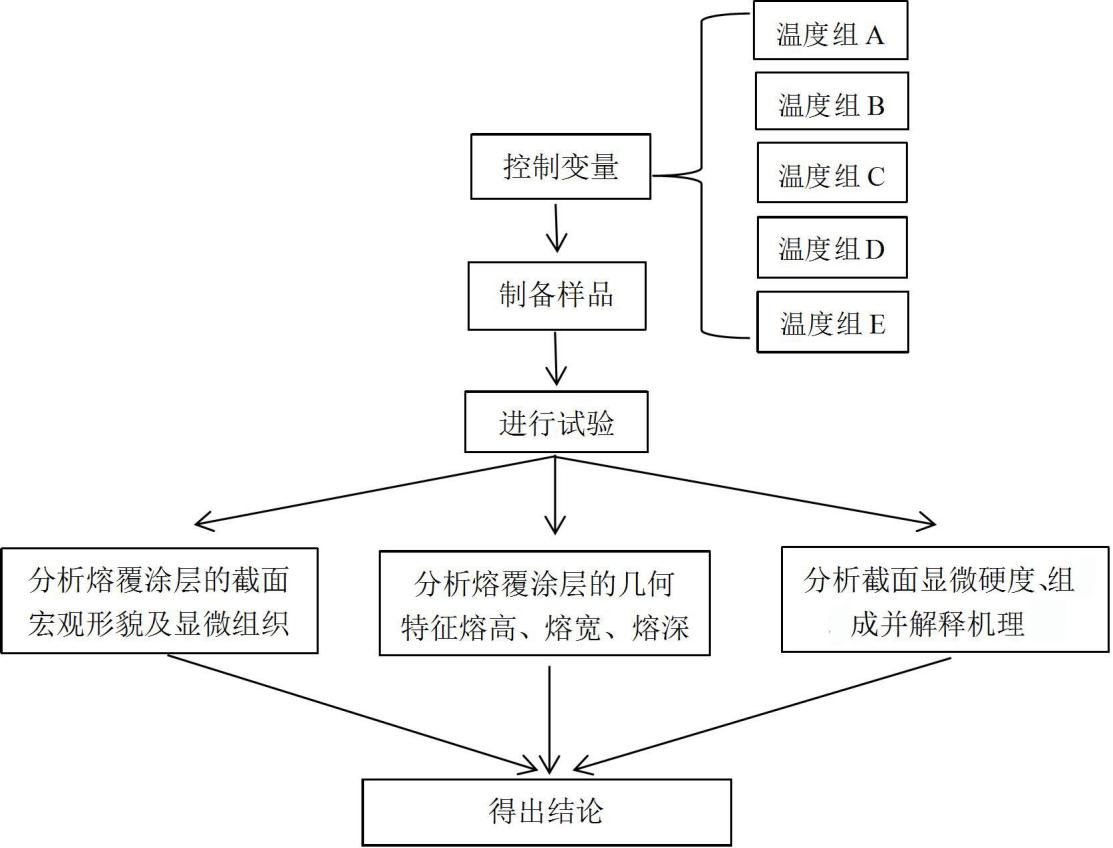
第二章 实验材料与方法 5
2.1 实验材料 5
2.1.1 基体材料 5
2.1.2 熔覆材料 5
2.2 试验设备与分析方法 6
2.2.1 激光熔覆设备 6
2.2.3 激光熔覆的实验流程 7
2.3 熔覆层宏观形貌及显微硬度分析 7
2.3.1 宏观形貌观察 7
2.3.2 微观组织形貌观察 8
2.4 熔覆层显微组织及硬度分析 8
第三章 基板预热温度对熔覆层几何特征的影响 10
3.1 预热温度对熔覆层几何特征影响 10
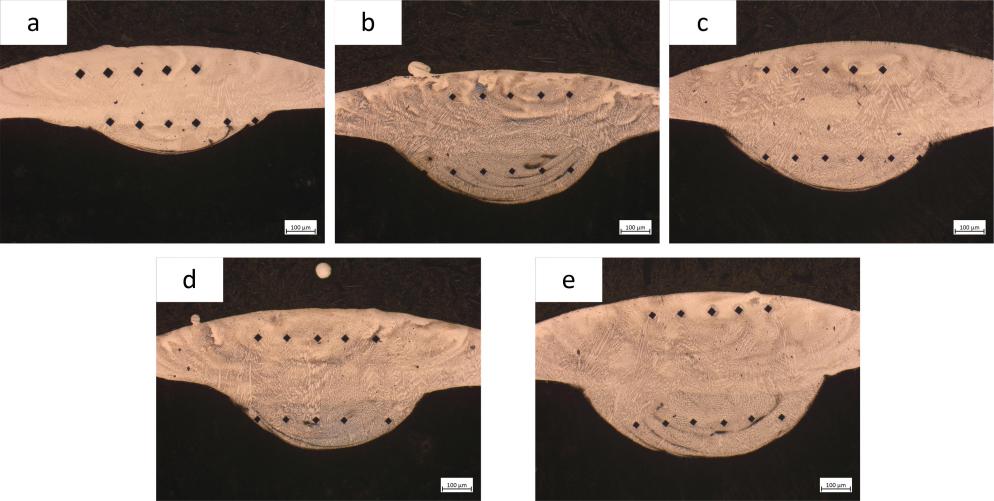
3.1.1 单道熔覆层的宏观形貌 10
3.1.2 单道熔覆涂层截面的宏观形貌 10
3.1.3 熔宽的影响 11
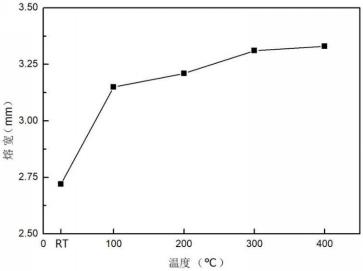
3.1.4 熔高的影响 12
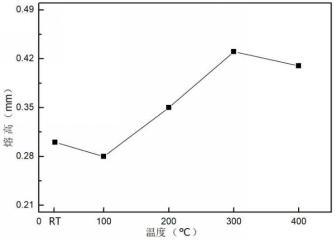
3.1.5 熔深的影响 13
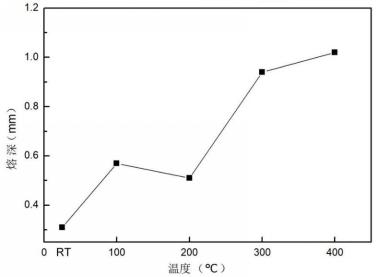
3.1.6 润湿角变化特征 13
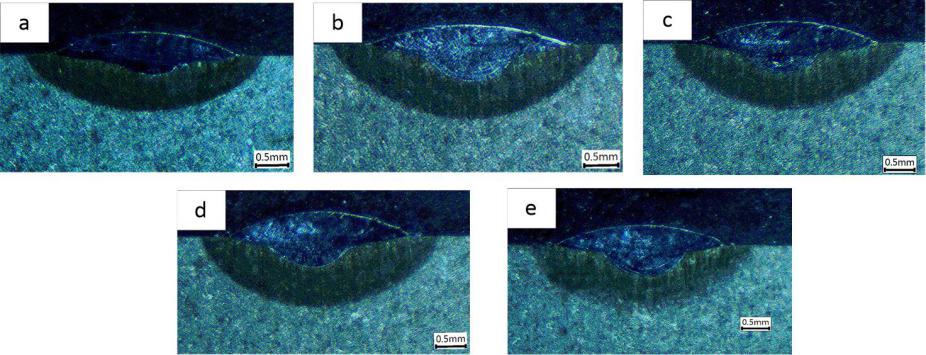
3.2 热影响区的变化 14
3.3 稀释率演变规律 15
3.4 本章小结 16
第四章 预热温度对熔覆层组织演变及性能的影响 18
4.1 熔覆层组织演变影响 18
4.1.1 熔覆层截面组织演变 18
4.1.2 熔覆层底部组织演变 18
4.1.3 熔覆层中部组织演变 19
4.1.4 熔覆层顶部组织演变 19
4.1.5 热影响区不同区域的显微组织 20
4.2 熔覆层显微硬度影响 21
4.2.1 熔覆层截面显微硬度分析 21
4.2.2 熔覆层顶部显微硬度分析 22
4.2.3 熔覆层底部显微硬度分析 23
4.3 本章小结 24
第五章 结论与展望 26
5.1 实验结论 26
5.2 展望 27
参考文献 28
致谢 30
第一章 绪论
1.1 研究背景及意义
现代化企业和工厂中,模具在各个领域内都得到了广泛的使用。模具对于我们现代化生产和产品的加工至关重要。不同的产品在制造过程中要使用不同的模具来制造,5CrNiMo模具钢是中小型热锻模具最常使用的模具材料[1]。5CrNiMo热作模具使用时要与高温金属接触,其温度最高可达1150℃。由于模具成型时温度的急剧下降,导致了金属液在进入模具时受到强大的冲击力,而这冲击会导致模具表面产生热疲劳裂纹进而失效。激光熔覆技术是利用高能激光束在材料表面进行辐射照射,通过一系列物理变化如迅速熔化,迅速扩展以及迅速凝固,在材料表面制备一种具有特殊性能的材料,使其更加耐磨耐蚀。激光熔覆技术不仅使材料表面的各项性能得到改善,还克服了于传统加工技术中难以解决的问题。因激光熔覆技术[2]具有能够与基体高度的结合、粉末有很广的选择范围、熔覆的自动化程度很高等许多优点,引起了各个行业以及各个方面的关注与重视,不断加大研究资金与力度。截至目前也取得了一些技术上的应用。
本文用5CrNiMo热作模具钢作为基体,对基板预热不同的温度后在其表面制备铁基合金单道熔覆涂层实验,研究基板的预热温度对单道熔覆层的几何特征和微观组织及性能的影响。
相关图片展示: