高湿印染污泥原位水份在热解过程中的作用特性毕业论文
2020-04-17 16:29:46
摘 要
印染污泥是由纺织厂废水进行处理后所产生的污泥,由于印染企业在生产过程中使用大量的染料、浆料、助剂等,所以印染污泥中有害物质含量较高,对生物以及环境的危害较大。除了有毒有害物质,印染污泥中也存在部分有机物,合理的处置方法可以将其作为资源进行利用,所以如何有效处理印染污泥逐渐成为许多国内外学者研究的重点。目前,热解方法因具有二次污染小、产物种类多样化以及能量回收率高等特点,逐渐获得研究者们的青睐。印染污泥同普通污泥一样,具有高含水率、低有机物和高灰分的特性,所以单独热解的产物品质则相对较低,而生物质则具有完全相反的特性。因此本文通过在印染污泥中添加生物质来改善原料特性,优化产物品质。本文主要研究内容为结合管式炉实验和HSC模拟考察印染污泥与不同生物质以不同比例为原料进行热解的三相产物分布和气体产物特性,其中添加的生物质分别为花生杆、花生壳、麦秆、棉杆以及木屑。本文的主要研究结果如下:
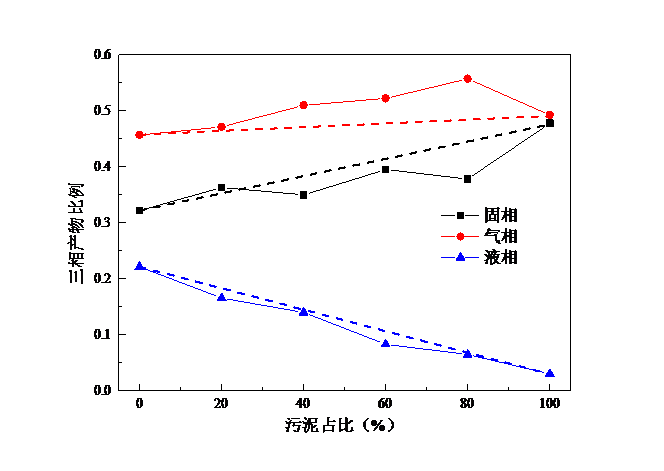
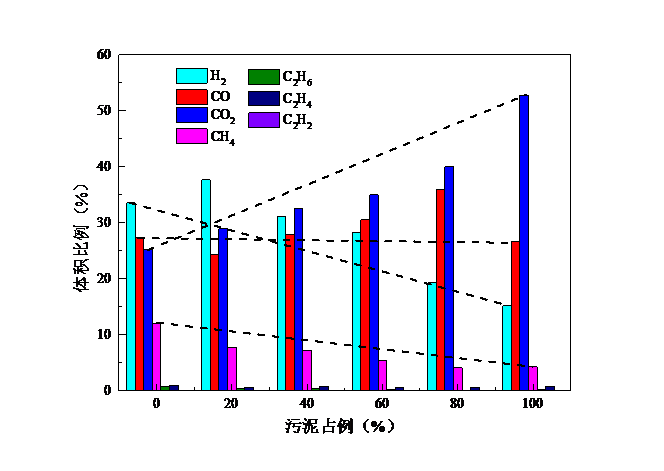
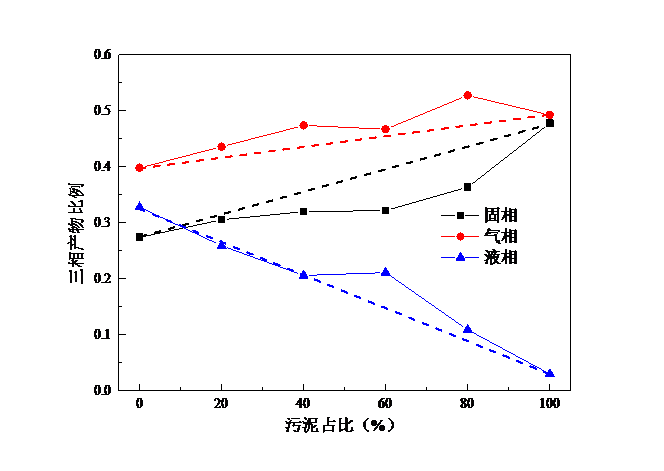
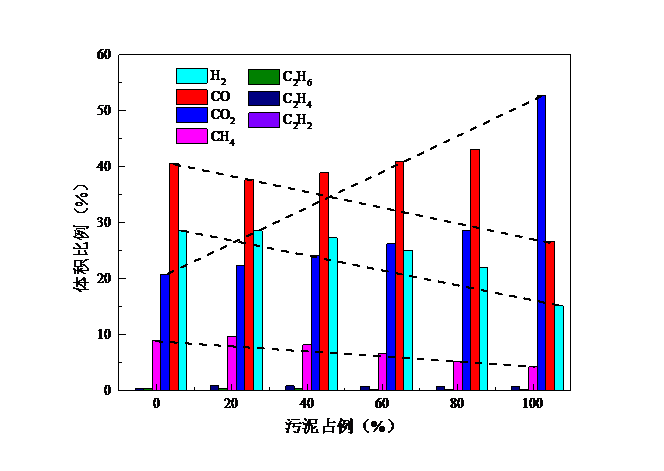
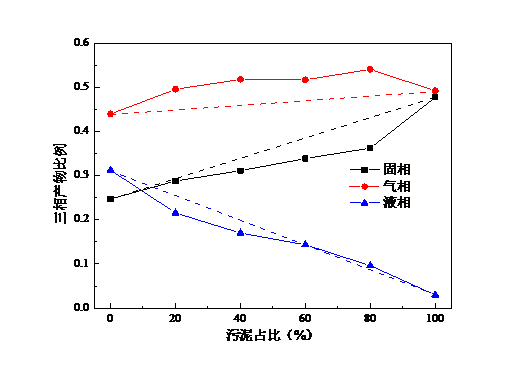
(1)通过印染污泥与生物质共热解实验可以看出,当污泥占比为80%时,CO产量最大且高于理论值,说明此时生物质与印染污泥二者共热解存在协同作用;当污泥占比为20%时,热解H2产量最大。当生物质为木屑和麦秆时,污泥占比0%时热解产生的CH4量最大,而当生物质为棉杆时,污泥占比20%时CH4产量最大。随着污泥占比的增大,固相和气相产物比例增大,而液相产物比例在减少,气体热值、产气率均呈下降趋势,碳转化率则呈上升趋势。因为污泥中有机质含量较少,热解产生的可燃气体也较少,所以随着污泥占比增大,产气率下降;此外,由实验得出的图中可知,随着污泥占比增大,CH4产量在总气体中占比减少,所以气体热值下降。
(2)通过HSC模拟可以看出,当生物质添加比为20%时,添加木屑进行热解的H2产量最大,当生物质添加比为40%、60%、80%和100%时,添加棉杆所产生的H2量最多;当生物质添加比为20%和40%时,添加花生壳进行热解得到的CO产量最大,当生物质添加比为60%、80%和100%时,添加麦秆热解所产生的CO量最大。此外,H2、CO以及CH4产量均随生物质添加比的增大而增加;对于CO2,当生物质为木屑时,其产量随木屑添加比的增大而减少,当生物质为花生杆、花生壳、麦秆及棉杆时,在低温段和高温段其产量随生物质添加比的增大而减少,在中温段则随之增加。对于不同生物质以相同比例添加,其所产生的H2、CO、CO2以及CH4含量大致相等,但随生物质添加比例的增大,各种生物质产气量之间的差别也越来越大。
(3)将实验结果与HSC模拟结果进行比较发现,当热解温度为1000℃时,随生物质添加比例的增大,H2、CO以及CH4产量增加,而CO2产量则随之减少。
关键词:印染污泥 生物质 热解 HSC模拟
Abstract
Textile dyeing sludge is produced by textile mill wastewater. Due to the use of a lot of dye, sizing, agent and additives, etc in the process of production, the content of harmful substances in the textile dyeing sludge is higher. As a result, it is more harmful to biology and environment. In addition to toxic and harmful substances, there is also organic matter in the textile dyeing sludge. Reasonable disposal methods can make it used as resources, so how to treat dyeing sludge effectively has become the focus of many domestic and foreign scholars. At present, pyrolysis has gradually become favored by researchers due to its characteristics of small secondary pollution, diversified products and high energy recovery rate. Textile dyeing sludge has the characteristics of high moisture content, low organic matter and high ash content, like ordinary sludge. Therefore, the product quality of separate pyrolysis is relatively low, while biomass has completely opposite characteristics. In this paper, biomass was added to textile dyeing sludge to improve raw material characteristics and optimize product quality. The main research content of this paper is to investigate the distribution of three-phase products and characteristics of gas products during pyrolysis of textile dyeing sludge and different biomass with different proportions through tubular furnace experiment and HSC simulation. The added biomass includes peanut stalk, peanut shell, wheat straw, cotton stalk and wood chips. The main research results are as follows:
- It can be seen through textile dyeing sludge and biomass co-pyrolysis experiments that. when the proportion of sludge is 80%, the CO yield is the largest and higher than the theoretical value. At this time, the co-pyrolysis of biomass and textile dyeing sludge was synergistic. When the proportion of sludge is 20%, the yield of H2 is the largest. When biomass is wood chips and wheat straw and sludge accounts for 0%, the amount of CH4 generated by pyrolysis is the largest . When biomass is cotton stalk and sludge accounts for 20%, CH4 yield is the largest .With the increase of sludge addition ratio, the proportion of solid and gas products increases, and the liquid phase is decreasing. The calorific value and the yield of the gas decreased, and the carbon conversion is on the rise. Because there is less organic matter in the sludge, and there is less combustible gas produced during the pyrolysis. Therefore, with the proportion of the addition of sludge increases, gas production rate decreases. In addition, it can be seen from the figure obtained from the experiment that with the increase of sludge addition ratio, the proportion of CH4 production decreased , so the calorific value of the gas goes down.
- It can be seen from the HSC simulation that when the biomass addition ratio is 20%, the yield of H2 was the highest when wood chips were added for pyrolysis. When the biomass addition ratio is 40%, 60%, 80% and 100%, the yield of H2 was the highest when cotton stalks were added for pyrolysis. When the biomass addition ratio is 20% and 40%, the CO yield obtained by adding peanut shell for pyrolysis is the largest. When the biomass addition ratio is 60%, 80% and 100%, the CO yield obtained by adding wheat straw for pyrolysis is the largest. In addition, the yield of H2, CO and CH4 increase with the increase of biomass addition ratio. For CO2, when biomass is wood chips, its yield decreases with the increase of sawdust addition ratio. When the biomass is peanut stalk, peanut shell, wheat straw and cotton stalk, at low and high temperature range, the yield decreases with the increase of biomass addition ratio and it increases in the middle temperature range. When different biomass is added in the same proportion, the contents of H2, CO, CO2 and CH4 are approximately equal. But with the increase of biomass proportion, the differences between biomass gas production are also increasing.
- Comparing the experimental results with the simulation results of HSC, we can find that when the pyrolysis temperature is 1000 ℃, with the increase of biomass proportion, the production of H2, CO and CH4 increases, while the production of CO2 decreases accordingly.
Keywords: textile dyeing sludge; biomass; pyrolysis; HSC simulation.
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract III
第一章 绪 论 1
1.1 研究背景及意义 1
1.2 印染污泥常规处理方法的简介 1
1.3 国内外印染污泥的处置现状 3
1.3.1 国外印染污泥处置现状 3
1.3.2 国内印染污泥处置现状 5
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: