氦气中等离子体射流阵列的放电模式及特性研究毕业论文
2020-05-24 12:39:32
摘 要
大气压低温等离子体射流是一种近几年来得到快速发展的新型大气压低温气体放电技术,因其装置简单,便于使用,相对于早期的介质阻挡放电,有着很多独特的优势。大气压二维等离子体射流阵列处理面积大,拥有更多的活性粒子,且不产生废弃物,在生物医学、材料、环境等领域有着广阔的应用。
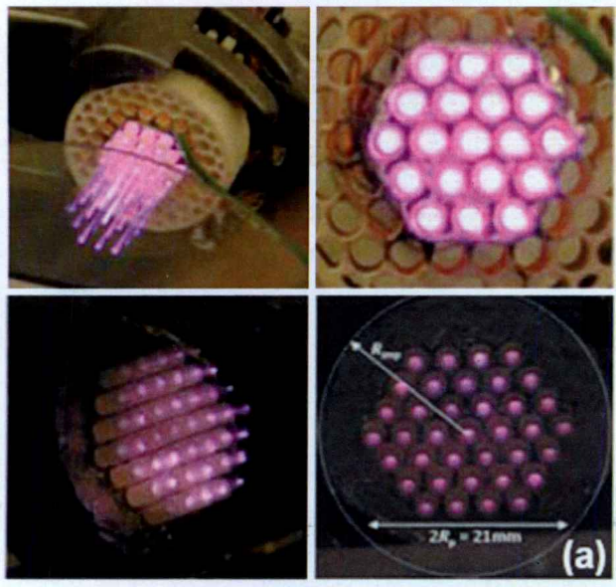
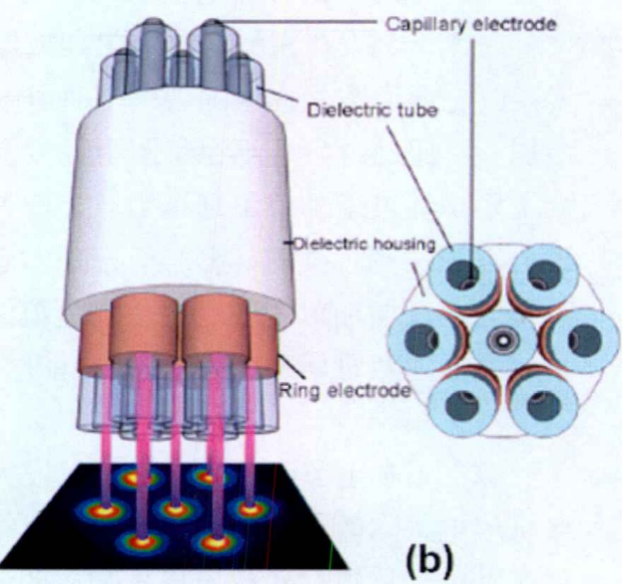
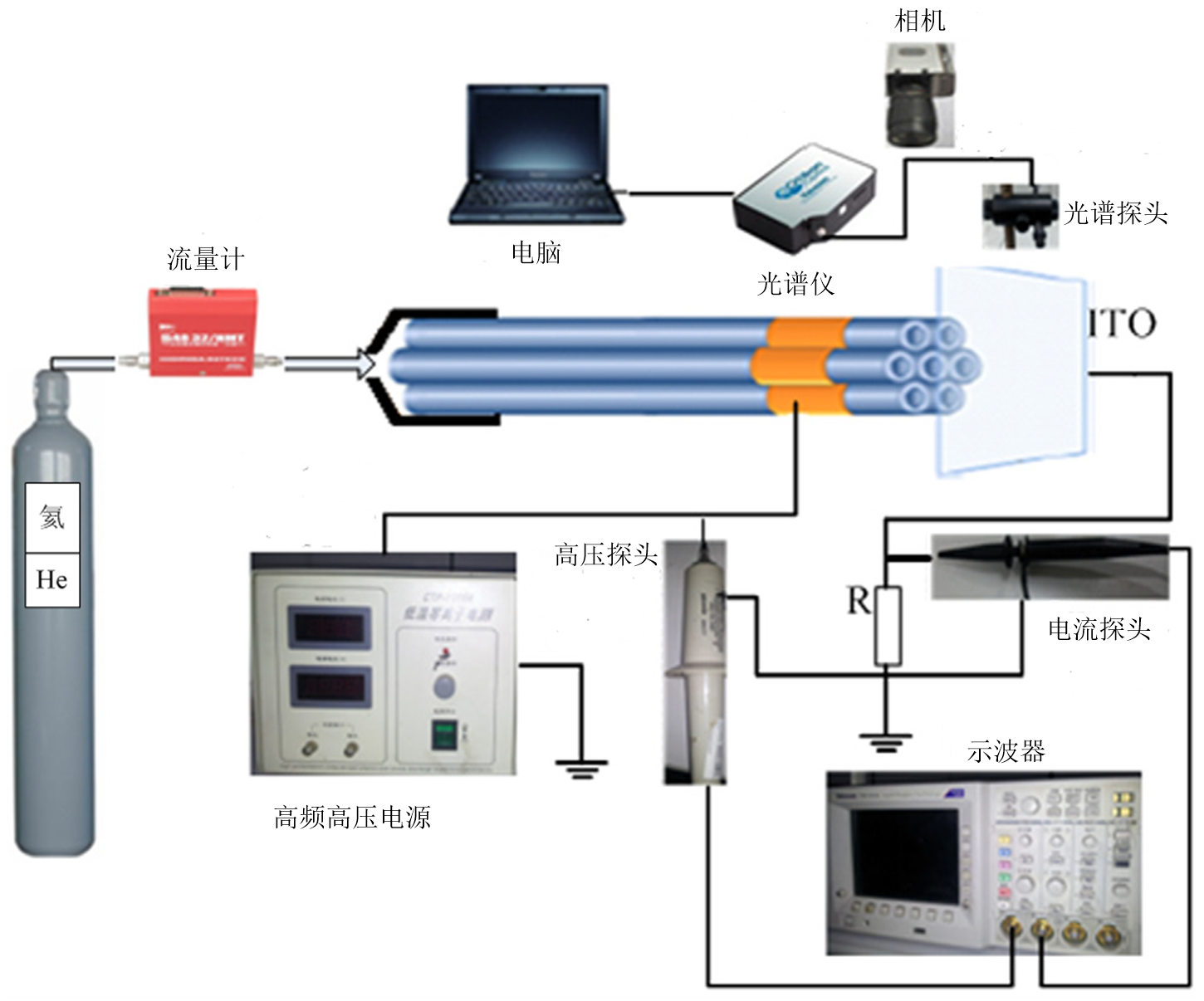
论文首本文建立大气压He等离子体实验装置和测量系统,使用环-板电极结构的七根并联的射流单元构成等离子体射流阵列, 研究了大气压等离子体射流从放电开始阶段到射流稳定阶段再到射流不稳定阶段的过程。通过测量得到的发光特性、光谱特性以及电气特性(电压电流波形、Lissajous波形),得到大气压射流阵列的放电演变规律。此外,研究了不同气体流速、外加电压和射流单元之间的距离对大气压等离子体射流的影响,在分析得到的数据的基础上,给出了两种模式下的等离子体射流的稳定运行参数。最后,仔细研究等离子体射流阵列的发展过程,通过分析总结,建立等离子体射流阵列的二维放电模型,分析所建立的放电模型,解释等离子体射流阵列形成不同放电模式以及相互转换的原因。
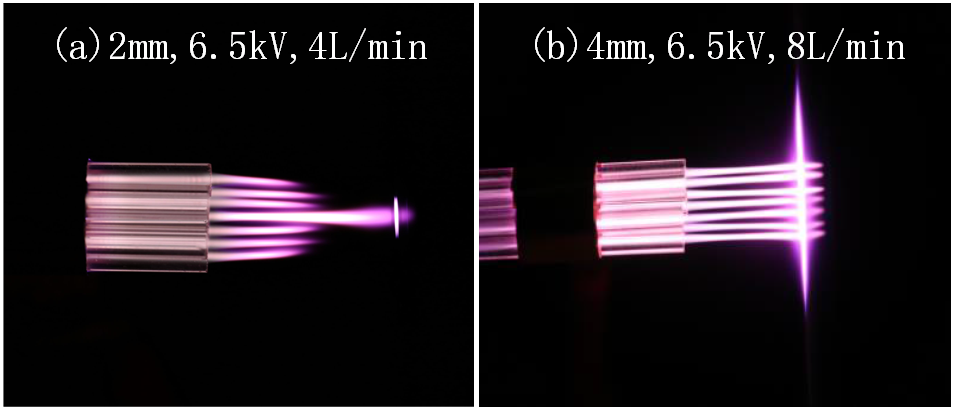
论文研究结果表明:组成射流阵列的射流单元间会存在复杂的耦合作用,通过改变射流单元之间的距离、气体流速、外加电压等因素,整个射流阵列的产生和放电模式都会产生变化。当射流单元之间的距离为0.2mm,流速在4L/min到6L/min之间,电压在5.5kV及以上时,射流放电模式为耦合模式;当射流之间的距离在4mm和6mm之间,气流速度在5L/min到8L/min之间,电压高于4kV时,等离子体羽呈现出均匀模式。射流之间的距离决定了等离子体射流产生哪种模式。气流的速度的变化直观地表现在等离子体羽的长度上,只有当气流达到一定的速度时,等离子体羽才会射到电极板上,从而分出均匀模式和耦合模式。而外加电压幅值只能影响等离子体羽的亮度和均匀程度。在提高射流阵列的气体流速、外加电压以及射流单元之间的距离时,若等离子体射流模式不发生变化,那么射流的放电功率以及传输电荷均是稳步增加的。在所有实验条件均相同的情况下,耦合模式的放电功率以及传输电荷均是大于均匀模式的。射流单元中的气流和空气中的流场相互作用可以决定射流阵列的放电模式[1],而这种相互作用与射流单元之间的距离息息相关。
关键词:大气压等离子体射流阵列 耦合模式 均匀模式 光学特性 电气特性
Discharge mode and its properties of the plasma jet array in helium
Abstract
Low temperature atmospheric pressure plasma jet has gained rapid development in recent years. As a new type of low atmospheric pressure gas discharge technology, its device is simple and easy to use. So it has many unique advantages with respect to the dielectric barrier discharge. Atmospheric pressure plasma jet dimensional array has large processing area and more active particles, and does not produce waste. So, it has broad application in the field of biological medicine materials, environment and other fields.
First, the experimental device and measurement system for the APPJ in He are established. Use seven parallel jet units with ring-board electrode structure constituting the plasma jet array. We study the atmospheric pressure plasma jet from the beginning of the discharge to jet stable phase, and then to jet unstable phase. By measuring the emission characteristics, the spectral characteristics and the electrical characteristics (voltage and current waveforms, Lissajous waveforms), we receive discharge evolution of atmospheric jet array. In addition, the effect of different gas flow rate, applied voltage and the distance of the jet units of atmospheric pressure plasma jet is studied in this paper. Based on the analysis of data obtained, the stable operation parameters of the plasma jet arrays of two modes are given. finally, we carefully study the development of the plasma jet array. Then through analysis and induction, we establish two-dimensional discharge model of the plasma jet arrays and explain the reasons that the plasma jet arrays form the different discharge modes and their conversion.
The results show that there is a complex coupling of the jet unit consisting of an array of jets. By changing gas flow rate, the applied voltage, the distance of the plasma jet units and other factors, the entire array and the discharge mode will change. When the distance of the jet units is 0.2mm and a flow rate of4L/min and 6L/min and the voltage is 5.5Kv and above, the jet discharge mode is an intense plasma mode. When the distance of jet units is between 0.4mm and 0.6mm and the airflow velocity is between 5L/min and 8L/min and voltage is higher than 4kV, the plasma plume shows the well-collimated plasma mode. Distance of the jet units determines which mode the plasma jet generate. The length of the plasma plume intuitively shows the changes of the airflow velocity. Only when the air flow reaches a certain speed, the plasma plume will hit the electrode plate. Thereby the intense plasma mode and the well-collimated mode are distinguished. And the amplitude of the applied voltage only affects the brightness and uniformity of the plasma plume. If the plasma mode does not change in raising the gas velocity, the applied voltage and the distance of jet units, the discharge power and the charge transmission are steadily increasing. Under all experimental conditions being equal, the discharge power and the charge transmission of the intense plasma mode are larger than that of the well-collimate mode. The interaction of the distance between jet units and air flow field can determine the discharge mode of the jet array. And the interaction is closely related to the distance of jet units.
Key words: Atmospheric pressure plasma jet array; intense plasma mode; the well-collimated plasma mode; Optical properties; Electrical characteristics
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract III
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 等离子体概述 1
1.2 大气压低温等离子体 2
1.3 介质阻挡放电与大气压等离子体射流阵列 3
1.3.1 介质阻挡放电 3
1.3.2 大气压低温等离子体射流 3
1.4 国内外研究现状 6
1.5 本文研究内容 8
第二章 实验装置的建立与测量方法 10
2.1 实验过程及测量装置 10
2.2 光学特性分析 11
2.3 电气特性分析以及参数计算 13
2.4 本章小结 16
第三章 气体流速对等离子体射流阵列的影响 17
3.1 不同气体流速下等离子体射流阵列的放电模式的变化 17
3.2 气体流速变化时等离子体射流阵列的放电特性的演变规律 19
3.3 本章小结 22
第四章 外加电压对等离子体射流阵列的影响 23
4.1 不同电压对二维He等离子体射流阵列放电模式的影响 23
4.2 外加电压变化时等离子体射流阵列的放电特性的演变规律 25
4.3 本章小结 26
第五章 射流单元之间的距离对等离子体射流阵列的影响 27
5.1 不同射流单元之间的距离对等离子体射流放电模式的影响 27
5.2 射流单元之间的距离变化时等离子体射流阵列的放电特性演变规律 28
5.3 本章小结 29
第六章 实验结果分析以及射流机理探讨 31
结论 34
参考文献 35
致谢 39
绪论
等离子体概述
等离子体是20世纪50年代以后逐渐发展壮大的一门学科,1950年前后开始的对受控核聚变的研究;19世纪中叶对天体物理学及20世纪开始的对空间物理学的研究;以及对低温等离子体技术应用的研究是这门学科主要的三个研究方向。
19世纪30年代起,科学家(如英国的麦克尔·法拉第、威廉姆·库克)对气体放电现象的观察研究被视为等离子体研究的初期。1879年英国的克鲁克斯首次使用“物质的第四态”描述当气体放电时产生的电离气体。在1928年,朗缪尔首次采用“Plasma”这个词来描述包含了电子、离子、中性原子和分子,具有一定电离度,总体上呈现中性的气体状态,于是等离子体物理学才真正问世。1924年,朗缪尔发现了等离子体的震荡现象。
在此同时,20世纪以来对空间等离子体的探索也不断进步。1902年,英国的亥维赛等为了解释无线电波可以远距离地面传播的现象,推测地球上空具有电离层,继而,1924年该假说被英国的阿普顿实验证实。1925年,美国的G.布莱特和M.A.杜福发明电离层垂直探测装置。十九世纪三十年代初,英国的S.查普曼和拉普顿相继提出了电离层的折射率公式,并发现了磁化等离子体的色散方程。
相关图片展示: