340th水冷管壳式换热器设计毕业论文
2020-06-20 18:54:41
摘 要
管壳式换热器是化工、炼油、动力、食品、轻工、原子能、制药、航空及其他许多工业部门广泛使用的一种通用设备。其具有可靠性高、适应性广等优点。因此,对管壳式换热器进行设计对掌握实际应用具有重要意义。
本文设计的换热设备是化工生产中使用的管壳式换热器中的固定管板式换热器。管程介质为冷却水,其设计压力为0.98MPa;壳程介质为HD330油,其设计压力为0.91MPa。由管程中的水冷却壳程中的热流体。本设计方法采用压力容器的常规设计方法,按照国标GB150-1998《钢制压力容器》、国标GB150-2011《压力容器》等技术法规执行。
设计内容主要包括:根据给出的设计参数,选定换热器的类型;查询冷热流体的物性参数对换热器进行热力计算,并且确定换热管的数量及管径以使换热器满足换热需求;再对管壳程及管板等零部件进行结构设计以及强度校核,主要包括材料的选择、具体尺寸的确定、开孔补强的计算和一些标准件的选用等;并用Aspen换热器设计软件对设计结果进行比较优化;最后,用AutoCAD绘制装配图及各零件图。
关键词:换热器 热力计算 结构设计 强度计算
Design of 340t/h Water-cooled Shell-and-tube Heat Exchanger
Abstract
Shell-and-tube heat exchanger is a general equipment widely used by chemical, oil refining, power, food, light industry, atomic energy, pharmaceutical, aviation and many other industrial sectors, which has high reliability and wide adaptability. Therefore, the design of shell-and-tube heat exchanger is of great significance to master the practical application.
The heat transfer equipment designed in this paper is the fixed tube sheet heat exchanger of the shell-and-tube heat exchanger used in chemical production. The tube medium is a cooling water with a design pressure of 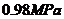 ; the shell medium is a HD330 oil with a design pressure of
; the shell medium is a HD330 oil with a design pressure of 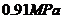 . The hot fluid in the shell is cooled by the water in the tube. The design method in this paper is the conventional design method of pressure vessel, according to GB150-1998 (steel pressure vessel), GB150-2011 (pressure vessel) and other technical regulations.
. The hot fluid in the shell is cooled by the water in the tube. The design method in this paper is the conventional design method of pressure vessel, according to GB150-1998 (steel pressure vessel), GB150-2011 (pressure vessel) and other technical regulations.
The design mainly includes: The type of heat exchanger is selected according to the given design parameters; The physical parameters of the hot and cold fluid are checked and the heat calculation is carried out on the heat exchanger. The number and diameter of the heat transfer tubes are determined so that the heat exchanger meets the heat exchange requirements; Then, structural design and strength check are carried on the tube side, shell side and tube sheet, mainly including the choice of materials, the determination of the specific size, the calculation of the hole reinforcement and the selection of some standard parts, etc; And the Aspen heat exchanger design software are used to optimize the design results; Finally, the assembly drawing and the parts of the map are mapped by AutoCAD.
Key Words: Heat exchanger; Heat calculation; Structural design; Strength checking
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 课题背景 1
1.2 发展现状及趋势 1
1.2.1 管程强化传热 1
1.2.2 壳程强化传热 2
1.2.3 管束强化传热 3
1.3 课题的工程价值及主要研究问题 3
第二章 换热器的热力计算 5
2.1 确定设计方案 5
2.1.1 确定换热器类型 5
2.1.2 流体在换热器中流动空间的选择 5
2.2 确定物性参数 5
2.3 估算传热面积 2
2.3.1 传热量 2
2.3.2 冷却水出口温度 2
2.3.3 逆流时的对数平均温差 3
2.3.4 估算传热面积 4
2.4 传热面结构设计 4
2.4.1 管径及管内流速 4
2.4.2 管程数及传热管数 4
2.4.3 管子排列方式及分程方法 5
2.4.4 拉杆 5
2.4.5 草图及相关结果 5
2.5 管程计算 6
2.5.1 管程接管直径 6
2.5.2 管程雷诺数 6
2.5.3 管程换热系数 6
2.6 壳程结构及壳程计算 6
2.6.1 折流板形式 6
2.6.2 折流板缺口高度 6
2.6.3 折流板间距及数目 7
2.6.4 折流板管子及缺口面积 7
2.6.5 折流板错流区计算 7
2.6.6 壳程流通截面积 8
2.6.7 错流区计算 8
2.6.8 壳侧计算 9
2.6.9 壁温计算 9
2.7 需用传热面积 10
2.8 阻力计算 10
2.8.1 管内参数计算 10
2.8.2 管程阻力计算 11
2.8.3 壳程阻力计算 12
2.9 本章小结 12
第三章 管壳式换热器结构及强度计算 13
3.1 壳体的设计及校核 13
3.2 前端管箱筒体设计 15
3.3 前端管箱封头计算 17
3.4 后端管箱筒体计算 19
3.5 后端管箱封头计算 21
3.6 换热管失稳应力分析 23
3.7 开孔补强计算 23
3.7.1 管箱短节的两个接管开孔 23
3.7.2 壳体的两个接管开孔 25
3.8 管板计算及校核 27
3.8.1 管板计算的有关参数及系数 27
3.8.2 管箱法兰 29
3.8.3 壳体法兰 30
3.8.4 系数计算 31
3.8.5 管板参数计算 32
3.9 管板的应力校核 33
3.9.1 仅有壳程压力下的危险组合工况 33
3.9.2 仅有管程压力下的危险组合工况 36
3.10 接管的选取 39
3.10.1 接管选材与选型 39
3.10.2 接管位置分布 39
3.11 支座的选择和计算 40
3.12 拉杆的选择和计算 41
3.13.1 结构形式的选择 41
3.13 定距管 43
3.14 本章小结 43
结 论 44
参考文献 45
致 谢 48
第一章 绪论
1.1 课题背景
生产生活中利用的换热装备中,管壳式换热器占大多数。对处于非常大温度和压力范围内的流体介质来说,管壳式换热器具有相对简单的结构和多用途应用的可能性[1]。另外,在换热设备的研究方面,管壳式换热器的研究水平一直处于较高的行列,因此它具有较完善且规范的设计流程。借助电脑程序进行换热器的设计同样取得了较大的发展,相比于传统的设计流程,借助电脑软件可以更加的准确并且大大地减少了误差。管壳式换热器自身具有很多长处,例如适用范围广、构造较精练、制造费用低、维护方便等,加之工艺以及理论的不断创新和进步,传统的管壳式换热器正扮演着重要的角色[2]。
1.2 发展现状及趋势
管壳式换热器作为工业行业中占主导地位的换热设备,其应用前景十分广阔,但其传热效率低的缺点也比较明显。强化管壳式换热器的传热过程,主要目标是为了能够在一定的时间与一定的传热面积中传导更多的热量,主要意义是在特定的装备投资与运送功耗的情况下,取得预期的传热量,从而使得装备的体量不断地增大。强化传热技术理论并不是针对某一方面展开的,它包括了管程、壳程和管束三个部分[3,4,5]。
1.2.1 管程强化传热
通过转变管子的外形和在管中增加内部部件这两种方式,能够使管内热传导得到增强。前者使用不同的换热管设计方案,对象包括不同类型的换热管,转变它们的形状,改变管内流体流动的速度和状态等。后者包括管内插物的设计,及通过管内绕丝花环、纽带等,实现管程的湍流程度[6,7]。这两种传热强化技术在学术界正在开展更为深切的研究。
螺旋槽纹管是一种装置, 这种管子是通过改变形状来使热传导增强。石景祯等人[8]对螺旋槽纹管进行仿真计算和实验研究,认为同轴套管换热器在强化传热上的表现更为优异。




