含硅酸盐酸再生液的处理方法研究毕业论文
2020-04-13 13:05:42
摘 要
近年来,钢铁行业发展迅速,钢铁需求量与日剧增,钢铁在一系列制造工艺中,其表面会不同程度的形成氧化铁皮以及杂物,这些物质的存在将会影响成品的美观以及耐腐蚀性能,需要用酸对其进行酸洗去除,然而酸液酸洗能力有限,一旦其中金属含量超标,就会严重影响酸洗质量。因此,钢制造企业就会产生大量不易处理的废酸。废酸危害巨大,如果直接加以排放,将会对环境与人体健康带来不可挽回的伤害,并且也会在很大程度上提高企业制造成本,浪费资源。
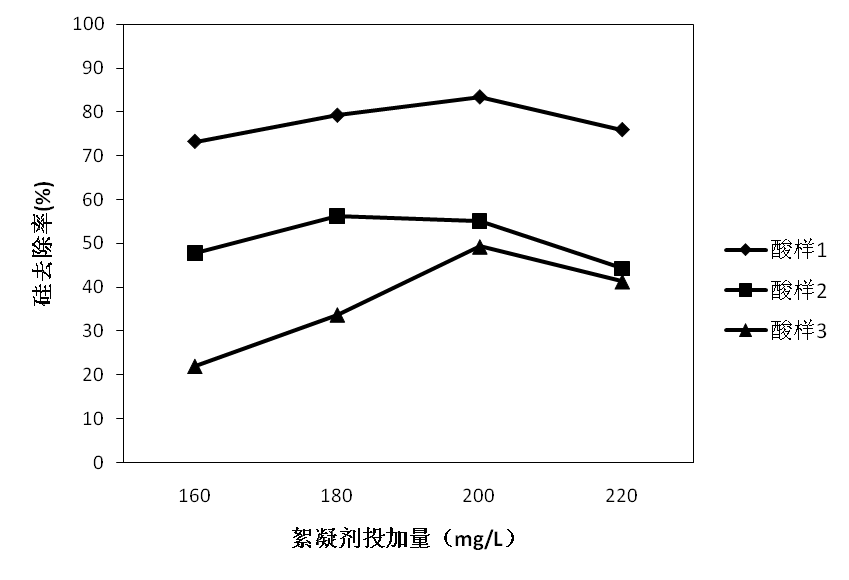
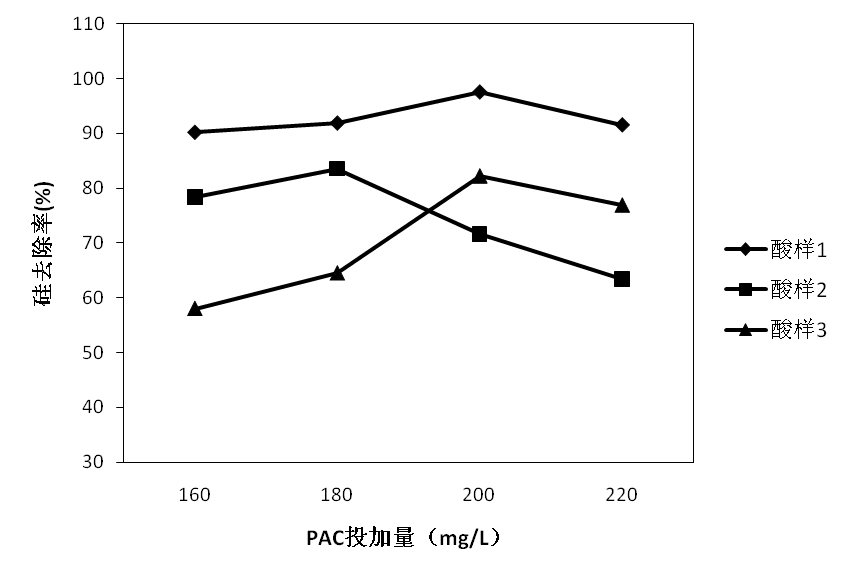
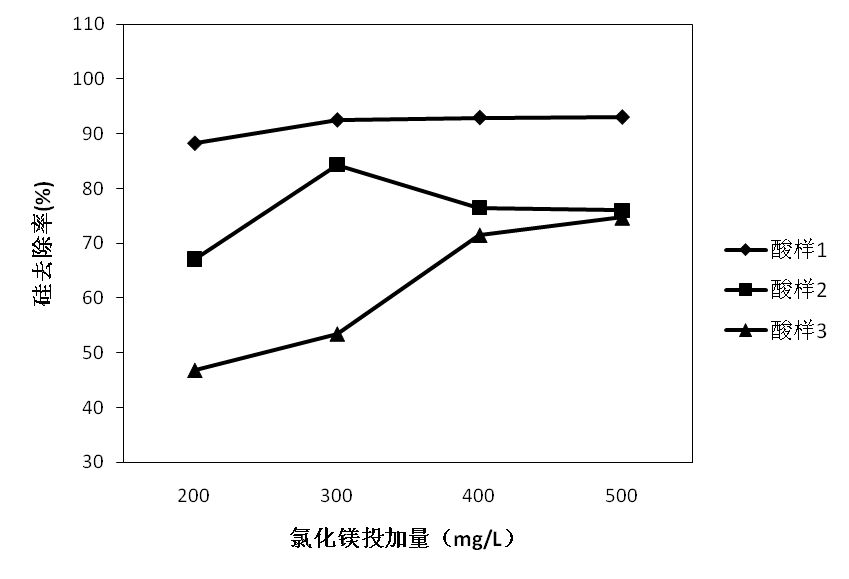
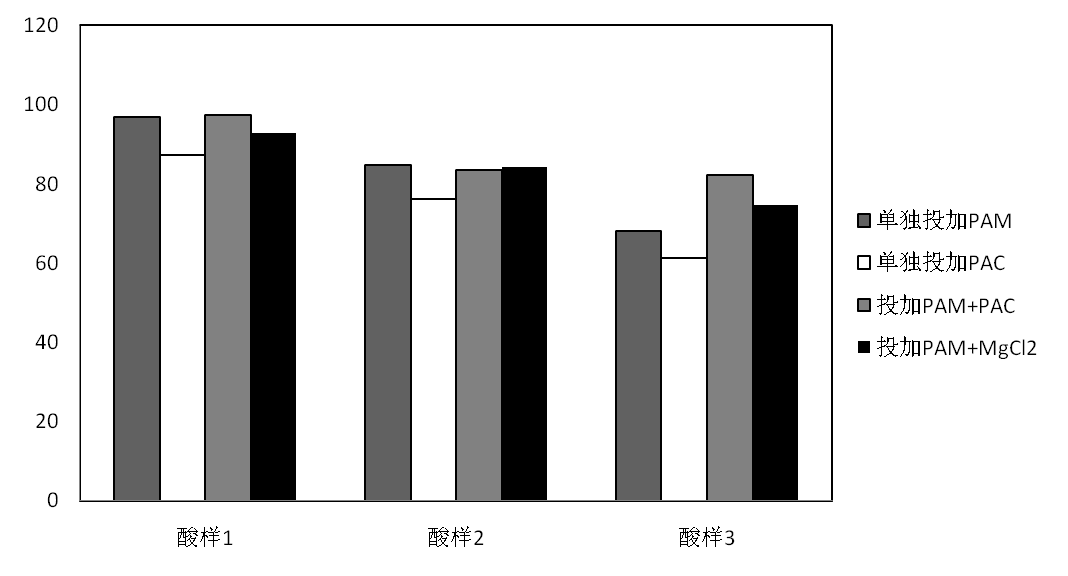
对于废盐酸的处理大多数企业采用喷雾焙烧法,这种方法处理废盐酸的同时将产生大量金属氧化物固体。由于酸液中含有SiO2,产生的副产物Fe2O3中将混杂有大量SiO2杂质,严重影响其回收价值。因此,本文将利用絮凝法对废酸中SiO2进行净化去除。本文将重点探究絮凝剂种类、最佳投量,絮凝剂与助凝剂搭配方式,沉淀时间,以及水力条件优化。实验结果发现:对于废酸1,投加助凝剂效果并不明显,建议单独投加絮凝剂聚丙烯酰胺,其最佳投量为60mg/L,在沉淀40min后,硅去除率达到96.9%,在絮凝剂最佳投加量下,以快速搅拌300r/min,时间10s,慢速混合120r/min,时间3min的形式,沉降时间为30min,最佳硅去除率可达98.4%;对于废酸2,投加助凝剂并不能很好的降低二氧化硅含量,建议单独投加絮凝剂聚丙烯酰胺,其最佳投量为80mg/L,在沉淀40min后,二氧化硅去除率达到84.7%,在最佳絮凝剂投加量下,以快速搅拌400r/min,时间10s,慢速混合160r/min,时间3min的形式,沉降时间30min,最佳硅去除率为92.31%;对于废酸3,单独投加絮凝剂聚丙烯酰胺,其最佳投量为80mg/L,硅去除率可达68%,而采用絮凝剂 助凝剂的复合投加形式,即投加80mg/L聚丙烯酰胺 PAC200mg/L,硅去除率可达82.2%,在单独投加絮凝剂下,以快速搅拌450r/min,时间15s,慢速混合200r/min,时间210s的形式,沉降时间为30min的形式,最佳硅去除率为81.0%,从经济节能角度,建议单独投加絮凝剂并采用完善后的水力条件。
关键字:硅酸盐,废盐酸,絮凝,助凝
Abstract:
In recent years, the steel industry has developed rapidly, and the demand for iron and steel has increased dramatically.Iron and steel in a series of manufacturing processes, its surface will be formed in varying degrees of oxide iron and debris, the presence of these substances will affect the aesthetic and corrosion resistance of the finished product, need acid to remove it,however, the acid pickling capacity is limited, once the metal content exceeds the standard, it will seriously affect the pickling quality.Therefore, steel manufacturing enterprises will produce a large number of refractory waste acid.Waste acid is a great harm. If it is discharged directly, it will bring irreversible damage to the environment and human health, and will also greatly improve the cost of manufacturing and waste of resources.
On the other hand, for most enterprises, they select spray culture method which through selling Fe2O3, grow their revenue. However, due to the silicon ion the acid have, the quantity of Fe2O3 is debased. In general, this study will use the process of flocculation to remove silicon ion from waste hydrochloric acid. Results showed: the waste acid 1 was suggested adding polyacrylamide(PAM) alone, the best optimum dosage was 60mg/L, after 40min precipitation, the removal of silicon reached 96.9%, in the optimum dosage, the rapid agitate strength was 300r/min, reaction time was 10s, the slow agitate strength was 120 r/min, reaction time was 3min, the removal of silicon reached 98.4%; as to the waste acid 2 was also suggested adding PAM alone, the best optimum dosage was 80mg/L, after 40min precipitation, the removal of silicon reached 84.7%, in the optimum dosage, the rapid agitate strength was 400r/min, reaction time was 10s, the slow agitate strength was 160 r/min, reaction time was 3min, after 30min precipitation, the removal of silicon reached 98.4%; as far as the waste acid 3 once added PAM alone, the best optimum dosage was 80mg/L, after 40min precipitation, the removal of silicon reached 68.0%, while used flocculation and coagulant together(PAM80mg/L PAC200mg/L), the removal of silicon reached 82.2%,in the optimum dosage, the rapid agitate strength was 450r/min, reaction time was 15s, the slow agitate strength was 200r/min, reaction time was 210s, after 30min precipitation, the removal of silicon reached 81.0%.From the point of view of economic energy saving, it is suggested to add flocculant alone and adopt the improved hydraulic conditions.
Key words:Silicate,Waste hydrochloric acid,flocculate,Coagulation aid
目录
第一章 绪论 1
1.1课题来源及研究背景 1
1.2含硅酸盐酸废液处理方法发展现状 2
1.2.1絮凝剂的种类 2
1.2.2助凝剂的影响 3
1.2.3水力条件的影响 4
1.3课题研究的目的及意义 4
1.4论文的主要研究内容 4
第二章 废盐酸脱硅处理工艺 6
2.1引言 6
2.2实验材料与设备 6
2.2.1实验材料 6
2.3实验装置与方法 7
2.3.1实验流程 7
2.3.2实验方法 8
2.4实验结果 8
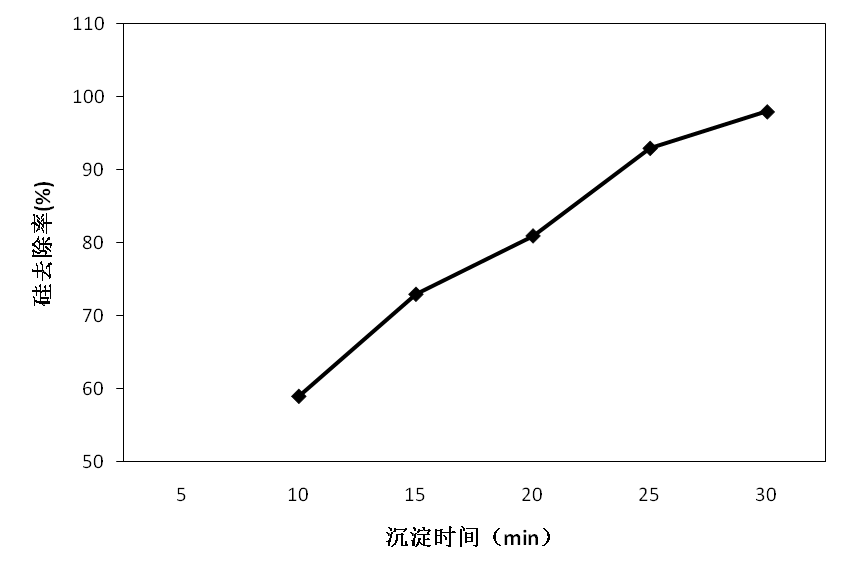
2.4.1硅杂质自然沉降 8
2.4.2药剂选择 9
2.4.2.1絮凝剂—PAM 9
2.4.2.2絮凝剂—聚合氯化铝(PAC) 11
2.4.2.3絮凝剂 助凝剂—PAM PAC 12
2.4.2.4助凝剂—氯化镁 13
2.4.3水力条件 15
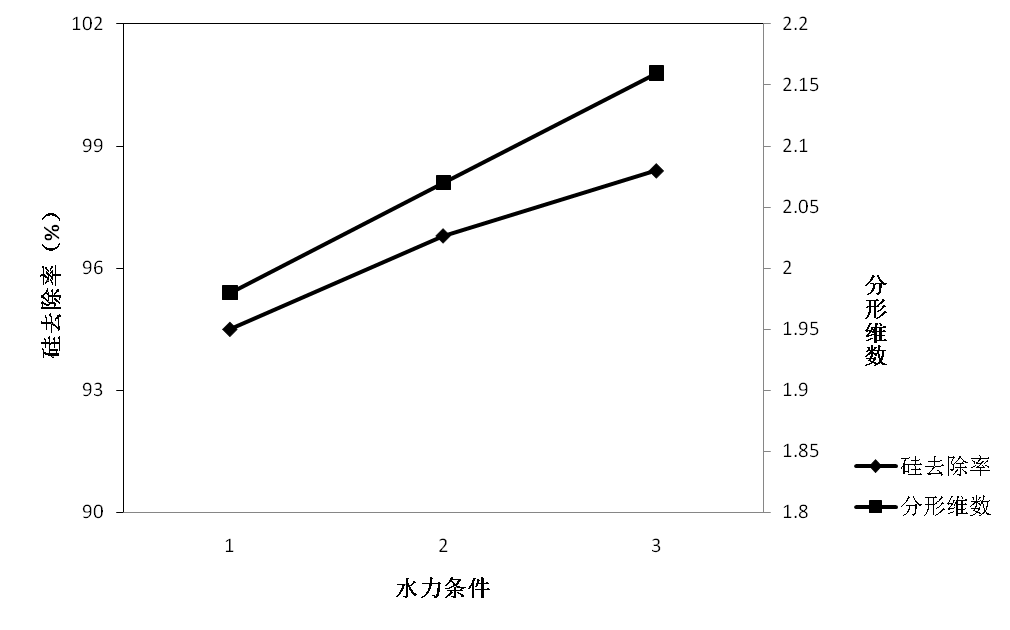
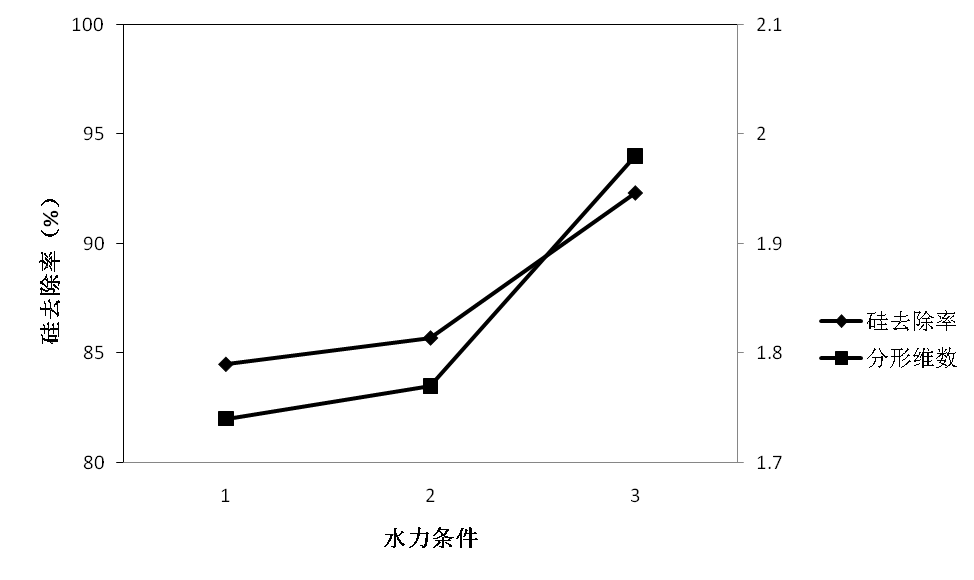
2.4.3.1酸样1 16
2.4.3.2酸样2 18
2.4.3.3酸样3 20
2.4.4处理效果 22
2.5本章总结 23
第三章 结论与展望 24
致谢 25
参考文献 26
第一章 绪论
1.1课题来源及研究背景
自新中国成立之后,随着城市发展需求不断加大,钢铁工业迅速发展。不论沿海城市还是内地都市,近两年钢铁工业蓬勃发展,一大批钢铁和铁合金、耐火材料等等辅助原料企业遍地开花,发展势头迅猛。
其中,以普通钢应用最为普遍。普通钢根据不同的条件,有不同的类别,其中依含碳量为评判标准,可以分为低碳钢(欲称熟铁)、中碳钢和铸铁三种。钢铁在我们生活中拥有极其广泛的应用。
钢铁制造过程中,不论低碳钢还是中碳钢都需要进行酸洗工艺。在普通钢酸洗过程中,盐酸以质优价廉的特点,成为众多钢铁行业中酸洗介质的选择。
普通钢酸洗工艺中主要采用连续酸洗,酸洗槽和漂洗槽为其主要设备。运行过程中,盐酸通过计量泵进入贮罐,由贮罐分配进入酸洗槽,在酸洗罐中,盐酸就会发挥作用,去除钢材表面的氧化铁皮。残留在钢材表面的酸将在漂洗槽中通过水洗去除。运行过程中,酸洗槽中酸液的金属离子含量不断升高,超过一定范围,其酸洗效果就会大打折扣,因此需要重新置换新酸液,为了更好的利用资源,保护环境,废酸液不会直接排放,而是采取相应措施,进行回收再生处理[1]。
目前对于废盐酸的再生处理,大量学者也在不断研究和探索,其技术也较为成熟。总的来说,直接焙烧法,萃取法,中和置换法以及膜分离法都是再生处理的一种。其中喷雾焙烧法应用最广泛,该方法主要利用焙烧炉,通过高温焙烧二氯化铁,从而生成盐酸和Fe2O3,一方面利用纯净水吸收盐酸气体,从而得到较高质量分数的再生盐酸,而另一方面,生成的氧化铁副产物也可以回收利用,带来富余价值[2]。近年来,随着这种副产物的价值收到越来越多的关注,逐渐有钢铁企业着手副产物的回收。因此,就目前来说,大多数企业越来越青睐于采用再生循环使用而替代原有的直接中和方法,从而更大程度上提高收益,降低成本。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: