十字换乘地铁车站结构地震响应分析毕业论文
2020-04-13 11:23:18
摘 要
随着我国对城市地下空间的深入开发,轨道交通成为了人们的重要交通方式。如今一些城市的地铁建设已经进入二轮和三轮建设,局限于有限的城市地下空间资源以及早期规划等因素,越来越多的相互穿越工程出现,以及为了线路之间换乘而形成的换乘站等交通枢纽节点。地铁车站具有运营时间长,人流量大的特点,特别是换乘车站。如果换乘车站遭到剧烈地震作用而发生破坏,必将遭受不可预估的经济损失和生命损失。再加上我国是一个地震多发国,因此对换乘车站进行地震响应分析非常有必要性。
针对上述问题,本文总结归纳了地下结构抗震的相关理论和分析方法,以相关的实际工程为背景,运用有限元分析软件Abaqus建立三维有限元模型。通过自由场/单一车站/换乘车站对比的方式,研究了车站周围土体及其自身的地震响应规律,主要包括:
- 换乘车站地表正中点的水平加速度小于单一车站和自由场。地铁车站对于土体表面水平加速度响应的影响存在相应的范围。
- 单一车站顶板处的水平加速度大于换乘车站,且增大幅度与地震波类型有关。
- 换乘车站顶板和中板间的相对位移相较于单一车站更小,且在两种地震波分别作用下,Kobe波产生的顶板和中板相对位移更大。
- 车站的两端存在端墙,使其刚度发生变化,导致换乘车站边缘部位的加速度幅值小于中间部位的加速度幅值。表明车站两端的端墙空间效应显著。
- 换乘车站层间位移角小于单一车站,其抗震性能较好。
关键词:换乘车站;地震响应;自由场;一致地震动
Abstract
With the further development of urban underground space in China, rail transit has become an important mode of transportation.. Nowadays, subway construction in some cities has entered two or three rounds of construction. limited to limited urban underground space resources and early planning, more intercrossing projects and transfer stations appear. Subway stations are characterized by long operation time and large passenger flow, especially transfer stations. If the transfer station is damaged by severe earthquake, it will suffer unpredictable economic loss and loss of life. In addition, China is an earthquake prone country, so it is necessary to analyze the seismic response of the transfer station.
In view of the above problems, this paper sums up the relevant theories and analysis methods of the earthquake resistance of underground structures. Taking the relevant practical engineering as the background, using the finite element analysis software Abaqus to establish the three-dimensional finite element model. Through the comparison of free field / single station / transfer station, the seismic response law of the station and its surrounding soil is studied, which mainly includes:
- The horizontal acceleration at the midpoint of the transfer station is less than that of the single station and the free field. The influence of station structure on the horizontal acceleration response of soil surface has a certain range.
- The horizontal acceleration at the roof of a single station is greater than that at the transfer station, and the amplitude of increase is related to the type of seismic wave.
- The relative displacement between the roof and the middle plate of the transfer station is smaller than that of the single station, and the relative displacement of the roof and the middle plate produced by the Kobe wave is larger than that of the single station.
- The end wall at both ends of the station changes its stiffness, which leads to the acceleration amplitude at the edge of the transfer station being smaller than the acceleration amplitude at the middle part. It shows that the spatial effect of the end wall at both ends of the station is significant.
- the interstory displacement angle of the transfer station is smaller than that of a single station, and its seismic performance is better.
Key words: transfer station; seismic response; free field; Uniform ground motion
目录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1引言 1
1.2国内外研究现状 1
1.3研究的基本内容、目标、拟采用的研究分析方法 3
1.3.1研究内容 3
1.3.2研究目标 3
1.3.3拟采取的技术方案及措施 3
第2章 计算模型及计算工况 5
2.1计算模型 5
2.1.1计算范围及边界条件 5
2.1.2本构模型及计算参数 7
2.1.3地震动输入 7
2.1.4阻尼设置与动力时步 8
2.2计算工况 8
2.3监测方案 9
2.3.1自由场工况监测方案 9
2.3.2单一车站-土体工况监测方案 10
2.3.3换乘车站-土体工况监测方案 11
2.4小结 12
第3章 数值计算结果分析 13
3.1 模态分析 13
3.2土体地震响应分析 13
3.2.1地表正中点水平加速度分析 13
3.2.2地表横向水平加速度幅值变化分析 17
3.2.3地表纵向水平加速度幅值变化分析 19
3.3车站结构地震响应分析 21
3.3.1顶板水平加速度分析 21
3.3.2车站顶板和中板相对位移分析 23
3.3.3顶板处水平加速度幅值变化分析 25
3.4小结 27
第4章 结论与展望 29
4.1结论 29
4.2展望 29
参考文献 31
致谢 33
第1章 绪论
1.1引言
当前我国城市化迅速发展,城市里的交通情况日趋恶化。交通拥堵开始变成各大城市通病,人们逐渐意识到发展地下交通的重要性。截止到2014年,全国共有22个都市拥有地铁,总数量达到95条,运营里程超过2900公里。以武汉为例,根据《武汉市第四轮轨道交通规划2017-2025》(图1.1所示),武汉将在未来建设14条(段)线路,长约 698.6公里。到2025年,武汉市的远景市域轨道交通线网总长将达到1100km,站点数量达到594座,线路数为25条,其中环线长60km。主城区范围的内线网规模将达到533km,站点数量365座。可见武汉地铁发展之迅速,地铁建设会为武汉未来的经济腾飞奠定基础。
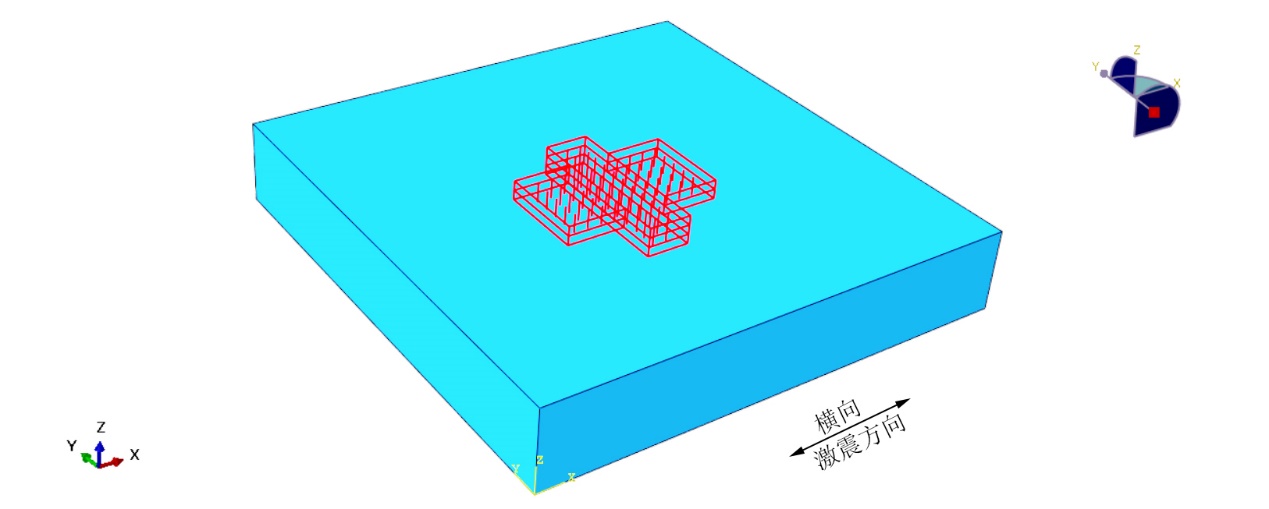
随着一些城市地铁建设进入第二轮和第三轮建设,局限于有限的城市地下空间资源以及早期规划等因素,越来越多的相互穿越工程出现,以及为了线路之间换乘而形成的换乘车站等交通枢纽节点,是典型的空间结构,平面问题已经不再适用。换乘车站是各条地铁线路的汇聚点,在地铁运营期间换乘车站的人流量非常庞大。换乘车站一旦在强烈地震作用下发生破坏,其后果和损失是无法预料的,而且换乘车站的修复难度也大于普通的单一车站。因此换乘车站的破坏在地下结构抗震设计中是一个不可忽视的问题。
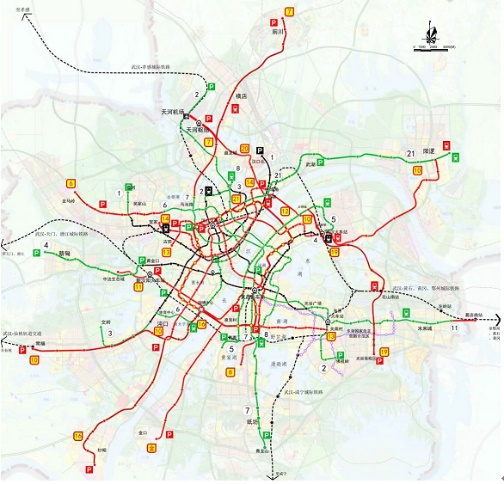
图1.1 武汉市轨道交通(2017-2025)建设规划方案图
1.2国内外研究现状
地下结构的抗震分析虽然发展历史较短,但迄今为止其研究成果丰富。但这些成果大多是针对单一隧道或地铁车站的抗震设计,对于换乘车站的地震响应及抗震计算方法还鲜有研究。由此可见,对于换乘车站地震响应的研究具有深远的理论和实践意义。
在国内,刘晶波[1]针对我国目前在地铁地下结构抗震方面缺少相关规范的现状,总结了我国在地铁地下结构抗震研究的多年经验,提出了地铁地下结构在抗震设计中的几个关键问题。陶连金[2]利用 FLAC3D对北京地区某一密贴地铁交叉结构进行了地震响应的数值模拟,对竖向地震作用下地铁车站密贴上穿地铁隧道结构体系的动力响应特性进行了深入研究。王国波[3]将一4孔紧邻交叠隧道进行简化,将其简化为不同间距的4孔平行重叠和4孔垂直交叉隧道,建立了三维计算模型,对紧邻多孔交叠隧道的动力响应特性进行研究,从结构的受力和变形两个方面评价其抗震性能。袁蕾[4]对某一地铁换乘车站进行地震动力响应分析,主要从结构的侧向变形、位移响应以及柱的内力响应等因素研究了不规则结构对其地震响应的影响。夏进平[5] 利用FLAC3D对在不同幅值加速度下以及不同厚度夹层土下,交叉隧道的地震响应特性进行分析,得出了交叉隧道结构的地震响应规律。赵光[6]以某一匝道与主隧道的交叉节点为例,建立了隧道结构-土体相互作用模型,对其进行了弹塑性动力时程计算。安军海[7]依据某地铁隧道近距离下穿矩形矿山法隧道,建立不同交叉角度的交叉结构三维模型,对其在水平强地震动作用下的地震响应特性进行了深入研究。陈磊[8]基于Abaqus,建立双层交叉隧道结构的三维模型,研究其在近场强地震动下的地震响应特性,并与单层隧道进行对比。黄俊[9]依据某一双隧道下穿单层车站结构进行振动台实验,以探究交叉结构的地震响应规律。胡建平[10]利用ADINA,研究了上覆土层厚度和衬砌厚度对浅埋交叉隧道地震动力相应规律的影响,并提出了相应的减震措施。李积栋[11]以北京地铁某一区间隧道为背景,基于FLAC3D建立密贴交叉隧道三维模型,研究了交叉隧道结构的地震动力响应规律。张宇[12]以某一T型交叉换乘车站为依据,考虑土-结构相互作用,利用Abaqus建立计算模型,以研究换乘车站的地震响应和损伤发展趋势。黄锐财[13]利用SAP2000建立换乘车站的二维有限元模型,对其进行地震响应分析。同时还运用MIDAS/GTS建立换乘车站的三维有限元模型,对其进行动力时程分析。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
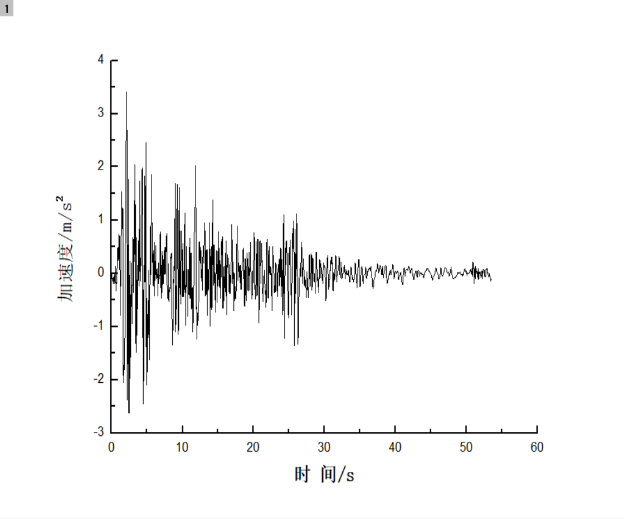
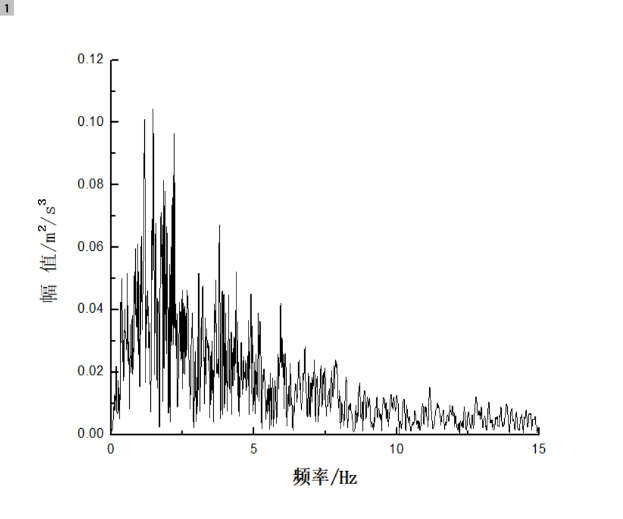
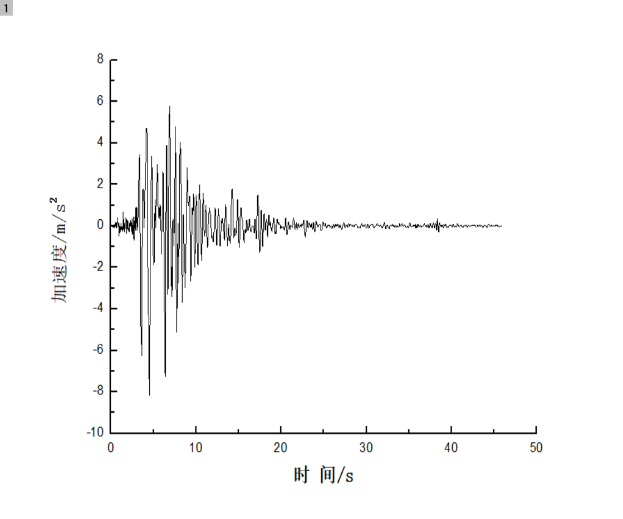
相关图片展示: