基于CFD模型的船用中速柴油机SCR排气管沉积物影响因素研究毕业论文
2020-04-12 09:00:15
摘 要
随着环境污染日趋严重,排放法规日益严格,为了使柴油机排放满足严格的标准,加装后处理系统成为了重要的解决途径,SCR因其较高的NOx转化效率以及良好的燃油经济性等优点被广泛使用于船舶柴油机。但是SCR系统在运行过程中会因尿素分解不完全而产生沉积物,对柴油机及SCR系统的稳定运行造成威胁。因此,对SCR排气管沉积物影响因素进行研究具有非常重要的意义。本文以船用中速柴油机作为研究对象,基于AVL FIRE 的SCR系统仿真模型,分别对喷孔个数(1、2、4、6、8)、喷射方向(0°、45°、90°、135°、180°)和喷嘴位置(3D、4.5D、6D、7.5D、9D)进行模拟计算,以转化效率和壁膜生成率为指标,分析这三个影响因素对SCR系统的影响规律,并给出了降低沉积物生成的建议。结果表明:(1)喷孔个数在1和2个时尿素碰壁严重,转化效率低并且壁膜生成严重;喷孔个数在4、6、8个时尿素喷雾雾化效果较好,NO转化效率提高并且壁膜的生成量减少。(2)喷射角度为0°、45°和135°时尿素喷雾分解比较完全并且碰壁情况减少,使得NO转化效率提高且壁膜生成量少;喷射角度为90°时尿素喷雾碰壁严重,壁膜生成量多; 180°时喷雾雾化效果不好,转化效率低。(3)喷嘴与首层催化剂的距离为3D、4.5D和6D时,NO转化效率低且壁膜生成量多;喷嘴与首层催化剂的距离为7.5D和9D时,尿素水溶液蒸发热解时间变长,分布更加均匀,使得转化效率高,壁膜生成量少。
关键词: SCR,沉积物,影响因素,转化效率,壁膜生成率
Abstract
With increasingly serious environmental pollution and increasingly stringent emission regulations, the addition of a post-processing system has become an important solution to meet the stringent standards for diesel engine emissions. SCR has the advantages of high NOx conversion efficiency and good fuel economy. It is widely used in marine diesel engines. However, during the operation of the SCR system, sediments are generated due to incomplete urea decomposition, which poses a threat to the stable operation of the diesel engine and the SCR system. Therefore, it is of great significance to study the influencing factors of SCR exhaust pipe deposits. This article takes the medium-speed diesel engine as the research object, and based on the SCR system simulation model of AVL FIRE, the number of orifices (1, 2, 4, 6 and 8) and the injection direction (0°, 45°, 90°, 135°, 180°) and nozzle positions (3D, 4.5D, 6D, 7.5D, 9D) were simulated, and the effect of these three influencing factors on the SCR system was analyzed using the conversion efficiency and wall film formation rate. Suggestions for reducing the formation of sediments are given. The results show that: (1) When the number of orifices is 1 and 2, the urea wall is severe, the conversion efficiency is low and the wall film is severe; the number of orifices is 4, 6 and 8; the effect of urea spray atomization is good, The NO conversion efficiency increases and the amount of wall film formation decreases. (2) The urea spray is completely decomposed at the spray angles of 0°, 45°and 135°, and the situation of wall collision is reduced, so that the NO conversion efficiency is increased and the amount of the wall film generated is small; when the spray angle is 90°, the urea spray hits the wall seriously, and the wall film The amount of production is large; spray atomization effect is not good at 180°, and the conversion efficiency is low. (3) When the distance between the nozzle and the first layer of catalyst is 3D, 4.5D and 6D, the NO conversion efficiency is low and the amount of wall film is much; when the distance between the nozzle and the first layer of catalyst is 7.5D and 9D, the urea solution evaporation and pyrolysis time As it becomes longer, the distribution of NH 3 is more uniform, resulting in higher conversion efficiency and less wall film formation.
Key Words: SCR, Deposits, Influcing factors, Conversion efficiency, Wall formation rate
目 录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 研究背景 1
1.1.1 NOx的生成机理及危害 1
1.1.2 排放法规 2
1.1.3 NOx控制技术 3
1.2 SCR技术介绍 5
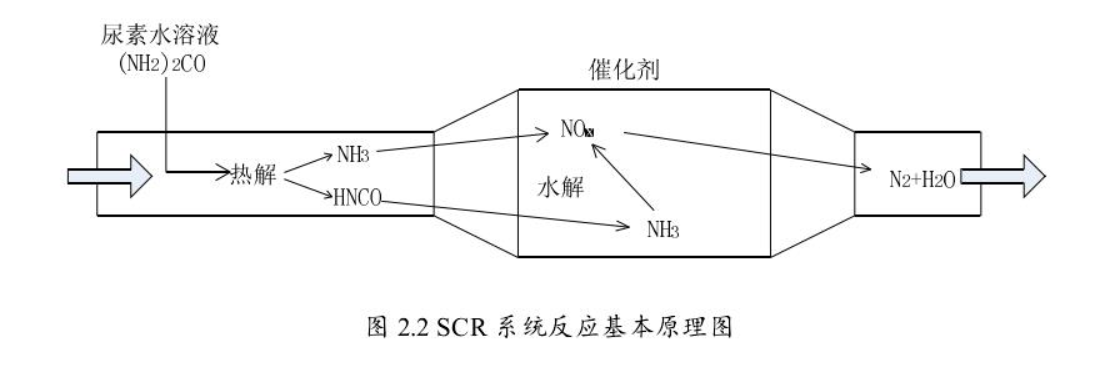
1.2.1 SCR原理 5
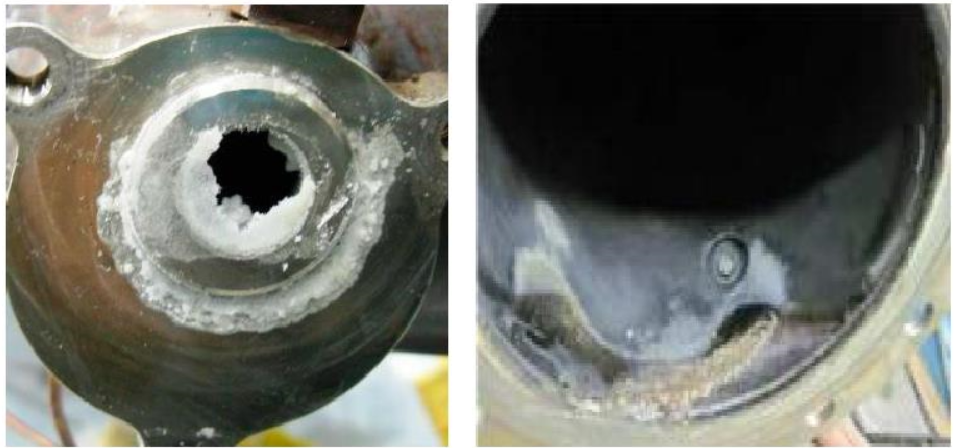
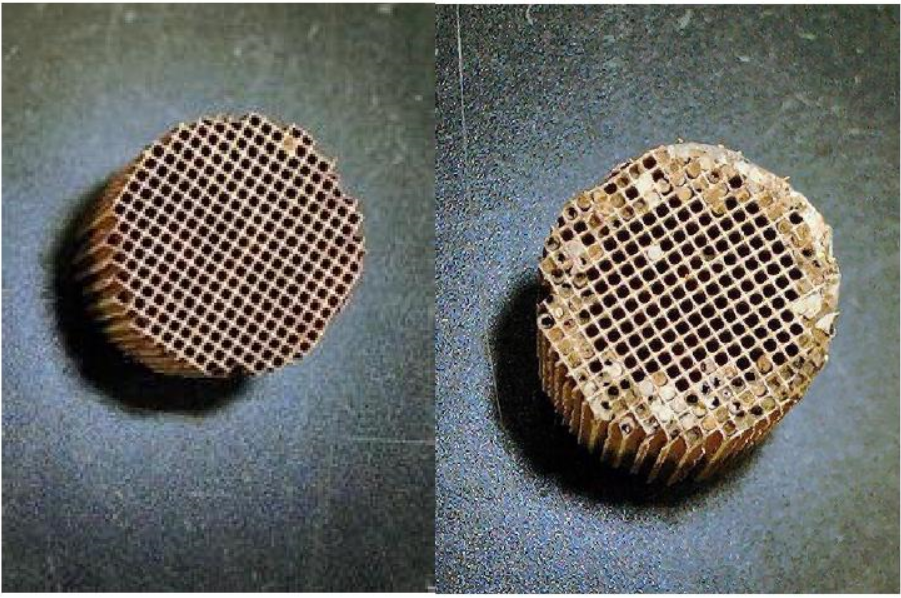
1.2.2 沉积物生成机理 7
1.2.3 沉积物的危害 10
1.3 国内外研究现状 10
1.3.1 沉积物影响因素研究现状 10
1.3.2 仿真模拟研究现状 11
1.4 本文主要研究内容 13
第2章 SCR系统三维模型的建立 15
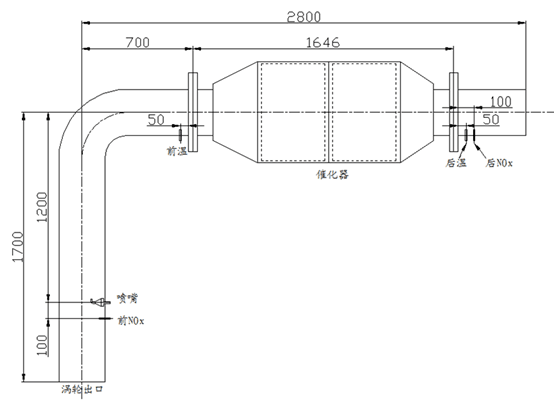
2.1 SCR模型体网格的划分 15
2.2边界条件的设置 18
2.3 子模型 21
2.3.1壁膜模型 21
2.3.2尿素蒸发热解模型 25
2.4本章小结 27
第3章 排气管沉积物的影响因素分析 28
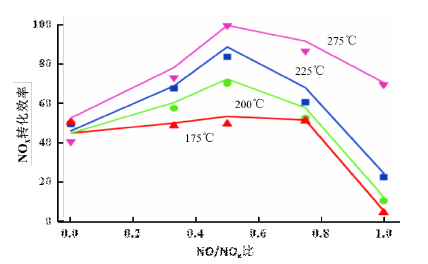
3.1喷孔个数的影响 28
3.2喷射角度的影响 31
3.3喷射位置的影响 34
3.4本章小结 37
第4章 总结与展望 39
4.1全文总结 39
4.2展望 39
参考文献 41
致谢 43
第1章 绪论
1.1 研究背景
我国作为全球第二大经济体,水上运输的繁荣发展是推动我国经济发展的强大动力。柴油机以其独特的转矩特性、较高的热效率和耐久性,被广泛应用于船舶行业,但船舶在航行中会持续排放氮氧化合物、含碳颗粒物和硫氧化合物等大气污染物。这些污染物能够随大气流动向内陆进行迁移,加重城市的空气污染,对人体健康和生态环境造成危害,因此控制污染物的排放已经成为全球共同面临的问题。随着环境污染越来越严重,全球的排放与控制法规也日趋严厉,单依靠机内处理措施很难达到目前以及未来排放法规的要求,因此,需要采用相应的后处理技术。
1.1.1 NOx的生成机理及危害
船舶柴油机尾气排放的氮氧化物(NOx)中NO和所占的比例高达90%~95%,所以控制NO和排放是减少NOx排放最有效的途径。有研究表明,全球每年船舶尾气排放NOx约5~6.9Tg(百万吨),占全球NOx排放总量的15%。对于船舶柴油机尾气中的NOx主要来源两个方面:一是空气中N、O元素进行反应产生NOx,称为“热氮氧化物”(Thermal NOx);二是燃料中的微量氮化物发生反应产生NOx,称之为“燃料氮氧化物”(Fuel NOx)。而NOx的生成主要由气缸内高温、富氧以及氮与氧在高温下的停留时间这三个因素决定。在空燃比一定的情况下,NO 的生成量随温度、转速、负荷的增加而增加,同时NO 的生成量也取决于在火焰前锋位置处是否富氧,当a大于l 时,氧气越浓,NO浓度就会越高;当空气过量系数a 稍大于1 时,NO的生成量达到最高;当a小于l,如果氧气稀薄,NO浓度就会下降,并且在燃烧时生成NO 的化学平衡需要的时间要比每一循环中燃烧反应时间长,所以为了降低NOx的生成,可以降低火焰的高峰温度、采用适当的空燃比和缩短高温持续时间[1]。
NOx对人的身体和生态环境都有严重的危害。NOx是形成光化学烟雾的重要原因,NO 在阳光作用下,发生化学反应产生一种称之为“光化学烟雾”的有毒气体,能导致眼病、咽喉炎、哮喘、肺气肿及其它慢性疾病,高浓度的NO 还会导致人体神经中枢发生障碍,严重时会使人有生命危险。此外,NOx是形成酸雨的重要原因,NOx升空雾化后与空气中的水结合,形成的酸雨不仅导致严重的生态问题,如致使湖泊呈酸性影响鱼类生存;致使土壤结板,影响土壤的透气性和渗水性,损坏植物的生长,造成农作物减产以及大面积草地和森林的枯黄;还能严重损害建筑物等基础设施,如故宫的大理石雕塑、埃及的狮身人面像等著名建筑都受到酸雨的腐蚀[2]。
1.1.2 排放法规
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: