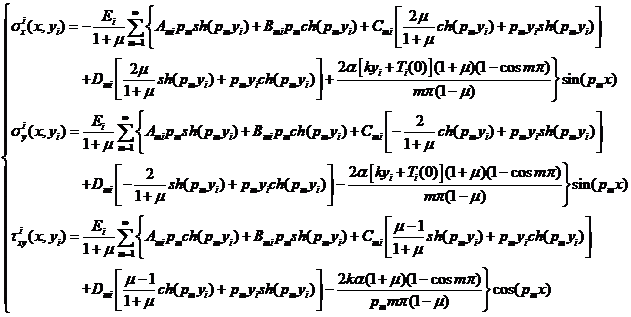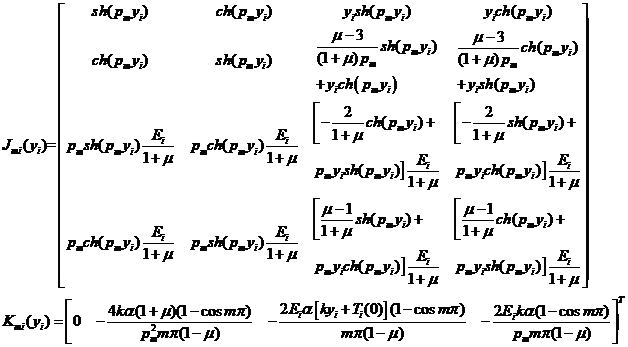温度对结构构件承载能力的影响研究毕业论文
2020-04-16 15:37:10
摘 要
本文考虑温度变化对杨氏模量的影响,研究了均布荷载和沿梁高线性变化的热荷载共同作用下简支梁的热弹性力学解。首先根据杨氏模量与温度的函数关系,导出杨氏模量沿梁高方向的分布方程。然后建立层合模型,将变物性参数方程转化成单层内的常物性参数方程,并给出单层梁的弹性力学解。利用相邻层界面处位移和应力连续的条件,通过矩阵递推推导出任意层梁与底层梁间的位移和应力的关系。最后利用简支梁上下表面已知的边界条件得到待定系数,从而得到梁内位移和应力的分布情况。本方法给出的计算结果收敛性很好。在参数分析中,分别研究了划分层数、热荷载和高跨比对梁力学性能的影响。结果表明,划分层数越多,结果越精确;热荷载越大,位移和应力也相应增大;梁的高跨比越大,梁中位移越小。
关键词:热弹性力学 杨氏模量 温度 层合模型 矩阵递推
Elasticity Solution of Simply Supported Beams Taking into Account the Variation of Young's Modulus with Temperature
Abstract
Taking into account the variation of Young's modulus with temperature,the elastic solution of the simply supported beams under thermo-mechanical loads was studied in this paper. Firstly, Young's modulus along the direction of the beams thickness was obtained based on the relationship between Young's modulus and temperature. Then, transform the varying physical parameter equation into the one with constant physical parameter in each layer by constructing laminate model. The solution of a single-layer beam was derived. Based on the continuity of displacements and stresses on the interface of neighboring layers, the relationships of displacements and stresses between any layer and the lowest layer were derived out by matrix recursion. Finally, the undetermined coefficients were obtained by means of the upper surface and lower surface conditions. And the displacements and stresses in the simply supported beams were obtained. The analysis shows that the present method has good convergence. Parametric analyses were performed to study the effects of various layers, thermal loads and thickness to span ratios on the mechanical properties of the beams. It shows that the more the layers are, the more accurate the results are; the larger the thermal loads are, the larger the displacements and stresses are; the larger the thickness to span ratio is, the smaller the displacements are.
Key Words: Thermo-elasticity; Young's modulus; Temperature; Laminate model; Matrix recursion
目 录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 课题背景与研究意义 1
1.2 研究历史和现状 2
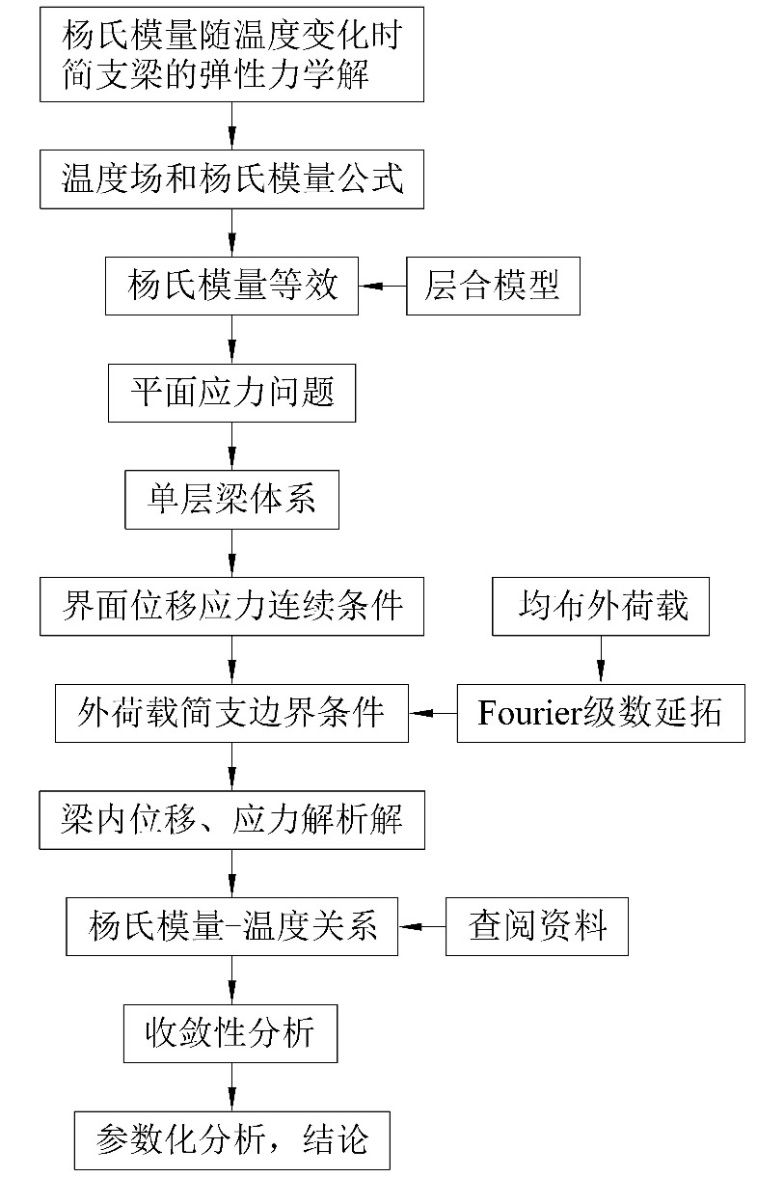
1.3 研究思路和技术路线 2
1.1.1 研究思路 2
1.1.2 技术路线 3
第二章 模型建立 4
2.1 温度场和杨氏模量公式 4
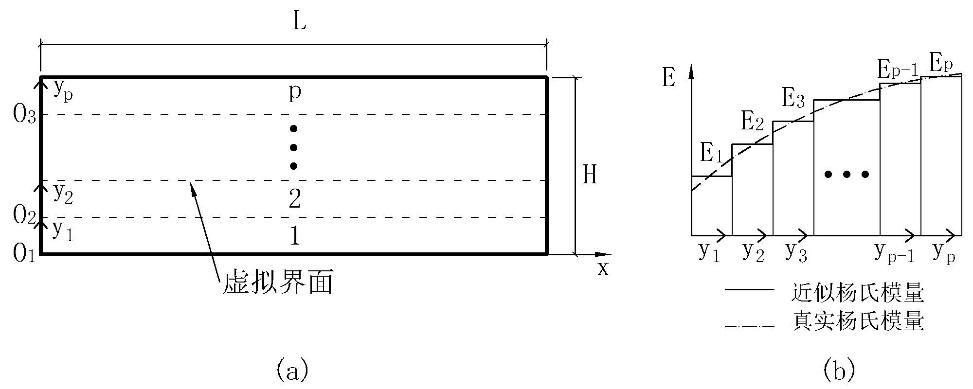
2.2 层合模型 4
第三章 模型求解 6
3.1 单层解 6
3.2 位移和应力的递推 8
3.3 待定系数的求解 10
第四章 结果分析 12
4.1 收敛性分析 12
4.2 参数分析 12
4.2.1 层数的影响 12
4.2.2 热荷载的影响 13
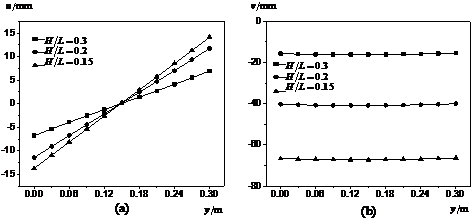
4.2.3 高跨比的影响 13
4.3 结论 14
参考文献 16
附 录 18
第一章 绪论
1.1 课题背景与研究意义
力和热是结构构件中常见的能量传递形式。在工程应用中,同时承受外力和温度作用的例子广泛存在,如火灾中倒塌的建筑(如图1-1(a)所示),穿过大气层时由于摩擦产生超高温的航天器(如图1-1(b)所示),夏季承受室内外温差作用的厂房屋面板等等。


图1-1(a) 火灾中倒塌的建筑;(b) 承受摩擦产生超高温作用的航天器
我们知道,结构构件在外力作用下会产生变形,从而会在构件内部产生应力和应变。但是,除了外力作用,温度的作用也会引起构件变形,热胀冷缩就是热变形的例子。当温度作用所引起的结构构件的胀缩受到约束时,就会在构件内部产生热应力。而热应力的作用会对结构的强度和刚度产生影响,有时甚至会导致出现裂缝,减少结构的使用寿命。
大体上来说,热应力的产生有三种情况[1]:第一种情况是考虑到大多数物体热胀冷缩的属性,当温度变化引起的热变形受到了外部的约束,则会在物体内产生应力;第二种情况是考虑同一物体内部温度分布不均匀的情况,即使物体可能不受外界约束,但是由于其内部各处的温度不同,每一部分会受到相邻部分的影响,因此不能自由地胀缩,从而也会产生热应力;第三种情况是考虑构件由不同材料组合起来的,即使构件受到均匀的温度作用,但由于不同组分材料的线胀系数不同,造成各组分之间相互制约,不能自由地胀缩,从而产生热应力。另外,温度对于材料物性参数的影响,尤其是对杨氏模量也有很大影响。一般而言,随着温度的升高,材料的杨氏模量会逐渐下降,导致材料的力学性能发生很大程度上的改变。
由于现代化的工程建设越来越多的使用梁式和板式结构,而温度变形影响又是结构设计中不可忽略的因素。分析梁板构件的热应力问题,可以提前采取相应的控制措施,以提高结构的承载能力和延长构件的使用寿命。因此对梁板热应力问题的研究具有十分重要的实际意义。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: