车用液力缓速器内部流场特性仿真及优化分析毕业论文
2020-04-13 11:43:18
摘 要
作为现代商用车重要的辅助制动器,各汽车厂商越来越重视液力缓速器的研究与开发.以前的研究的方向主要是增大制动力矩,随着研究的深入,人们逐渐开始重视液力缓速器的其他性能,如控制策略以及散热系统的设计,降低空转损耗等。这次毕业设计,利用CFD软件研究缓速器的内部流场分布,进而根据流场分布来优化其结构,文章介绍了缓速器的原理,发展历史等方面。此外,还对液力缓速器的发展现状以及未来的发展趋势进行了一些展望。在具体研究方面,使用三维建模软件CATIA根据已有数据建立液力缓速器三维模型,其中叶片倾角固定为30,后期根据仿真的需要进行适当简化,在仿真时使用ANSYS中的Workbench模块进行网格划分,流域建立等前期准备,之后将模型导入Fluent中进行流场仿真,得到缓速器内部流场的流体运动状态云图(速度,压力):为了找出可以将液力缓速器空转时产生的损耗最小情况,我们改变动轮和静轮的叶片的倾斜角度,由此产生不同的仿真数据,之后进行对比,得出最适合的缓速器内部结构。
研究结果表明,缓速器叶片的偏移角度越大,在较大转速,相同充液量的前提下,产生的制动力矩越大,这时的空转损失也是越大,故而在满足制动力矩需求的情况下,尽可能小的选择叶片偏移角度,市场上大多数液力缓速器的叶片偏移角度为30°。
关键词:液力缓速器,流场分析,Workbench,Fluent
Abstract
As an important auxiliary brake for modern commercial vehicles, various automobile manufacturers pay more and more attention to the research and development of hydraulic retarders. The direction of previous research is mainly to increase the braking torque. As the research deepens, people gradually begin to pay attention to liquid. The other performance of force retarder, such as control strategy and cooling system design, reduce idle loss and so on. This graduation project, using CFD software to study the internal flow field distribution of the retarder, and then optimize its structure according to the flow field distribution, the article introduces the principle, development history and other aspects of the retarder. In addition, some prospects for the development status of the retarder and its future development are also presented. In terms of specific research, a three-dimensional model of the hydraulic retarder was established using the three-dimensional modeling software CATIA based on the existing data, in which the blade inclination angle was fixed at 30, and was later appropriately simplified according to the needs of the simulation. In the simulation, the Workbench module in ANSYS was used for the simulation. Grid preparation, basin establishment and other preliminary preparations, and then the model was imported into Fluent for flow field simulation. In order to find the least loss that can occur when the hydraulic retarder is idling, we change the tilt angle of the blades of the moving and stationary wheels. , resulting in different simulation data, then compared to find the most suitable retarder internal structure.
The research results show that the larger the offset angle of the retarder blade, the greater the braking torque generated under the premise of larger rotational speed and the same liquid filling amount, and the greater the idle loss at this time, the more satisfactory the brake is. In the case of torque demand, the blade deflection angle is selected as small as possible, and most of the hydraulic retarders on the market have a blade offset angle of 30°.
Keywords: hydraulic retarder, flow field analysis, Workbench, Fluent
目 录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1研究背景 1
1.2 液力缓速器 2
1.2.1液力缓速器的制动力矩的计算公式 2
1.2.2液力缓速器的制动力矩的控制方式 3
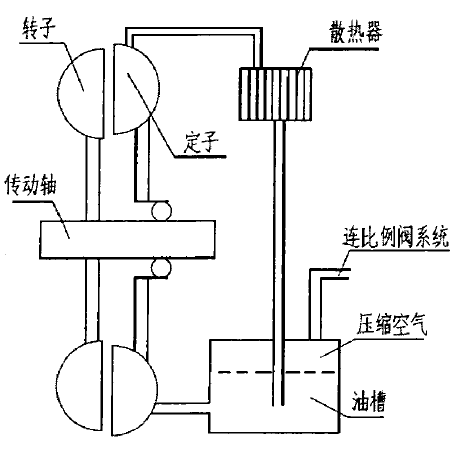
1.2.3液力缓速器的结构 4
1.2.4液力缓速器特点 4
1.2.5液力缓速器的工作原理 7
1.2.6液力缓速器的发展趋势 7
第2章 计算流体动力学基础理论 9
2.1计算流体动力学的定义 9
2.2计算流体动力学的一般步驟 9
2.3计算流体动力学的控制方程 10
2.3.1质量守恒方程 10
2.3.2动量守恒方程 10
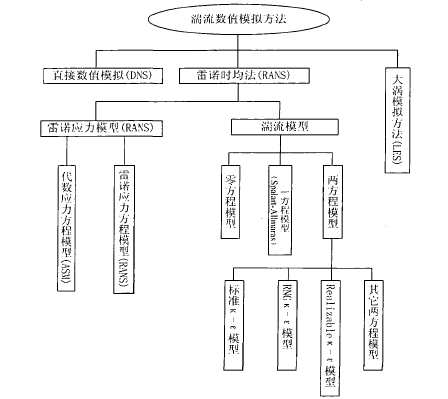
2.4 湍流方程 11
2.3.1 湍流 11
2.3.2湍流的数值模拟方法 11
2.4 湍流模型的近壁处理 12
2.5 本章小结 12
第3章 计算流体动力学基础理论 13
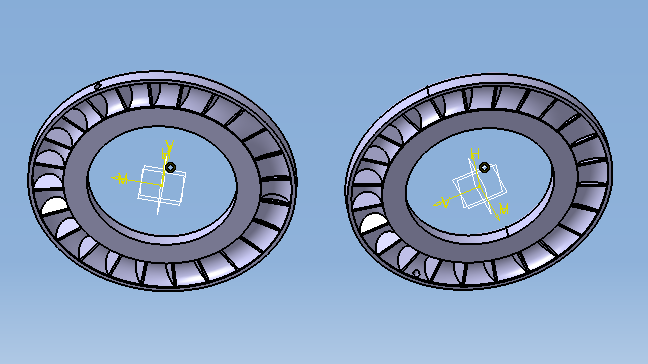
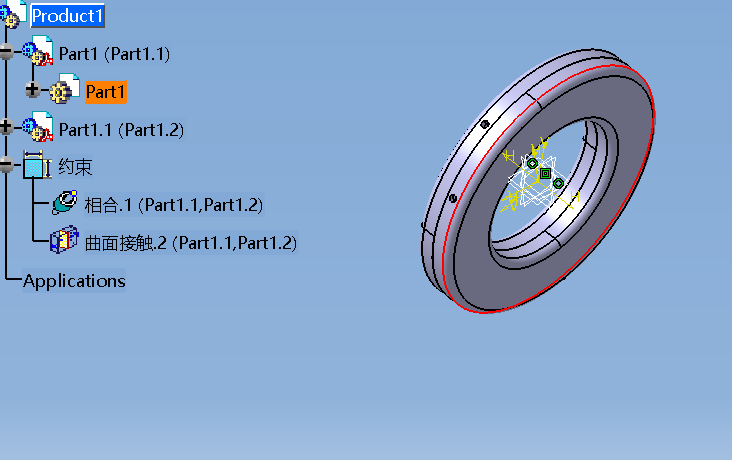
3.1缓速器三维模型的建立 13
3.2网格划分工具meshing软件简介 14
3.3 计算流体动力学通用软件FLUENT 14
3.4 仿真参数的设置 15
3.4.1 计算模型的简化 15
3.4.2流域划分 15
3.4.3 网格划分 17
3.4.4 湍流模型的选择 19
3.4.5边界条件的确定 19
3.5本章小结 19
第4章 液力缓速器流场分析 20
4.1仿真结果分析 20
4.1.1制动力矩分析 21
4.1.2 内部流场特性分析 23
4.2优化分析 23
4.3本章小结 27
第5章 全文总结与展望 28
5.1全文总结 28
5.2展望 29
参考文献 30
致谢 31
第1章 绪论
1.1研究背景
时代在发展,随着科技的进步,人们的生活水平日渐提高,物质方面的需求也变得多种多样,这对现代的物流系统有了很高的要求,作为现代物流运输的主力,道路运输发展越来越快,对商用车的行驶可靠性,安全性,高效性的要求也越来越高,在商用车制动时,除了只安装传统的摩擦制动装置已经不能满足要求,必须提供辅助制动装置[1]。经过人们几十年的探索,发现液力缓速器作为辅助制动装置,辅助制动效果和经济性具佳,尤其是对重型商用车辆,加装液力缓速器之后可,可以大大降低行车制动器的磨损加剧和过热失效的概率,延长制动系统的寿命,大大提高了行驶安全性。
常用于车辆的辅助制动器主要有液压制动,空气阻力制动,发动机排气制动,电涡流式制动,液力制动这五种方式
1.液压制动:液压制动装置的原理是由工作介质对泵轴提供制动力矩来实现辅助制动的功能,同时,将车辆运动的动能通过液流体介质转化为内能,之后再通过散热系统传导到外界。液压制动使用工况范围广,在车辆行驶的任意工况点都提供足够的的制动力矩.但液压泵自身存在一定的机械磨损,使用一段时间之后,制动的性能会有所降低,而且随着重型车辆需要的制动要求的提高,制动器的外部尺寸变得越来越大,这在很大程度上限制了液压制动的制动功率的提高。
2.空气阻力制动: 这种制动方式的原理是突然增大的车身空气阻力或安装于车辆尾部空气阻力伞(可以在需要时弹出)产生制动力. 这种制动方式的制动过程比较平稳不存在冲击,一般应用于高速赛车和航天飞机上,空气阻力制动对制动条件的要求十分严格,路况必须要求很好,这就使得其在普通车辆和军用车辆上应用的可能性很低.
3.发动机排气制动: 在发动机排气管中安装一个可控的阀门,当需要进行辅助制动时,电子控制系统会将阀门调整为关闭状态,这样在发动机运行的排气冲程中会产生负功,这样就产生了需要的辅助制动力矩,实际上,此时的发动机被转化为一个空气压缩机,没有做功,通过压缩空气,将又传动系统传来的动能转化为空气的热能,达到辅助制动的目的。但是排气制动缺点也很明显,会在车辆行驶时产生很大的噪音.
4.电涡流式制动: 转动的圆盘,固定的磁极和线圈这三部分组成了电涡流制动器。在需要辅助制动介入时,将制动器内部的线圈通电,产生磁场,圆盘在线圈通电产生的磁场中转动,由电磁感应来产生电涡流,在电涡流和磁场相互作用下,得到需要的制动力矩[2]在低转速区域,主传动轴转速低于500 r/min时,电涡流制动器的制动转矩会快速变小;在高转速区域,转速高于700r/min时,一般会得到制动力矩的最大值。电涡流式制动的缺点和液压制动一样,在制动器尺寸一定时,所能提供的制动转矩相对较小.如:常用于3.5~ 6t商用车上的电涡流式制动器,其重量约为90kg,而所能提供的最大制动转矩大约为500Nm。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: