基于图像处理技术的射流阵列均匀性光学诊断方法研究毕业论文
2020-07-09 20:31:17
摘 要
大气压等离子体射流是在介质阻挡放电的基础上兴起的一种新型放电技术, 具有灵活的设计结构并且等离子体通过空气射流输送到待处理材料的表面,在材料改性处理,医疗灭菌和成膜领域具有广泛的应用前景。 大气压等离子体喷射系统通过增加下游的等离子体羽流处理区域来响应对大面积表面处理的需求。然而研究表明,各相邻射流单元之间的耦合作用影响了射流阵列空间均匀性,进而影响了大面积处理效果。目前,对射流阵列射流间相互作用和均匀性的影响因素实验研究尚不完善,运行条件(气体流速和电压幅值等)、电极结构和驱动电源类型等主要影响因素对射流阵列均匀性的影响研究需要进一步实验充实。
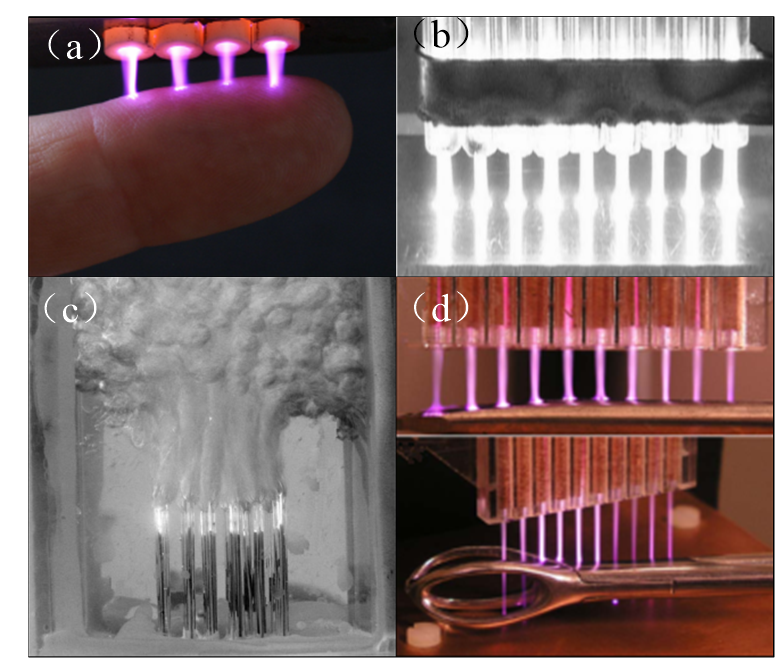
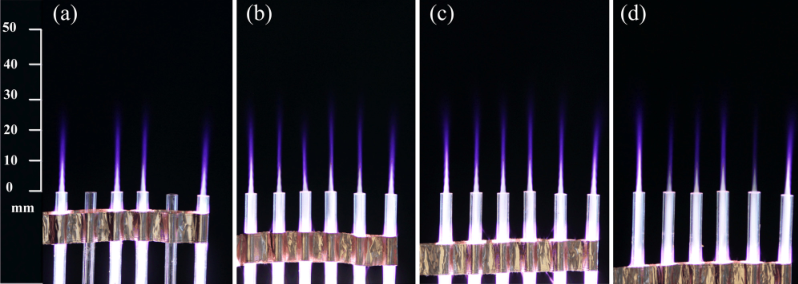
为获得大面积和均匀稳定的大气压等离子体射流,本文首先在大气压He中建立一维针环电极结构等离子体射流阵列发生装置并通过光学、电气和流场等测量诊断研究了工作气体流速和外加电压幅值对相邻射流单元之间相互作用的影响,同时利用MATLAB图像处理方法对摄像机拍摄的等离子体射流阵列图像进行处理分析,结合射流长度,直径,偏转角,灰度平均值这四个特征参数,比较和分析了电压幅度和气体流量等操作条件对射流系列均匀性的影响。其次,建立一维He环环电极结构射流阵列,研究此电极结构下运行条件对射流阵列均匀性影响,并与针环电极结构射流阵列进行对比分析,利用MATLAB的图像处理方法对电极结构影响射流阵列均匀性的相关特征参数进行分析。最后在大气压He中比较了不同运行条件下高频交流和纳秒脉冲激励针环电极射流阵列的放电特性,研究分析了驱动电源类型对射流阵列均匀性的影响。
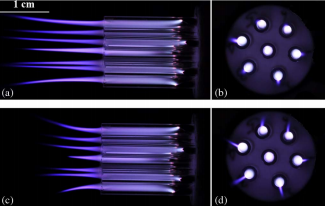
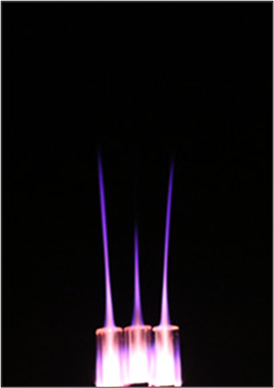
研究结果表明:等离子体羽偏转角随着电压幅值的增大而增大,随着气体流速的增大而减小。偏转角大小不一致主要由于相邻射流之间存在静电排斥力导致。相同实验条件下,相比于针环电极结构射流阵列等离子体羽偏转,环环电极结构射流阵列各射流单元均基本呈直线传播,环环电极射流阵列具有良好的均匀性。相比于高频交流激励射流阵列出现两侧等离子体羽偏转,纳秒脉冲射流阵列各射流单元均基本呈直线传播,表现的性状也更好。
本文实验研究有助于更好的理解射流阵列射流单元之间相互作用机理,通过改变运行条件、电极结构和驱动电源等主要影响因素提高射流阵列均匀性,来获得大面积可控稳定的大气压等离子体射流。
关键词: 等离子体射流阵列 均匀性 运行条件 电极结构 电源类型
ABSTRACT
Atmospheric pressure plasma jet is a new type of discharge technology that rises on the basis of dielectric barrier discharge. It has a flexible design structure and can transmit plasma to the surface of the material to be treated through the blowing of air currents, in the process of material modification and medical extinction. Bacteria, thin film deposition and other fields have a wide range of application prospects. Atmospheric pressure plasma jet arrays satisfy large area surface treatment requirements by increasing the processing area of the downstream plasma plume. However, studies have shown that the coupling effect between adjacent jet units affects the spatial uniformity of the jet array and further affects the large area treatment. effect. At present, the experimental research on the influencing factors of the interaction and uniformity of the jet array jets is not perfect, and the influence of the main influencing factors such as the operating conditions (gas flow rate and voltage amplitude, etc.), the electrode structure and the type of drive power on the uniformity of the jet array Research needs further experimentation and enrichment.
In order to obtain a large-area and uniform atmospheric pressure plasma jet, a one-dimensional needle-electrode-structured plasma jet array generation device was first established in atmospheric pressure He and the working gas flow rate and the external flow rate were studied through optical, electrical, and flow field measurement diagnostics. The influence of the voltage amplitude on the interaction between adjacent jet units, and the processing and analysis of the plasma jet array images taken by the camera using the MATLAB image processing method, combining the jet length, diameter, deflection angle, and average gray value The characteristic parameters, the effect of the operating conditions such as voltage amplitude and gas flow rate on the uniformity of the jet array were compared and analyzed. Next, a one-dimensional He-loop-loop electrode structure jet array was established. The influence of the operating conditions under this electrode structure on the uniformity of the jet array was studied, and compared with the needle-loop electrode structure jet array. The image processing method of MATLAB was used to influence the structure of the electrode. The characteristic parameters of array uniformity are analyzed. Finally, in the atmospheric pressure He, the discharge characteristics of the needle-ring electrode jet array under high frequency AC and nanosecond pulse excitation under different operating conditions were compared, and the influence of the type of driving power on the uniformity of the jet array was analyzed.
The results show that the deflection angle of plasma plume increases with the increase of voltage amplitude and decreases with the increase of gas flow velocity. The inconsistency of the deflection angle is mainly due to the electrostatic repulsive force between adjacent jets. Under the same experimental conditions, compared with the deflection of the plasma jet of the array of needle ring electrode structures, the jet units of the ring-loop electrode structure are basically linearly propagating, and the annular-ring electrode jet array has a good uniformity. Compared with the high-frequency alternating current excitation jet array, the deflection of the plasma plumes on both sides occurs. The jet elements of the nanosecond pulse jet array are basically linearly propagating and the performance is better.
This experimental study helps to better understand the interaction mechanism between jet array jet units, and improves the uniformity of the jet array by changing the operating conditions, electrode structure, and driving power, and other major influence factors, to obtain large-area controlled and stable atmospheric pressure plasma. Jet flow.
KEYWORDS :Plasma jet array;Uniformity;0perating conditions;Electrode structure;Power type
目录
第一章 绪论 1
1.1大气压低温等离子体 1
1.2 等离子体射流 1
1.3等离子体射流阵列 2
1.4国内外研究进展分析 3
1.4.1 射流阵列均匀性影响因素及作用机理 4
1.4.2 研究现状总结 5
1.5本文主要研究内容 5
第二章 实验系统 7
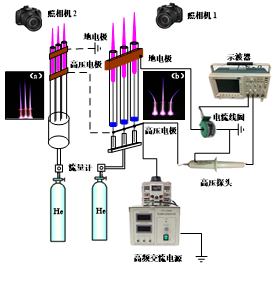
2.1 实验平台与诊断系统的建立 7
2.2射流光学图像处理 8
2.2.1图像灰度化 8
2.2.2图像滤波去噪 9
2.2.3灰度直方图增强 11
2.2.4 图像边缘提取 12
2.3射流阵列均匀性参数提取 14
2.3.1射流高度提取 14
2.3.2射流直径提取 15
2.3.3射流偏转角 15
2.3.4射流灰度均匀性提取 15
2.4本章小结 16
第三章 运行条件对高频电源激励针环电极射流阵列均匀性影响 17
3.1引言 17
3.2气体流速对射流阵列均匀性的影响 17
3.3电压幅值对射流阵列均匀性的影响 20
3.4本章小结 23
第四章 电极结构对射流阵列均匀性影响 25
4.1引言 25
4.2实验条件 25
4.3环环电极结构运行条件对射流阵列均匀性的影响 26
4.3.1 气体流速对环环电极结构射流阵列均匀性的影响 26
4.3.2 电压幅值对环环电极结构射流阵列均匀性的影响 29
4.4环环与针环射流阵列均匀性比较 32
4.5本章小结 32
第五章 电源类型对射流阵列均匀性影响 34
5.1引言 34
5.2电源类型对放电特性的影响 34
5.3纳秒脉冲激励运行条件对射流阵列均匀性的影响 34
5.3.1 气体流速对纳秒脉冲射流阵列均匀性的影响 35
5.3.2 电压幅值对纳秒脉冲射流阵列均匀性的影响 38
5.4 本章小结 41
第六章 结论 42
参考文献 44
第一章 绪论
1.1大气压低温等离子体
等离子体状态是固体,液体和气体状态之后天然材料存在的第四种形式,通常存在于宇宙中。等离子体由正负离子、电子、基态分子原子、激发态分子原子以及光子等构成,是在宏观上呈现电中性的基团。19世纪20年代Langmuir和Tonks首次将等立体这一术语引入,用来描述气体放电产生的物质形态。根据动力学温度划分,分为高温等离子体和低温等离子体。其中,高温等离子体也称为平衡态等离子体,其离子温度和电子温度基本一致。而低温等离子体在常温下发生,电子温度高,离子温度低,也被称为非平衡态等离子体。相比高温等离子体,低温等离子体可在大气压下产生,生产难度低,更有利于工业化生产[1-5]。目前,低温等离子体技术已广泛应用于臭氧生成、废气处理等生产和生活领域。
气体放电是产生低温等离子体简单有效的方式,按照气体放电形式不同,低温等离子体的产生方式主要包括电弧放电 (Arc Discharge)、火花放电 (Spark Discharge)、电晕放电 (Corona Discharge)、辉光放电 (Glow Discharge) 、弥散放电 (Diffuse Discharge)、滑动放电 (Gliding Discharge) 、介质阻挡放电 (Dielectric Barrier Discharge, DBD)、大气压等离子体射流 (Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet, APPJ)等。其中大气压等离子体射流(APPJ)是在介质阻挡放电(DBD)的基础上兴起的一种新型放电技术, 它在改性处理、医疗灭菌等领域方面有着广泛的应用前景,近年来受到了广泛的关注[5-7]。
1.2 等离子体射流
典型的等离子体射流发生设备如图1-1所示,通过向介质管中注入工作气体(He, Ar等),在电极上施加高电压,反应器放电产生等离子体并由工作气体吹出形成大气压等离子体射流。相较于传统DBD,大气压等离子体射流(APPJs)具有灵活的设计结构并且能够通过气流的吹送将等离子体输送到待处理材料的表面,消耗功率小且产生的等离子体温度接近于室温,对于待处理对象没有尺寸限制,因此其广泛地应用于生物医疗、杀菌消毒、表面改性处理以及薄膜沉积等领域。近年来,研究者对大气压等离子体射流装置的开发除了工作气体(Ar、He、Ne等惰性气体),主要包括反应器电极结构和驱动电源的变化。
相关图片展示: